-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Mathematics and Statistics
p-ISSN: 2162-948X e-ISSN: 2162-8475
2016; 6(5): 197-202
doi:10.5923/j.ajms.20160605.01

The Role of Root System in Classification of Symmetric Spaces
1Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Science and Arts – Khulais, University of Jeddah, Saudi Arabia
2Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Education, Alzaeim Alazhari University (AAU), Khartoum, Sudan
Correspondence to: M-Alamin A. H. Ahmed, Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Science and Arts – Khulais, University of Jeddah, Saudi Arabia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2016 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Inthis paper we have introduced a thorough study of Lie algebra, disclosing its contribution to classification of symmetric spaces via root systems. Any Lie algebra is associated to its Lie group through the exponential mapping, and also the Lie algebra corresponds to a given root system which gives its classification. A symmetric space can be represented as a coset space and so we can introduce a symmetric space algebraically using Lie groups and their Lie algebras, then by introducing restricted root systems we can classify symmetric spaces. We gave the theoretical background of this classification with some examples which helps in understanding and further study of this topic.
Keywords: Lie algebra, Cartan subalgebra, Root system, Symmetric Space
Cite this paper: M-Alamin A. H. Ahmed, The Role of Root System in Classification of Symmetric Spaces, American Journal of Mathematics and Statistics, Vol. 6 No. 5, 2016, pp. 197-202. doi: 10.5923/j.ajms.20160605.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Symmetric spaces are special topic in Riemannian geometry, they were earlier studied and classified by Elie Cartan (1869- 1951), and since then many scholars studied them and gave many of their applications in mathematics, physics and other scientific fields [3]. Symmetric spaces can be introduced through different approaches. For instance algebraically they can be introduced through Lie groups and their Lie algebras or geometrically by using curvature tensor. They can be viewed as Riemannian manifolds with point reflections [2], or with parallel curvature tensor or as a homogeneous space with special isotropy group or a Lie group with a certain involution and so on. The Fundamental property of Lie theory is that one may associate with any Lie group G a Lie algebra
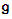 [1] & [4] & [6]. The Lie algebra is a vector space with properties that make it possible to deal with using tools of linear algebra. The Lie group G is almost completely determined by its Lie algebra
[1] & [4] & [6]. The Lie algebra is a vector space with properties that make it possible to deal with using tools of linear algebra. The Lie group G is almost completely determined by its Lie algebra 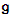 There is a basic connection between the two structures given by exp:
There is a basic connection between the two structures given by exp: 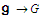 [5] & [7]. For many scientific problems, the complicated nonlinear structure of the Lie group can be reformulated using the exponential map in the Lie algebra, and this makes it easy to use tools of linear algebra especially when we use Cartan subalgebras.A Lie group also is a differentiable manifold, and this make it possible to join symmetric spaces as differentiable manifolds also. Root systems are also the key ingredient in the classification of finite –dimensional, simple Lie algebras. Corresponding to a simple Lie algebra ɡ we have a Cartan decomposition and so we have a root system. Since a symmetric space is a homogeneous space that can be represented as a coset space by using Lie groups and their Lie algebras, so Lie algebras and their root systems play a fundamental role in classification of symmetric spaces [3]. This classification is a continuous field of scientific research. So we aim at giving the tools for this classification in our current paper.
[5] & [7]. For many scientific problems, the complicated nonlinear structure of the Lie group can be reformulated using the exponential map in the Lie algebra, and this makes it easy to use tools of linear algebra especially when we use Cartan subalgebras.A Lie group also is a differentiable manifold, and this make it possible to join symmetric spaces as differentiable manifolds also. Root systems are also the key ingredient in the classification of finite –dimensional, simple Lie algebras. Corresponding to a simple Lie algebra ɡ we have a Cartan decomposition and so we have a root system. Since a symmetric space is a homogeneous space that can be represented as a coset space by using Lie groups and their Lie algebras, so Lie algebras and their root systems play a fundamental role in classification of symmetric spaces [3]. This classification is a continuous field of scientific research. So we aim at giving the tools for this classification in our current paper. 2. Lie Algebra
- A Lie algebra
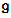 is a vector space with skew – symmetric bilinear map, called Lie bracket and written as
is a vector space with skew – symmetric bilinear map, called Lie bracket and written as 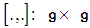
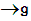 which satisfies the Jacobi identity
which satisfies the Jacobi identity 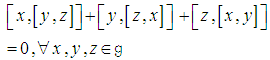
2.1. The Lie Algebra of a Lie Group
- This is defined as the tangent space to the Lie group at the identity. Here are some examples of important Lie algebras:
2.1.1. Examples
- For a field k of characteristic zero, we have the classical matrix algebras
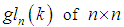 matrices over k,
matrices over k, 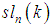 the subalgebra of
the subalgebra of 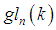 of those
of those 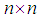 matrices with determinant one. There are also the algebras
matrices with determinant one. There are also the algebras 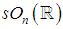 of
of 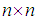 orthogonal real matrices, or
orthogonal real matrices, or 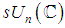 of
of 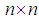 unitary complex matrices. The bracket operation for all these is given by
unitary complex matrices. The bracket operation for all these is given by 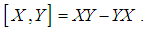
2.2. Definition (Ideals, Simple and Semisimple Lie Algebras)
- An ideal I of a Lie algebra ɡ is a vector space of ɡ such that
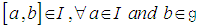 A simple Lie algebra is the one which has no proper ideal. Also a semisimple Lie algebra is the one which is a direct sum of simple Lie algebras.
A simple Lie algebra is the one which has no proper ideal. Also a semisimple Lie algebra is the one which is a direct sum of simple Lie algebras.2.2.1. Example
- Let
 be the set of all
be the set of all 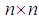 matrices of trace 0.
matrices of trace 0. 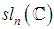 is an ideal of
is an ideal of 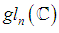 which is nonzero. So
which is nonzero. So 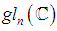 is not simple.
is not simple.2.3. Theorem [3]
- For a matrix group
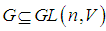 (general linear group), the set
(general linear group), the set 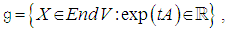 is a Lie algebra, called the Lie algebra of G.
is a Lie algebra, called the Lie algebra of G.2.4. Proposition [4]
- Let
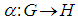 be a continuous homomorphism between matrix groups. Then there exists a unique Lie algebra homomorphism
be a continuous homomorphism between matrix groups. Then there exists a unique Lie algebra homomorphism 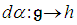 such that the following diagram commutes:
such that the following diagram commutes: 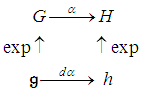
2.5. Definition (The Adjoint Representation)
- Let ɡ be a Lie algebra over k. A representation of ɡ is a Lie algebra homomorphism
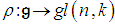 for some n called the degree of the representation. We define a mapping
for some n called the degree of the representation. We define a mapping 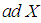 from a Lie algebra to itself by
from a Lie algebra to itself by 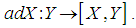 The mapping
The mapping 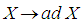 is a representation of the Lie algebra called the adjoint representation. It is an automorphism.
is a representation of the Lie algebra called the adjoint representation. It is an automorphism. 3. Root System
- A root system
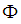 is a set of vectors in
is a set of vectors in 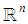 such that:i)
such that:i) 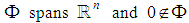 ii)
ii) 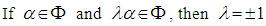 iii) If
iii) If 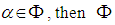 is closed under reflection through the hyperplane normal to
is closed under reflection through the hyperplane normal to 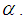 iv) If
iv) If 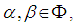 then
then 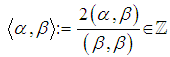 | (3.1) |
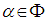 are called roots. If
are called roots. If 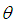 is the angle between
is the angle between 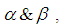 then the possible values of
then the possible values of 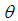 are:
are: 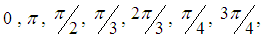
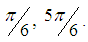 This can be shown using the relation
This can be shown using the relation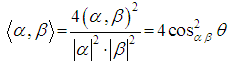 | (3.2) |
3.1. Examples
- (i)
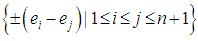 is the root system of the Lie algebra
is the root system of the Lie algebra 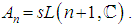 (ii) The set of standard basis vectors and their opposites
(ii) The set of standard basis vectors and their opposites 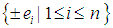 is a root system.
is a root system.3.2. The Weyl Group [5]
- The symmetry of a root system defined by reflection through the hyperplane perpendicular to
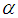 is given by
is given by 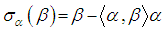 | (3.3) |
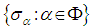 is the weyl group of the system.
is the weyl group of the system.3.3. Decomposable and Indecomposable Root System
- A root system
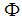 is said to be decomposable if it can be written as
is said to be decomposable if it can be written as 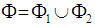 such that
such that 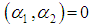 for all
for all 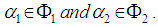 We say
We say 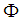 is indecomposable if it is not decomposable.Every root system can be written as the disjoint union of indecomposable root systems.
is indecomposable if it is not decomposable.Every root system can be written as the disjoint union of indecomposable root systems.3.4. Positive and Simple Roots
- A positive root is one such that its first non-zero element (in the chosen basis) is positive. If we denote the set of positive roots by
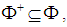 they satisfy : (1)
they satisfy : (1) 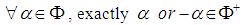 (2) If
(2) If 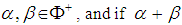 is a root, then
is a root, then 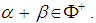 The negative roots are the nonpositive roots. A simple root for
The negative roots are the nonpositive roots. A simple root for 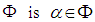 if it is not the sum of two other positive roots. We denote the set of simple roots by
if it is not the sum of two other positive roots. We denote the set of simple roots by 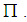 To find a set of simple roots, we must determine firstly when two roots may be added together. If the angle
To find a set of simple roots, we must determine firstly when two roots may be added together. If the angle 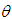 between the two roots
between the two roots 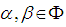 is strictly obtuse, then
is strictly obtuse, then 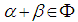 , If
, If 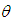 is strictly acute and
is strictly acute and 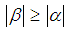 then
then 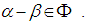
3.5. Theorem [4]
- Every root system has a set of simple roots such that each
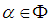 may be written as a linear combination of elements of
may be written as a linear combination of elements of 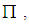 that is
that is 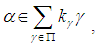 with
with 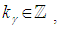 and each
and each 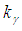 has the same sign.
has the same sign.3.6. Lemma [4]
- The set of simple roots
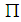 is an independent set, and is a basis for
is an independent set, and is a basis for 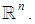
3.7. Height of a Root
- If we fix a base
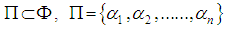 so that
so that 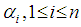 are simple roots, for a root
are simple roots, for a root 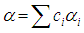 we define
we define 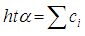 as the height of
as the height of 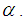 In an irreducible root system shorter roots are called short and longer roots are called long.
In an irreducible root system shorter roots are called short and longer roots are called long.3.8. Proposition [4]
- Let
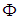 be an irreducible root system. Then at most two different root lengths occur in
be an irreducible root system. Then at most two different root lengths occur in 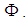
3.9. Remark
- Any root is an image of a simple root under the action of the weyl group.Using the closure of
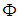 under reflections
under reflections 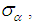 that is elements of the weyl group, we can reconstruct the entire root system. Any root is an image of a simple root under the action of the weyl group.
that is elements of the weyl group, we can reconstruct the entire root system. Any root is an image of a simple root under the action of the weyl group.3.10. Classification of Root System and Lie Algebra
- In most of books of Lie algebras we find the classification theorem. In brief, there are the classical irreducible root systems
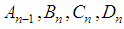 represented in
represented in 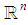 as:
as: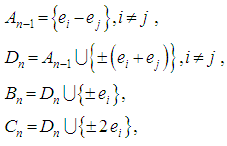 Where
Where 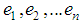 are an orthonormal basis of
are an orthonormal basis of 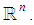 The dimension of the system is indicated by its subscript, so all span
The dimension of the system is indicated by its subscript, so all span 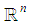 except
except 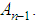 Also we have the exceptional root systems
Also we have the exceptional root systems 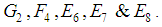
4. Root System and Cartan Subalgebra
- Suppose
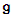 is a complex simple Lie algebra with a vector space basis
is a complex simple Lie algebra with a vector space basis 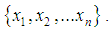 With respect to this basis we can discuss the structure of the Lie algebra
With respect to this basis we can discuss the structure of the Lie algebra  . So we find the structure constants
. So we find the structure constants 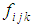 such that
such that 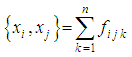 | (4.1) |
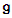 through the constants
through the constants 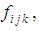 s. So we find what is called Cartan subalgebra.
s. So we find what is called Cartan subalgebra.4.1. Cartan Subalgebra 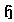
- A cartan subalgebra
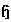 for a Lie algebra
for a Lie algebra 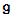 is a subalgebra satisfying the following conditions:i)
is a subalgebra satisfying the following conditions:i) 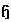 is a maximal abelian subalgebra of
is a maximal abelian subalgebra of 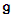 .ii) For each
.ii) For each 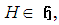 the endomorphism
the endomorphism 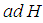 of
of 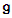 is semisimple. A cartan subalgebra is diagonalizable subalgebra which is maximal under set inclusion. Its dimension is the rank of
is semisimple. A cartan subalgebra is diagonalizable subalgebra which is maximal under set inclusion. Its dimension is the rank of 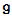 .All Cartan subalgebras of a Lie algebra
.All Cartan subalgebras of a Lie algebra 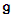 are conjugate under automorphisms of
are conjugate under automorphisms of 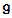 , and they have the same dimension. Define the basis
, and they have the same dimension. Define the basis 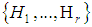 for
for 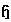 . Since
. Since 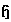 is abelian,
is abelian, 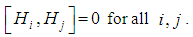 We extend this basis for
We extend this basis for 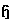 to a basis for
to a basis for 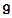 , and then we get a much simpler basis for
, and then we get a much simpler basis for 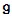 with convenient commutator relations.The adjoint operators for
with convenient commutator relations.The adjoint operators for 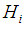 form a representation of
form a representation of 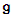 , called the adjoint representation. These operators
, called the adjoint representation. These operators 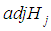 have a set of common eigenvectors, and more over, by the spectral theorem we have decomposition of
have a set of common eigenvectors, and more over, by the spectral theorem we have decomposition of 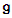 into shared eigenspaces
into shared eigenspaces 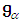 of the adjoint operators as
of the adjoint operators as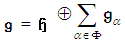 | (4.2) |
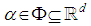 are eigenvalues of
are eigenvalues of 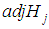 on the eigenspace
on the eigenspace 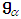 , in particular
, in particular 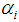 is the eigenvalue for
is the eigenvalue for 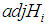 on
on 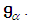 For each
For each 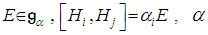 are called the roots of
are called the roots of 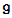 .Also we can write
.Also we can write 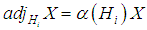 | (4.3) |
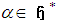 (the dual space of
(the dual space of 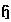 ).
).4.1.1. Theorem [3]
- Every semisimple Lie algebra over
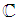 contains a Cartan subalgebra.
contains a Cartan subalgebra.4.2. The Extended Basis for the Lie Algebra ɡ
- Let
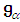 be the span of
be the span of 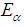 for each
for each 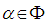 (the set of root system). Then we may extend the basis
(the set of root system). Then we may extend the basis 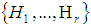 for
for 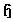 into a basis
into a basis 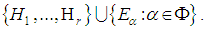 For
For 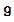 that satisfies the commutator relations
that satisfies the commutator relations 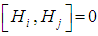 and
and 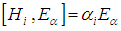 , so we reach the following fact, which can be shown by using the Killing form of
, so we reach the following fact, which can be shown by using the Killing form of 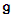 , for more details see [1] & [3].
, for more details see [1] & [3].4.3. Fact [3]
- For the basis
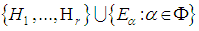 of
of  , the structure constants are:
, the structure constants are: 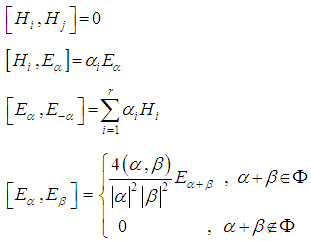
5. Symmetric Spaces
- These are spaces which possess the properties of symmetry and homogeneousness, they have many applications, this is because they have mixed algebraic and geometric properties. The beginning for these spaces is that they are spaces with parallel curvature tensor, later they were introduced through different approaches. They have much in common. Any symmetric space has its own special geometry, Euclidean, elliptic and hyperbolic are some of these geometries. They were first classified by Cartan who gave eleven classes of symmetric spaces in his classification. For more details of symmetric spaces see [2] & [3]. In this paper we disclose the relation between Lie algebras, root systems and symmetric spaces. Then we reach some results. The restricted root systems are associated to symmetric spaces, just like ordinary root systems are associated to groups.
5.1. Lie Groups and Lie Algebras in Symmetric Spaces
- A symmetric space can be represented as a coset space. Also a symmetric space is associated to what is called an involutive automorphism of a given Lie algebra. Several different involutive automorphisms can act on the same algebra, so we normally have several different symmetric spaces deriving from the same Lie algebra.If the field of the Lie algebra is the field of real, complex or quaternion numbers, the Lie algebra is called a real, comlex or quaternion algebra.The classical Lie algebras
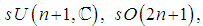
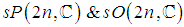 correspond to root systems
correspond to root systems 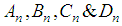 respectively. Also we have the five exceptional algebras corresponding to root systems
respectively. Also we have the five exceptional algebras corresponding to root systems 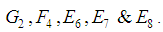 Each of these complex algebras in general has several real forms associated to it. These real forms correspond to the same Dynkin diagrams [3] and root systems as the complex algebras.The semi (simple) complex algebra
Each of these complex algebras in general has several real forms associated to it. These real forms correspond to the same Dynkin diagrams [3] and root systems as the complex algebras.The semi (simple) complex algebra 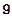 decomposes into a direct sum of root spaces:
decomposes into a direct sum of root spaces: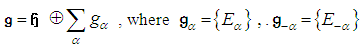 In general for any simple Lie algebra, the commutation relations determine the Cartan subalgebra and raising and lowering operators, that in turn determine a unique root system, and correspond to a given Dynkin diagram. In this way we can classify all the simple algebras according to the type of root system it possesses.
In general for any simple Lie algebra, the commutation relations determine the Cartan subalgebra and raising and lowering operators, that in turn determine a unique root system, and correspond to a given Dynkin diagram. In this way we can classify all the simple algebras according to the type of root system it possesses.5.1.1. An Involutive Automorphism of a Lie Algebra
- Let ɡ be a Lie algebra of the Lie group
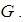 The mapping
The mapping 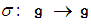 that preserves the algebraic operations on
that preserves the algebraic operations on 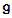 is called an automorphism of
is called an automorphism of 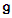 . If
. If 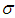 is linear automorphism satisfying
is linear automorphism satisfying 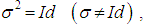 so
so 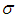 has eigen values
has eigen values 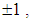 it splits the algebra
it splits the algebra 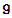 into orthogonal eigenspaces corresponding to these eigen values. This mapping
into orthogonal eigenspaces corresponding to these eigen values. This mapping 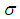 is called an involutive automorphism.
is called an involutive automorphism.5.1.2. Complexification and Real Form of a Lie algebra
- A complexification of a real Lie algebra is obtained by taking linear combinations of its elements with complex coefficients. The real Lie algebra
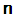 is a real form of the complex algebra
is a real form of the complex algebra 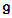 if
if 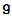 is the complexification of
is the complexification of 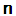 .
.5.2. Symmetric Spaces as Coset Spaces
- If
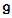 is a compact Lie algebra,
is a compact Lie algebra, 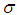 an involutive automorphism of
an involutive automorphism of 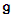 , and
, and 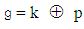 where:
where: 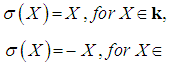 | (4.2.1) |
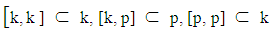 | (4.2.2) |
5.2.1. The Weyl Unitary Trick and Cartan Decomposition
- If we multiply elements in p mentioned above by i ( the imaginary unit ), this is called weyl unitary trick, so we construct a new non- compact algebra.
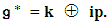 This is called a Cartan decomposition, and k is a maximal compact subalgebra of
This is called a Cartan decomposition, and k is a maximal compact subalgebra of 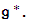 The coset spaces
The coset spaces 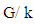 and
and 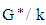 are symmetric spaces.
are symmetric spaces. 5.2.2. Example
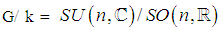 is a symmetric space of compact type and the related symmetric space of non-compact type is
is a symmetric space of compact type and the related symmetric space of non-compact type is 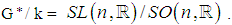
5.3. Normal and Compact Real Forms of the Complex Lie Algebra
- The normal real form of a complex Lie algebra consists of the subspace in which the coefficients in its decomposition to cartan subalgebra and other subspace are real. On the other hand, the compact real form of the complex Lie algebra is obtained from the real form by the Weyl unitary trick.Classification of all the real forms of any complex Lie algebra can be done by enumeration of all involutive automorphisms of its compact form.
5.3.1. Example
- The normal real form of the complex algebra
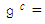
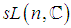 is the non – compact algebra
is the non – compact algebra 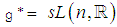 where
where 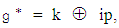 k is the algebra of real, skew – symmetric and traceless
k is the algebra of real, skew – symmetric and traceless 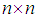 matrices. This algebra from the compact real form
matrices. This algebra from the compact real form 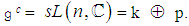
5.4. Restricted Root System
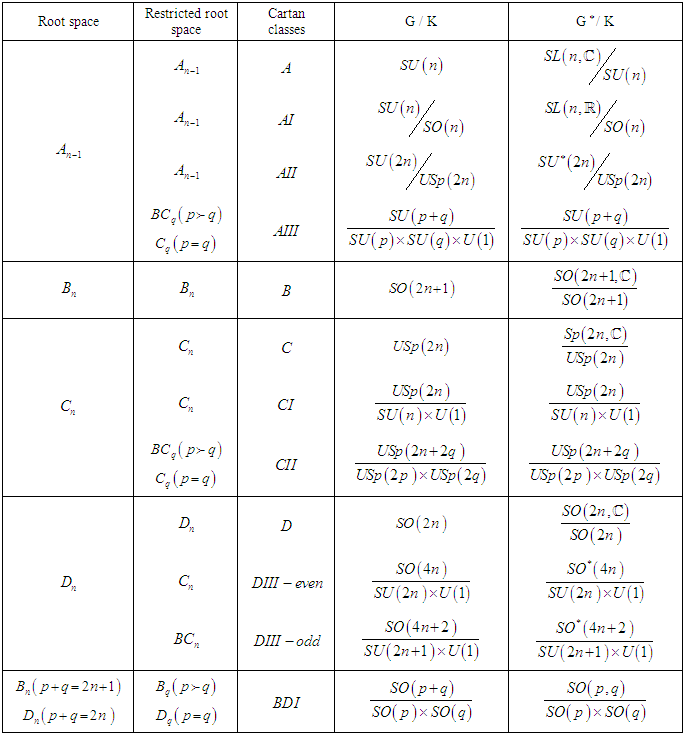
- As a Lie algebra corresponds to a given root system, each symmetric space corresponds to a restricted root system, where these restricted root systems are important in some physical applications. In some texsts these roots are often referred to in tables without explicitly mentioned that they are restricted.Generally the restricted root systems will be different from the original, inherited root system if the Cartan subalgebra lies in k (the symmetric subalgebra). To find the restricted root system we define an alternative Cartan subalgebra that lies partly (or entirely) in p (or ip) where p is a subspace of the algebra ɡ. For more details of restricted root systems see [1] & [3].The following table discloses restricted root spaces associated to Cartan classes of symmetric spaces (see Table 1).
|
5.4.1. Example
- The algebra
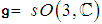 has a root system of type
has a root system of type 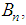 its compact real form is
its compact real form is 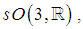 and its only non – compact real form is
and its only non – compact real form is 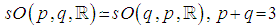 , obtained by applying the involution
, obtained by applying the involution 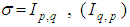 to
to 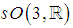 . There are two Riemannian symmetric spaces associated with the algebra
. There are two Riemannian symmetric spaces associated with the algebra 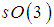 , the sphere
, the sphere 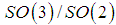 and the double – sheeted hyperboloid
and the double – sheeted hyperboloid 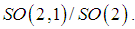
6. Conclusions
- - Classification of Lie algebras is an important tool in classification of symmetric spaces.- Root systems give the basic classes of classification of symmetric spaces - Compact and non-compact symmetric spaces can be discussed by using the algebraic approach to these spaces, namely as a coset spaces of Lie groups and their Lie algebras, then by using associated root systems we can apply the classification machinery.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML