-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Mathematics and Statistics
p-ISSN: 2162-948X e-ISSN: 2162-8475
2018; 8(4): 96-98
doi:10.5923/j.ajms.20180804.03

On the Lattice Structure of Cyclic Groups of Order the Product of Distinct Primes
Rosemary Jasson Nzobo1, Benard Kivunge2, Waweru Kamaku3
1Pan African University Institute for Basic Sciences, Technology and Innovation, Nairobi, Kenya
2Department of Mathematics, Kenyatta University, Nairobi, Kenya
3Pure and Applied Mathematics Department, Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology, Nairobi, Kenya
Correspondence to: Rosemary Jasson Nzobo, Pan African University Institute for Basic Sciences, Technology and Innovation, Nairobi, Kenya.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2018 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

In this paper, we give general formulas for counting the number of levels, subgroups at each level and number of ascending chains of subgroup lattice of cyclic groups of order the product of distinct primes. We also give an example to illustrate the concepts introduced in this work.
Keywords: Lattice, Cyclic Group, Subgroups, Chains
Cite this paper: Rosemary Jasson Nzobo, Benard Kivunge, Waweru Kamaku, On the Lattice Structure of Cyclic Groups of Order the Product of Distinct Primes, American Journal of Mathematics and Statistics, Vol. 8 No. 4, 2018, pp. 96-98. doi: 10.5923/j.ajms.20180804.03.
1. Introduction
- A subgroup lattice is a diagram that includes all the subgroups of the group and then connects a subgroup H at one level to a subgroup K at a higher level with a sequence of line segments if and only if H is a proper subgroup of K [1]. The study of subgroup lattice structures is traced back from the first half of 20th century. For instance in 1953, Suzuki presented the extent to which a group is determined by its subgroup lattice in [2].In [2], Suzuki argued that isomorphic groups have the same lattice structure. Also, in [3], Birkhoff and Mac Lane showed that up to isomorphism, there is only one cyclic group of order n. Hence for each n, there is exactly one subgroup lattice structure representing any cyclic group of order n.Jez in [1] deduced that the subgroup lattice structure of a cyclic group of prime power order (that is, when
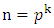 where p is prime and k is a natural number) is a single chain. In [1], it was also shown that if G is a finite group and the subgroup lattice of G is a single chain, then G is cyclic. That is, a finite group has a single chain subgroup lattice if and only if it is isomorphic to
where p is prime and k is a natural number) is a single chain. In [1], it was also shown that if G is a finite group and the subgroup lattice of G is a single chain, then G is cyclic. That is, a finite group has a single chain subgroup lattice if and only if it is isomorphic to  In [4], P'alfy showed that the subgroup lattice of a cyclic group
In [4], P'alfy showed that the subgroup lattice of a cyclic group  where n and m are distinct primes has two ascending chains and three levels. Furthermore, P'alfy argued that any group whose subgroup lattice is formed by two chains is isomorphic to
where n and m are distinct primes has two ascending chains and three levels. Furthermore, P'alfy argued that any group whose subgroup lattice is formed by two chains is isomorphic to 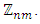 That is, a finite group has a subgroup lattice with two ascending chains if and only if it is isomorphic to
That is, a finite group has a subgroup lattice with two ascending chains if and only if it is isomorphic to 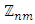 for primes
for primes 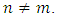 In this paper, we present general formulas for finding the number of levels, subgroups at each level and number of ascending chains of cyclic groups of order
In this paper, we present general formulas for finding the number of levels, subgroups at each level and number of ascending chains of cyclic groups of order 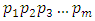 where
where 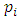 are distinct primes.
are distinct primes.2. Preliminaries
- Definition 2.1 ([6]) Let L be a non empty set and < be a binary relation.1. A partially ordered set, poset
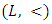 is called a lattice if for every a,b in L, both
is called a lattice if for every a,b in L, both 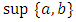 and
and 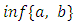 belong to L.2. The lattice whose elements are the subgroups of the group G with the partial order relation being set inclusion is called the subgroup lattice of the group G and is denoted by
belong to L.2. The lattice whose elements are the subgroups of the group G with the partial order relation being set inclusion is called the subgroup lattice of the group G and is denoted by 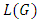 .Definition 2.2 ([6]) Let G be a group. A sequence
.Definition 2.2 ([6]) Let G be a group. A sequence 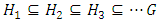 of subgroups of G is called an ascending chain.Theorem 2.3 ([3]) Up to Isomorphism, there is exactly one cyclic group of order n.Theorem 2.4 ([2]) Isomorphic groups have the same subgroup lattice diagram.Theorem 2.5 ([5]) If
of subgroups of G is called an ascending chain.Theorem 2.3 ([3]) Up to Isomorphism, there is exactly one cyclic group of order n.Theorem 2.4 ([2]) Isomorphic groups have the same subgroup lattice diagram.Theorem 2.5 ([5]) If 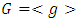 is a cyclic group of order n, then each subgroup of G has the form
is a cyclic group of order n, then each subgroup of G has the form 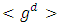 where d is a unique positive divisor of n.Theorem 2.6 ([5]) In a finite cyclic group, each subgroup has order dividing the order of the group. Conversely, given a positive divisor of the order of the group, there is a subgroup of that order.Theorem 2.7 ([5]) If
where d is a unique positive divisor of n.Theorem 2.6 ([5]) In a finite cyclic group, each subgroup has order dividing the order of the group. Conversely, given a positive divisor of the order of the group, there is a subgroup of that order.Theorem 2.7 ([5]) If 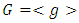 is a cyclic group of order n and
is a cyclic group of order n and 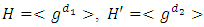 are subgroups of G where
are subgroups of G where 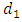 and
and 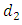 are positive divisors of n, then
are positive divisors of n, then 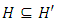 iff
iff 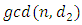 divides
divides 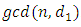 .
.3. Main Results
- Theorem 3.1 If G is a cyclic group of order
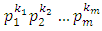 where
where 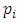 are distinct primes and
are distinct primes and 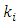 are positive integers and let
are positive integers and let 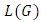 be a subgroup lattice of G, then
be a subgroup lattice of G, then 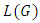 has
has 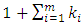 .Proof: Every subgroup of G is of the form
.Proof: Every subgroup of G is of the form 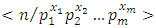 where
where 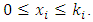 Subgroups at
Subgroups at 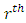 level are such that
level are such that 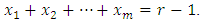 The sum of these powers at the first, second to the last level are
The sum of these powers at the first, second to the last level are 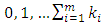 respectively which form arithmetic progression
respectively which form arithmetic progression 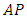 with the first term
with the first term 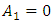 , common difference
, common difference 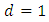 and the last term
and the last term 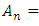
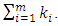 The number of levels,
The number of levels, 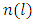 is the number of terms of this
is the number of terms of this 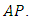 It follows that,
It follows that, 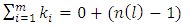 which gives
which gives 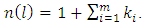 Remarks: Levels are counted from below, that is from the trivially group
Remarks: Levels are counted from below, that is from the trivially group 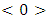 to the group G.Corollary 3.2 If G is a cyclic group of order
to the group G.Corollary 3.2 If G is a cyclic group of order 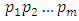 where
where 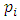 are distinct primes and
are distinct primes and 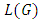 is a subgroup lattice of G, then
is a subgroup lattice of G, then 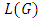 has
has 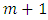 levels.Proof: Follows from Theorem 3.1 where
levels.Proof: Follows from Theorem 3.1 where 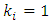 for all
for all 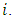 Theorem 3.3 If G is a cyclic group of order
Theorem 3.3 If G is a cyclic group of order 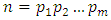 where
where 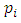 are distinct primes and
are distinct primes and 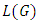 is a subgroup lattice of G, then the number
is a subgroup lattice of G, then the number 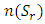 of subgroups a
of subgroups a 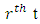 level of
level of 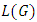 is given by
is given by 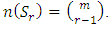 Proof: For
Proof: For 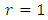 the result is trivially true since the trivial group is the only subgroup at the first level and we have
the result is trivially true since the trivial group is the only subgroup at the first level and we have 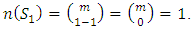 Subgroups at the second level
Subgroups at the second level 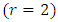 are of the form
are of the form 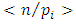 for
for 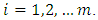 Since for each prime
Since for each prime 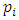 there is a unique subgroup
there is a unique subgroup 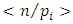 of G, the total number of subgroups of this form is the number of ways of choosing (without repetition) one prime
of G, the total number of subgroups of this form is the number of ways of choosing (without repetition) one prime 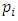 from m primes. Hence there are
from m primes. Hence there are 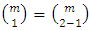 subgroups at the second level.Again, subgroups at the third level
subgroups at the second level.Again, subgroups at the third level 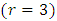 are of the form
are of the form 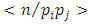 for
for 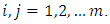 Since for each product
Since for each product 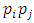 there is a unique subgroup
there is a unique subgroup 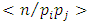 of G, the total number of subgroups of this form is the number of ways of choosing (without repetition) two primes
of G, the total number of subgroups of this form is the number of ways of choosing (without repetition) two primes 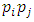 from m primes. Hence there are
from m primes. Hence there are 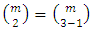 subgroups.In a similar way, subgroups at the
subgroups.In a similar way, subgroups at the 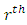 level are generated by divisors of the form
level are generated by divisors of the form 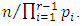 Since there is a unique subgroup for each divisor of this form, we choose (without repetition)
Since there is a unique subgroup for each divisor of this form, we choose (without repetition) 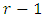 primes
primes 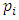 from
from 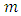 primes hence there are
primes hence there are 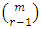 subgroups at the
subgroups at the 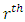 .Lemma 3.4 If G is a cyclic group of order
.Lemma 3.4 If G is a cyclic group of order 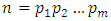 where
where 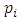 are distinct primes and
are distinct primes and 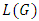 is a subgroup lattice of G, then for every subgroup H of G at
is a subgroup lattice of G, then for every subgroup H of G at 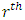 level, there are
level, there are 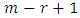 chains towards
chains towards 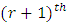 level.Proof: At the first level
level.Proof: At the first level 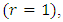 there is only trivial group which is the subgroup of all m subgroups of the second level. But we also have
there is only trivial group which is the subgroup of all m subgroups of the second level. But we also have 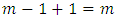 hence the result is true for
hence the result is true for 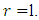 For
For 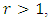 subgroups at the
subgroups at the 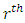 level are of the form
level are of the form 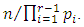 Since G is cyclic, given two subgroups of G,
Since G is cyclic, given two subgroups of G, 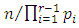 and
and 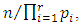 we have
we have 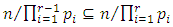 iff
iff 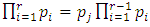 for
for 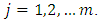 Since
Since 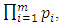 and there are
and there are 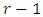 distinct primes in the product
distinct primes in the product 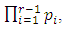 we remain with
we remain with 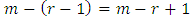 choices of
choices of 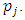 Hence there are
Hence there are 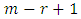 subgroups of G at
subgroups of G at 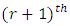 level such that
level such that 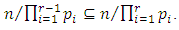 Theorem 3.5: If G is a cyclic group of order
Theorem 3.5: If G is a cyclic group of order 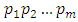 where
where 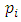 are distinct primes and
are distinct primes and 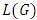 is a subgroup lattice of G, then the total number of chains
is a subgroup lattice of G, then the total number of chains 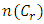 from
from 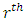 level to
level to 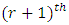 level of
level of 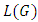 is given by
is given by 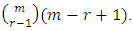 Proof: The number of chains from
Proof: The number of chains from 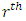 level to
level to 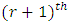 level is the product of the number of subgroups at
level is the product of the number of subgroups at 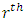 with the number of chains per subgroup from
with the number of chains per subgroup from 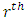 level to
level to 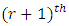 level. From Theorem 3.3 and Lemma 3.4, the number of chains from
level. From Theorem 3.3 and Lemma 3.4, the number of chains from 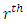 level to
level to 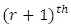 level of
level of 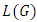 is then given by
is then given by 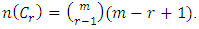 Theorem 3.6: If G is a cyclic group of order
Theorem 3.6: If G is a cyclic group of order 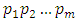 where
where 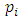 are distinct primes and
are distinct primes and 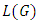 is a subgroup lattice of G, then the number of ascending chains
is a subgroup lattice of G, then the number of ascending chains 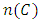 from
from 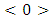 to G is
to G is 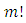 Proof: From Lemma 3.4, the number of chains per subgroup from
Proof: From Lemma 3.4, the number of chains per subgroup from 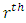 level to
level to 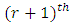 level is given by
level is given by 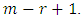 To get the total number of ascending chains from the trivial subgroup to G is simply taking products of these numbers over all levels. It follows that,
To get the total number of ascending chains from the trivial subgroup to G is simply taking products of these numbers over all levels. It follows that, 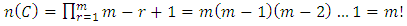 Example 3.7: Let G be a cyclic group of order
Example 3.7: Let G be a cyclic group of order 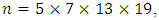 here
here 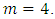 The lattice of G is as shown below;
The lattice of G is as shown below;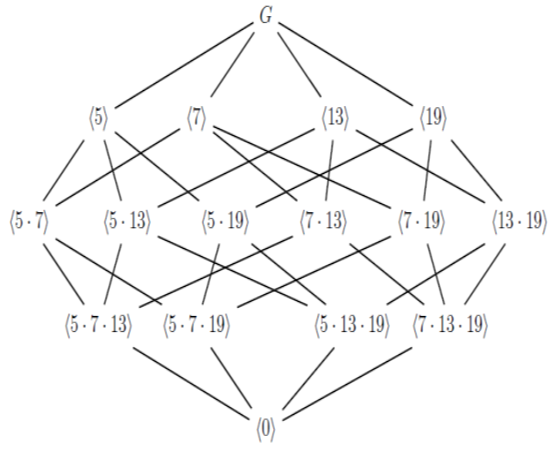 | Figure 1. The lattice of a cyclic group G |
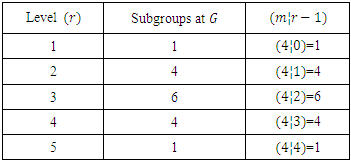
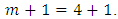 This justifies Corollary 3.2.To justify Theorem 3.3 for the number of subgroups at each level, we use the following table.
This justifies Corollary 3.2.To justify Theorem 3.3 for the number of subgroups at each level, we use the following table.
|
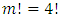 as stated in Theorem 3.6. These chains are:
as stated in Theorem 3.6. These chains are:
4. Conclusions
- General formulas for number of levels, the number of subgroups at each level and the number of ascending chains are presented. It was proved that the number of subgroups at the
 level of a lattice structure
level of a lattice structure 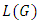 of a cyclic group of order the product of m distinct primes is given by m combination
of a cyclic group of order the product of m distinct primes is given by m combination 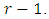 Furthermore, it was proved that the number of ascending chains of
Furthermore, it was proved that the number of ascending chains of 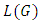 is given by
is given by 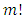 In future work, we will study the lattice structure of cyclic groups of order the product of m prime powers. We will deduce general formulas for finding the number of subgroups at each level and number of ascending chain.
In future work, we will study the lattice structure of cyclic groups of order the product of m prime powers. We will deduce general formulas for finding the number of subgroups at each level and number of ascending chain. Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML