| [1] | A.J. Nicholson, (2007), “Road network unreliability: impact assessment and mitigation”, nternational Journal of Critical Infrastructures, vol. 3, issue 3/4, pages 346-375. |
| [2] | Bellman R.E, Zadeh L.A. (1970),”decision making a fuzzy environment”, management Science, 17, 141 – 164. |
| [3] | Castillo, Oscar, Melin, Patricia, (2008), “Type-2 Fuzzy Logic: Theory and Applications”, Studies in Fuzziness and Soft Computing. Springer. |
| [4] | Dalalah D, Magableh S. (2008). “A remote fuzzy multicriteria diagnosis of sore throat”, Telemed J E Health. |
| [5] | Didier Dubois, Walenty Ostasiewicz, Henri Prade, (2000),” Fuzzy Sets: History and Basic Notions”, Fundamentals of Fuzzy Sets Volume 7 of the series The Handbooks of Fuzzy Sets Series pp 21-124. Springer. |
| [6] | H. J. Zimmermann, (1992), “Methods of application of fuzzy mathematical programming in R.R”. |
| [7] | Harish Garg, S.P. Sharma, Monica Rani, (2013), “Weibull fuzzy probability distribution for analysing the behaviour of pulping unit in a paper industry”, International Journal of Industrial and Systems Engineering ,Volume 14, Issue 4. |
| [8] | Hsien-Chung Wu, (2004), “Fuzzy reliability estimation using Bayesian approach”, Computers & Industrial Engineering Volume 46, Issue 3, Pages 467–493. |
| [9] | Hsien-Chung Wu, (2006), “Fuzzy Bayesian system reliability assessment based on exponential distribution”, Applied Mathematical Modelling Volume 30, Issue 6, Pages 509–530. |
| [10] | Kailash C. Kapur. Michael Pecht, (2014), “Reliability Engineering”, Wiley Publishing. |
| [11] | M. A. El-Damcese, Dina. A. Ramadan, (2015), “Analyzing System Reliability Using Fuzzy Mixture Generalized Linear Failure Rate Distribution”, American Journal of Mathematics and Statistics, 5(2): 43-51. |
| [12] | M. A. Hussian, Essam A. Amin, (2017), “Fuzzy reliability estimation based on exponential ranked set samples “International Journal of Contemporary Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 12, no. 1, 31-42. |
| [13] | Military Handbook Electronic Reliability design handbook, MIL – HDBK – 338B, 1 October 1998, super sending Mil – HDBK 338A, 12 October 1988. |
| [14] | Nayereh Bagheri Khoolenjani, Fateme Shahsanaie, (2016), “Estimating the parameter of Exponential distribution under Type-II censoring from fuzzy data”, Journal of Statistical Theory and Applications, Vol. 15, No. 2, 181-195. |
| [15] | Nozer D. Singpurwalla and Jane Booker, (2004), “membership function and probability measures of fuzzy sets”, Journal of the American Statistical Association, Vol.99, No. 467. |
| [16] | R. Seising, (2006), “Proposals for Future Developments in Fuzzy Set Technology”, Fuzzy Systems, 2006 IEEE International Conference. |
| [17] | Shafiq, Muhammad, (2017),“ Classical and Bayesian Inference of Pareto Distribution and Fuzzy Life Times”, Pakistan Journal of Statistics, Vol. 33 Issue 1, p15-25. |
| [18] | Sunil S. Bhamare, Om Prakash Yadav, Ajay Rathore, (2007), “Evolution of reliability engineering discipline over the last six decades: a comprehensive review”, International Journal of Reliability and Safety , Volume 1, Issue 4. |
| [19] | Way Kuo, Wei-Ting Kary Chien, Taeho Kim, (1998), “Reliability, Yield, and Stress Burn-In”, Springer. |
| [20] | Yager and L.A. Zadeh, (1992), “Introduction to fuzzy logic in intelligent systems”, Klumer Academic publishers Bosten, 97 – 120. |
| [21] | Zadeh L. A., (1968), “Measures of fuzzy event”, dept. of electrical engineering and computer sciences university of California, Berkeley. |
| [22] | Zhaojun Li, Kailash C. Kapur, (2013), “Some Perspectives to Define and Model Reliability Using Fuzzy Sets”, Quality Engineering Volume 25, Issue 2. |



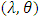 , where the scale parameter
, where the scale parameter 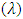 is estimated by moments, and maximum likelihood, then we work on estimating fuzzy reliability function
is estimated by moments, and maximum likelihood, then we work on estimating fuzzy reliability function 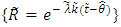 , where
, where 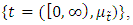
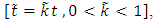
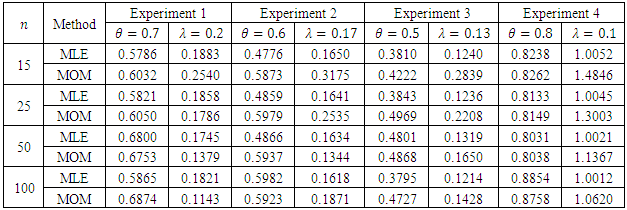
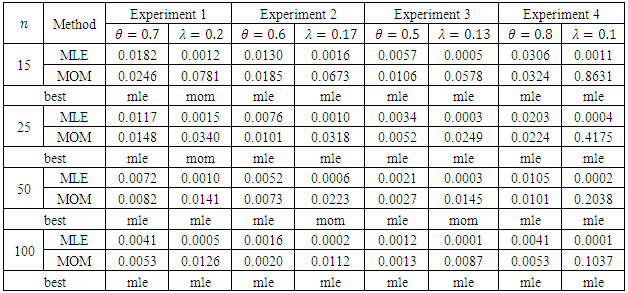
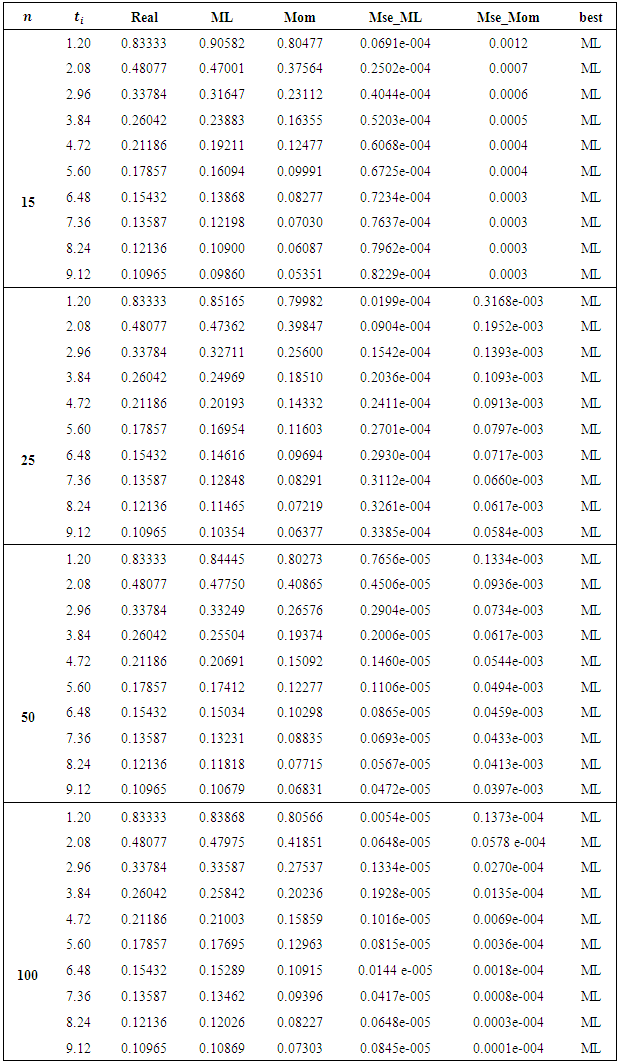
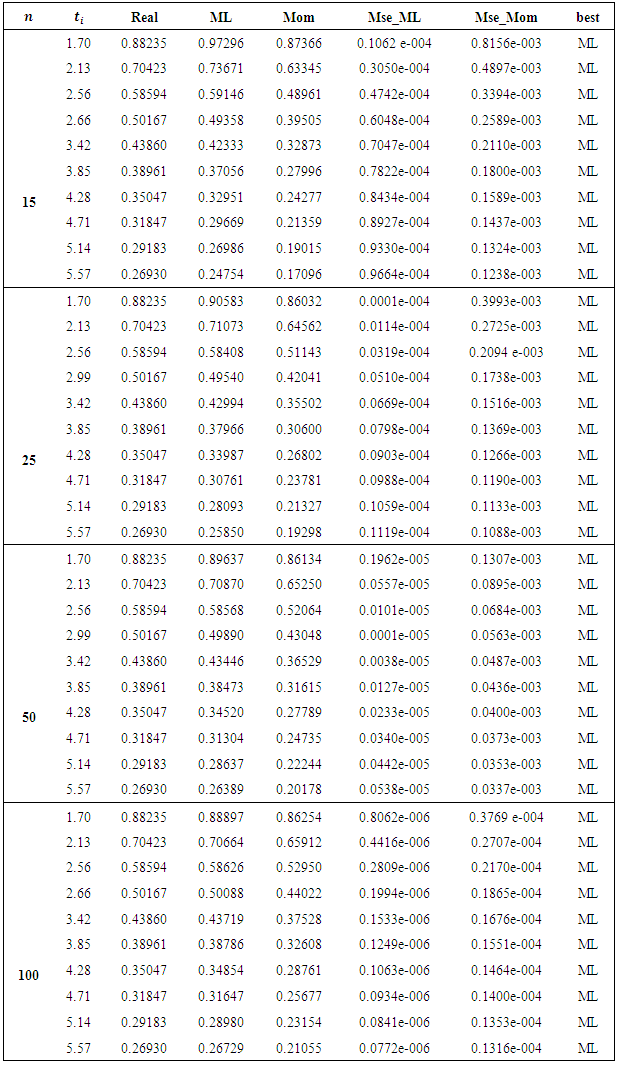
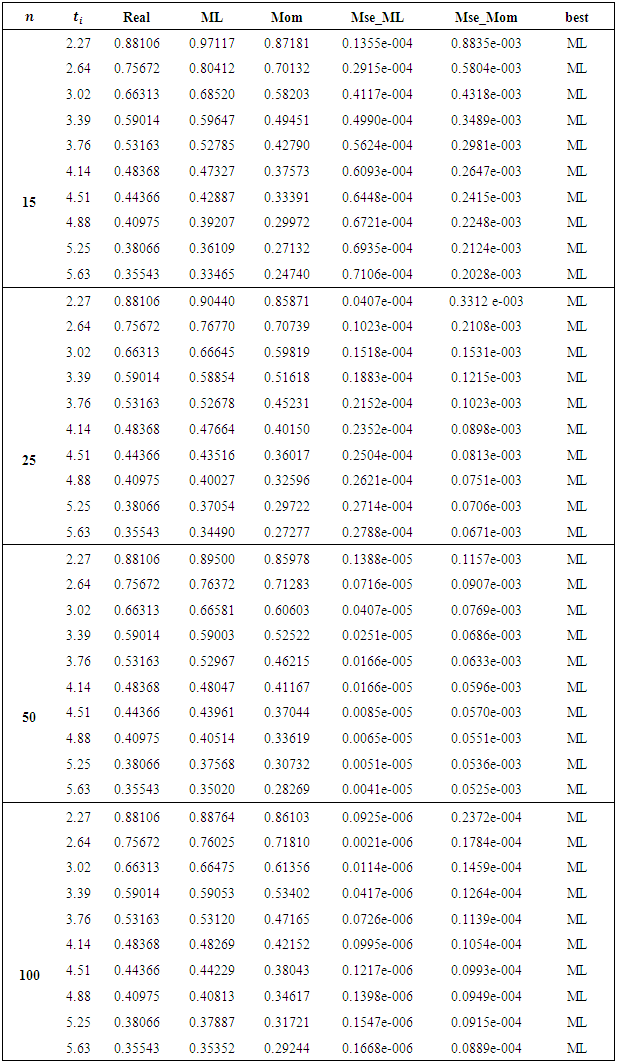
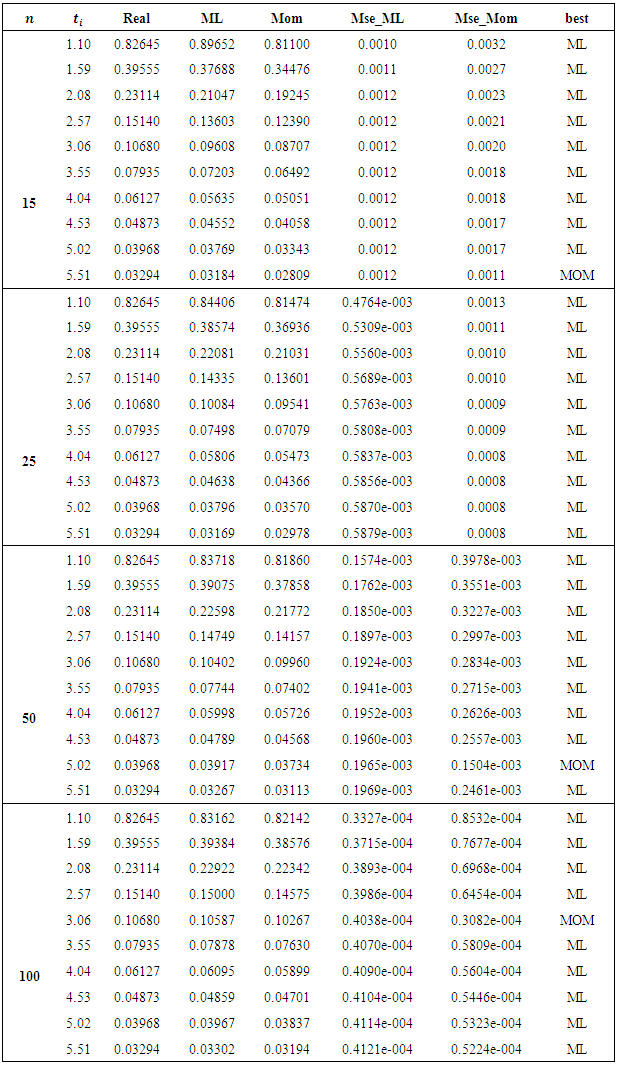
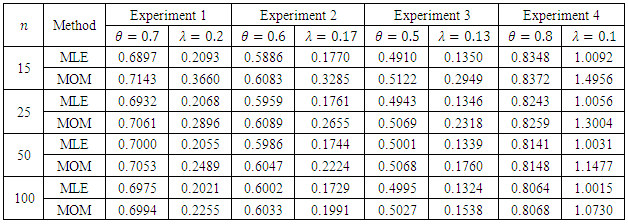
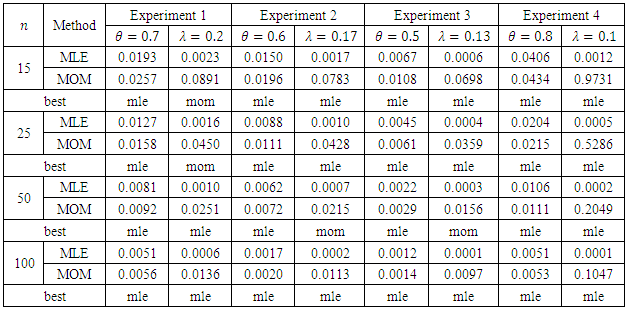
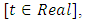 we introduce all the tables of estimators of
we introduce all the tables of estimators of 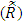 , by different two methods, and the results are compared using statistical measure mean square error (MSE).
, by different two methods, and the results are compared using statistical measure mean square error (MSE).
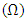 , is a collection of all possible outcomes of random experiments, but the fuzzy subset
, is a collection of all possible outcomes of random experiments, but the fuzzy subset 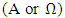 is defined by the membership function denoted by
is defined by the membership function denoted by 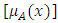 which produce [0,1] for all
which produce [0,1] for all 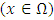 , so
, so 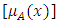 is mapping function into [0,1], and [4];
is mapping function into [0,1], and [4];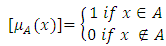 And the fuzzy set has the properties;Ÿ The height of a fuzzy set denoted by
And the fuzzy set has the properties;Ÿ The height of a fuzzy set denoted by 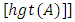 is the maximum of the membership grades of A, i.e [8]
is the maximum of the membership grades of A, i.e [8] 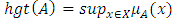 Ÿ A fuzzy set A is normal if
Ÿ A fuzzy set A is normal if 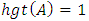 Ÿ The support of a set A is the crisp subs of A with non – zero membership grades [3];
Ÿ The support of a set A is the crisp subs of A with non – zero membership grades [3];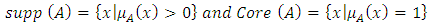 Ÿ Many other notations related to fuzzy sets are [3];
Ÿ Many other notations related to fuzzy sets are [3];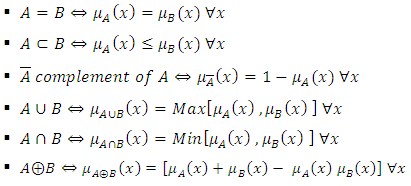 Since out research deals with fuzzy probability distribution and reliability, so we need to explain some probability measures of fuzzy events, then of reliability function [16].v The reliability of a device of a system represent the probability that it will give satisfactory performance for a specified period under specific operating conditions which is denoted by [R(t)] where;
Since out research deals with fuzzy probability distribution and reliability, so we need to explain some probability measures of fuzzy events, then of reliability function [16].v The reliability of a device of a system represent the probability that it will give satisfactory performance for a specified period under specific operating conditions which is denoted by [R(t)] where;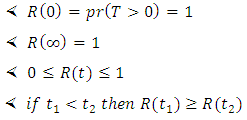
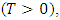 then the reliability function
then the reliability function 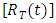 is;
is;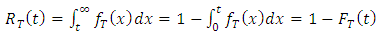
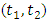 is;
is;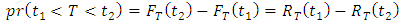
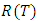 or the probability of a device not failing prior to sometime (t), is given by;
or the probability of a device not failing prior to sometime (t), is given by;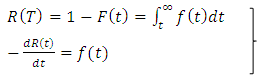
 can be expressed by reliability function as;
can be expressed by reliability function as;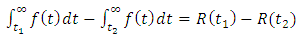
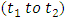 is denoted by
is denoted by 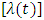 , which is given by;
, which is given by;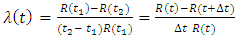
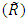 , which is a function of a fuzzy set
, which is a function of a fuzzy set 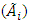 [18, 19].Let
[18, 19].Let 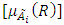 represent the degree of membership (R) in
represent the degree of membership (R) in 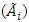 , then;
, then;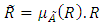
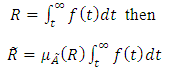
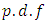 of two parameters exponential is defined by [10];
of two parameters exponential is defined by [10];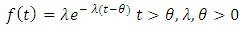
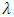 is scale parameter,
is scale parameter, 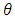 is location parameter, and its cumulative distribution is [10];
is location parameter, and its cumulative distribution is [10];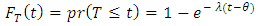
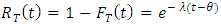
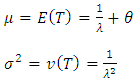 The failure rate function (hazard function);
The failure rate function (hazard function);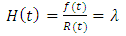
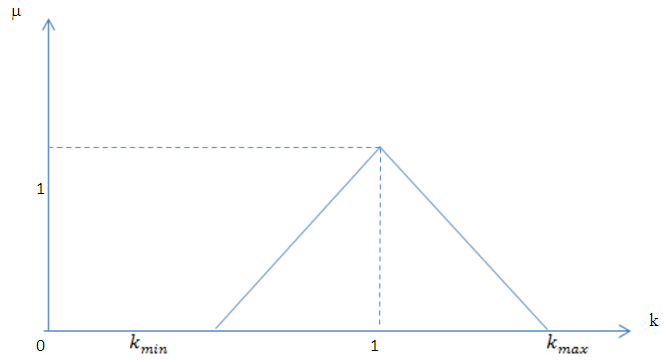
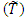 are fuzzy number [7];
are fuzzy number [7];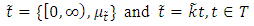 Then the vagueness is a real triangular fuzzy number,
Then the vagueness is a real triangular fuzzy number, 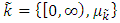 ;
;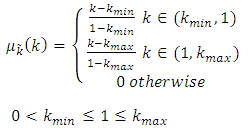
 When the random variable (T) have a crisp exponential probability function
When the random variable (T) have a crisp exponential probability function 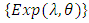 , then the corresponding fuzzy random variable
, then the corresponding fuzzy random variable 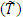 with fuzzy exponential probability distribution
with fuzzy exponential probability distribution 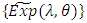 , with the following characteristics;For all
, with the following characteristics;For all 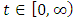 , the cumulative fuzzy distribution function [10];
, the cumulative fuzzy distribution function [10];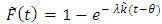
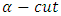 fuzzy distribution function where
fuzzy distribution function where 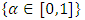 , we have
, we have 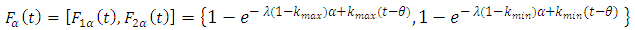
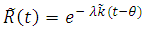 Then
Then 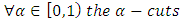 of fuzzy reliability function can be written as;
of fuzzy reliability function can be written as;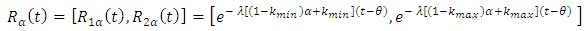
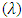 by;
by;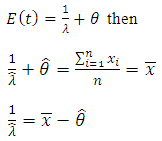
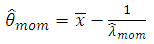
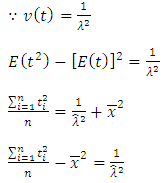
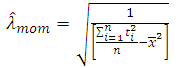
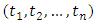 be random sample from (9), then;
be random sample from (9), then;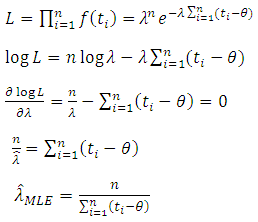 Then according to different values of
Then according to different values of 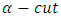 and to specified value of
and to specified value of 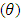 , we can estimate fuzzy reliability function;
, we can estimate fuzzy reliability function;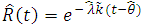
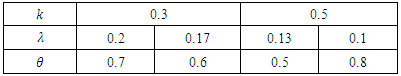
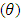 is found to be MLE, also for fuzzy reliability
is found to be MLE, also for fuzzy reliability 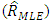 when
when 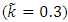 . We conclude that the fuzzy estimator of (R) is best than ordinary estimator since it takes all the variation under consideration.
. We conclude that the fuzzy estimator of (R) is best than ordinary estimator since it takes all the variation under consideration. Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML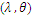 , when
, when 
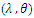 , when
, when