-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Mathematics and Statistics
p-ISSN: 2162-948X e-ISSN: 2162-8475
2015; 5(3): 111-122
doi:10.5923/j.ajms.20150503.02
Analysis of Gini’s Mean Difference for Randomized Block Design
Elsayed A. H. Elamir
Department of Statistics and Mathematics, Benha University, Egypt & Management & Marketing Department, College of Business, University of Bahrain, Kingdom of Bahrain
Correspondence to: Elsayed A. H. Elamir, Department of Statistics and Mathematics, Benha University, Egypt & Management & Marketing Department, College of Business, University of Bahrain, Kingdom of Bahrain.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2015 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Analysis of Gini’s mean difference (ANOMD) for a randomized block design is derived where the total sum of difference (TSD) is partition into exact block sum of difference (BLSD), exact treatment sum of difference (TRSD) and within sum of difference (WSD). This exact partition is used for comparison of several mean and median values. The exact partitions are derived by getting rid of the absolute function from Gini’s mean difference (GMD) by using the idea of redefined the GMD as a weighted average of the data with sum of weights zero. ANOMD has advantages: offers meaningful measure of dispersion, does not square data, and the TSD does not depend on fixed location while BLSD, TRSD and WSD are depending on fixed location. Two ANOMD graphs are proposed. However, two tests for mean and median are proposed under the assumption of normal distribution. The ANOMD is compared with ANOVA and the effect sizes are shown that the percentage of explained variation based on ANOMD is more than the one based on ANOVA.
Keywords: ANOVA, Effect sizes, Normal distribution, Gini’s cofficient
Cite this paper: Elsayed A. H. Elamir, Analysis of Gini’s Mean Difference for Randomized Block Design, American Journal of Mathematics and Statistics, Vol. 5 No. 3, 2015, pp. 111-122. doi: 10.5923/j.ajms.20150503.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Gini’s mean difference (GMD) depends on all pairwise distances rather than square of the data and has been used as an alternative to the standard deviation in many fields. The Gini’s coefficient is a most used measure of inequality; see, [1], [2] and [3]. It is known that the GMD has asymptotic relative efficiency of 98% at the normal distribution and more efficient than standard deviation if the normal distribution is contaminated by a small fraction; see, [8], [5] and [6]. It may also offer certain pedagogical advantages; see, [7]. For extensive discussion and comparisons; see [6] and [8] and the references therein. The population GMD is defined as
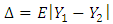 It can be estimated from the sample using many formulas such as
It can be estimated from the sample using many formulas such as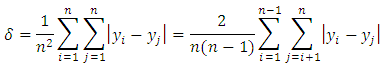 See, for example, [8].A random variable has a normal distribution with location parameter
See, for example, [8].A random variable has a normal distribution with location parameter 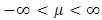 and scale
and scale  if its probability density function is
if its probability density function is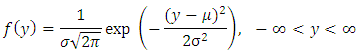 The normal distribution has
The normal distribution has 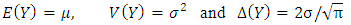 Therefore,
Therefore,  This will be used later in simulation studies.A randomized complete block design is a restricted randomization design in which the experimental units are first sorted into homogeneous rows, called blocks, and the groups (treatments) are then assigned at random within the blocks; see, [9]. The model for a randomized complete block design containing the comparison of no interaction effects, when both the block and treatment effects are fixed and there are B blocks (BL) and G groups (TR), is as
This will be used later in simulation studies.A randomized complete block design is a restricted randomization design in which the experimental units are first sorted into homogeneous rows, called blocks, and the groups (treatments) are then assigned at random within the blocks; see, [9]. The model for a randomized complete block design containing the comparison of no interaction effects, when both the block and treatment effects are fixed and there are B blocks (BL) and G groups (TR), is as 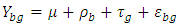
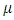 is a constant,
is a constant, 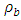 are constants for the block (row) effects,
are constants for the block (row) effects, 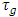 are constants for the group (column) effects and
are constants for the group (column) effects and 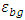 are independent normally distributed with mean 0. Analysis of Gini’s mean difference (ANOMD) for a randomized block design is derived where the total sum of difference (TSD) is partition into exact block sum of difference (BLSD), exact treatment sum of difference (TRSD) and within sum of difference (WSD). The exact partitions are derived by getting rid of the absolute function from Gini’s mean difference (GMD) by using the idea of redefined the GMD as a weighted average of the data with sum of weights zero. TSD does not depend on any fixed location and this is logic where TSD is the total of all pairwise distances while BLSD, TRSD and WSD are depending on any fixed location. This exact partition is used for comparison of several mean and median values. A simulation study is conducted to obtain the critical values for the ratios of mean BLSD to mean WSD and mean TRSD to mean WSD based on normal distribution. Two ANOMD graphs are proposed based on BLSD and WSD. However, two tests for means and medians are proposed under the assumption of normal distribution. The effect size measures are suggested under ANOMD. These measures are shown that the percentage of explained variation based on ANOMD is more than the percentage of explained variation based on ANOVA. Representation of GMD as a weighted average is presented in Section 2. The partitions of TSD into exact BLSD and exact WSD are derived in Section 3. The critical values for ratios are obtained in Section 4. Two graphs are proposed in Section 5. ANOMD tests for mean and median with effect sizes are studied in Section 6. Section 7 is devoted to conclusion.
are independent normally distributed with mean 0. Analysis of Gini’s mean difference (ANOMD) for a randomized block design is derived where the total sum of difference (TSD) is partition into exact block sum of difference (BLSD), exact treatment sum of difference (TRSD) and within sum of difference (WSD). The exact partitions are derived by getting rid of the absolute function from Gini’s mean difference (GMD) by using the idea of redefined the GMD as a weighted average of the data with sum of weights zero. TSD does not depend on any fixed location and this is logic where TSD is the total of all pairwise distances while BLSD, TRSD and WSD are depending on any fixed location. This exact partition is used for comparison of several mean and median values. A simulation study is conducted to obtain the critical values for the ratios of mean BLSD to mean WSD and mean TRSD to mean WSD based on normal distribution. Two ANOMD graphs are proposed based on BLSD and WSD. However, two tests for means and medians are proposed under the assumption of normal distribution. The effect size measures are suggested under ANOMD. These measures are shown that the percentage of explained variation based on ANOMD is more than the percentage of explained variation based on ANOVA. Representation of GMD as a weighted average is presented in Section 2. The partitions of TSD into exact BLSD and exact WSD are derived in Section 3. The critical values for ratios are obtained in Section 4. Two graphs are proposed in Section 5. ANOMD tests for mean and median with effect sizes are studied in Section 6. Section 7 is devoted to conclusion.2. Representation of GMD as a Weighted Average
- Let
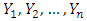 be a random sample from a continuous distribution with, density function
be a random sample from a continuous distribution with, density function  , quantile function
, quantile function 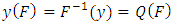 ,
, 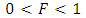 , cumulative distribution function
, cumulative distribution function 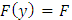 and
and  the order statistics. There is a relationship between the second L-moment and GMD where the second L-moment is a half GMD, therefore
the order statistics. There is a relationship between the second L-moment and GMD where the second L-moment is a half GMD, therefore 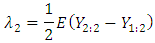 Hence,
Hence, From [9] and [10] this can be estimated as
From [9] and [10] this can be estimated as 
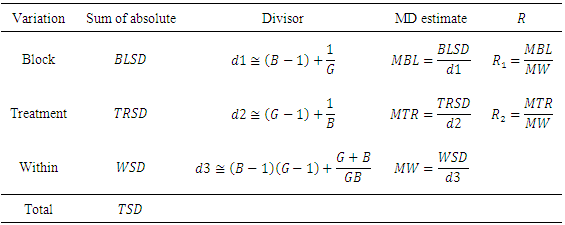
3. Exact GMD Partitions about Mean and Median
- Assume there are G different groups (treatments) with individuals in each group
 , with block
, with block 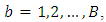 and
and 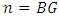 . Let
. Let  is the total deviation
is the total deviation 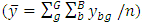 ,
, 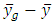 is the deviation of group mean
is the deviation of group mean around total mean,
around total mean, 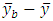 is the deviation of block mean
is the deviation of block mean  around total mean and
around total mean and 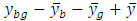 is the error or within.The sample GMD is
is the error or within.The sample GMD is  This can be rewritten without order and taking the rank of y as
This can be rewritten without order and taking the rank of y as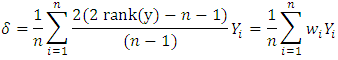 This is a weighted average form where
This is a weighted average form where Note that,
Note that, 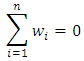 Therefore, the total sum of differences (TSD) is considered as
Therefore, the total sum of differences (TSD) is considered as 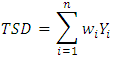 This is the most important equation to obtain the exact analysis of total differences as follows.Theorem 1In a randomized complete block design the total sum of differences about mean is partitions as
This is the most important equation to obtain the exact analysis of total differences as follows.Theorem 1In a randomized complete block design the total sum of differences about mean is partitions as 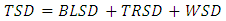 where
where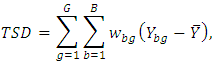
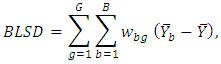
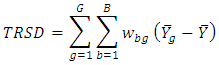
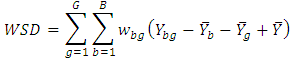 and
and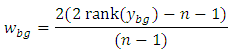 Proof:Where
Proof:Where  , the total sum of differences is
, the total sum of differences is By adding and subtracting
By adding and subtracting  and taking the summation over both
and taking the summation over both 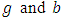 then
then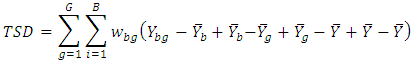 Therefore,
Therefore,  Theorem 2In a randomized complete block design the total sum of differences about median is partitions as
Theorem 2In a randomized complete block design the total sum of differences about median is partitions as 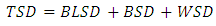 where
where
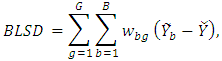

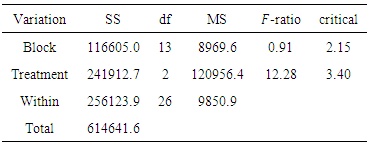
 Proof: same as mean.Comparison with ANOVAThe analysis of variance (ANOVA) for a randomized complete block design is
Proof: same as mean.Comparison with ANOVAThe analysis of variance (ANOVA) for a randomized complete block design is 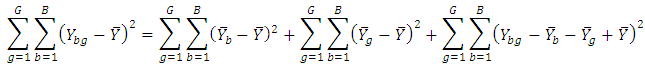 See; for example, [12].The analysis of Gini’s mean difference (ANOMD) for a randomized complete block design is
See; for example, [12].The analysis of Gini’s mean difference (ANOMD) for a randomized complete block design is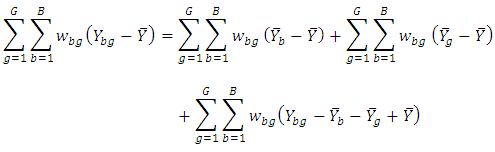 Note that:1. ANOMD replaces the square in ANOVA by weights and that ensures stability in statistical inferences.2. ANOMD can be extended to any measure of location (median) easily where TSD does not depend on any fixed location and this is logic where TSD is the sum of all pairwise distances. Illustrative exampleTo have an idea on how the method work. Table 1 shows TSD partition for a hypothetical data. Note that,
Note that:1. ANOMD replaces the square in ANOVA by weights and that ensures stability in statistical inferences.2. ANOMD can be extended to any measure of location (median) easily where TSD does not depend on any fixed location and this is logic where TSD is the sum of all pairwise distances. Illustrative exampleTo have an idea on how the method work. Table 1 shows TSD partition for a hypothetical data. Note that, 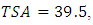
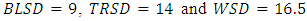 and the total is 39.5 that gives exact partitions.
and the total is 39.5 that gives exact partitions.
|
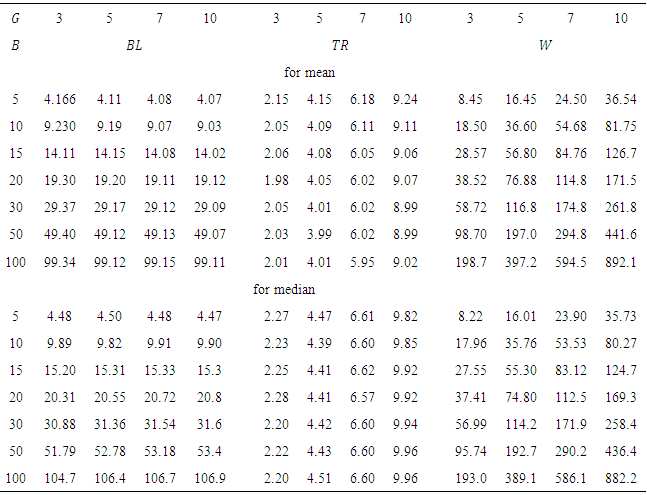
3.1. Divisors and ANOMD Tables
- ANOMD is introduced and used to test for population means and medians under the following assumptions. 1. The observations are random and independent samples from the populations.2. The distributions of the populations from which the samples are selected are normal.3. The
 of the distributions in the populations are equals.A simulation study is conducted to compute the suitable divisors for scaled BLSD, TRSD and WSD using the following steps:1. For selected design simulate data from normal distribution using a very large number N.2. Compute
of the distributions in the populations are equals.A simulation study is conducted to compute the suitable divisors for scaled BLSD, TRSD and WSD using the following steps:1. For selected design simulate data from normal distribution using a very large number N.2. Compute 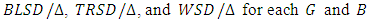 .3. Compute the average for each one.
.3. Compute the average for each one.
|
|
|
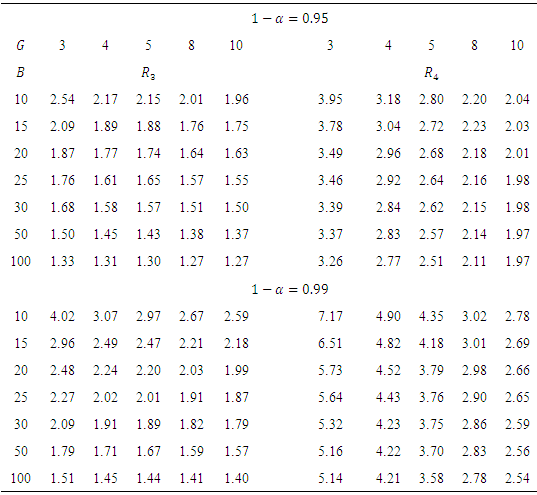
4. Simulation Approach for Critical Values
- The following steps are used to obtain the critical values:1. For any given design simulate data from normal distribution using large number N.2. Compute R for each N.3. Use quantile function in software R to obtain the required quantile for R.
|
|
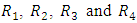 based on normal distribution for different values of B and G.
based on normal distribution for different values of B and G.5. Graphic Presentation
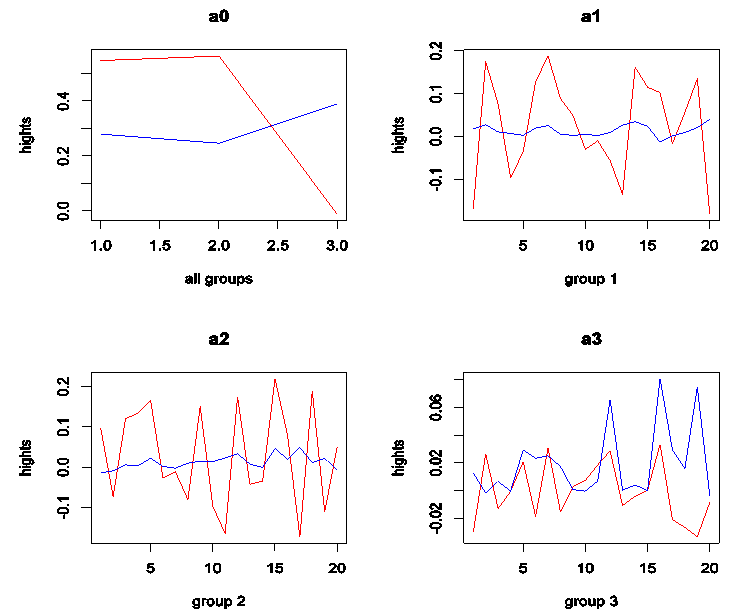
5.1. ANOMD General Plot
- This plot is for all groups to detect shifts in means or medians. The
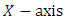 contains the index of the groups and the
contains the index of the groups and the 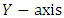 contains the heights for the sum of
contains the heights for the sum of  , and
, and 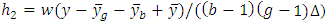 for each group. Note that mean is used as an example. Separate curves are drawn for sum of
for each group. Note that mean is used as an example. Separate curves are drawn for sum of 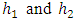 . The points on each curve are connected by lines. This graph should reflect the heights, shifts, and patterns among all groups.
. The points on each curve are connected by lines. This graph should reflect the heights, shifts, and patterns among all groups. 5.2. ANOMAD Individual Plot
- This plot is for each group to detect shifts inside the group. The
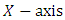 contains the index of the data for each group
contains the index of the data for each group  and the
and the 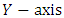 contains the heights,
contains the heights, 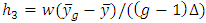 and
and 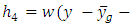
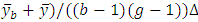 for each value. Separate curves are drawn
for each value. Separate curves are drawn  . The points on each curve are connected by lines. This graph should reflect the heights, shifts and patterns in each group.Figures 1, 2 and 3 show that: 1. When means or medians are equals the two lines will be near from each other and most likely that there will be interference among them or the treatment line may be down the within line; see, Figures 1 and 2 a0. In this case it will not be clear pattern in each group and the heights will be almost the same for on each group; see, Figures 1 and 2 a1, a2 and a3. This may be indicating a strong evidence for no shifts in means or medians.2. When mean(s) or median(s) are not equals the treatment line will start to go up until it may be separated from the within line; see, Figure 3 a0. In this case it will be clear pattern in group(s) with clear different gaps or heights; see, Figure 3 a1, a2 and a3. It is clear that the second group has a different pattern from others. This may give a strong evidence for shift (s) in mean(s) or median(s).
. The points on each curve are connected by lines. This graph should reflect the heights, shifts and patterns in each group.Figures 1, 2 and 3 show that: 1. When means or medians are equals the two lines will be near from each other and most likely that there will be interference among them or the treatment line may be down the within line; see, Figures 1 and 2 a0. In this case it will not be clear pattern in each group and the heights will be almost the same for on each group; see, Figures 1 and 2 a1, a2 and a3. This may be indicating a strong evidence for no shifts in means or medians.2. When mean(s) or median(s) are not equals the treatment line will start to go up until it may be separated from the within line; see, Figure 3 a0. In this case it will be clear pattern in group(s) with clear different gaps or heights; see, Figure 3 a1, a2 and a3. It is clear that the second group has a different pattern from others. This may give a strong evidence for shift (s) in mean(s) or median(s).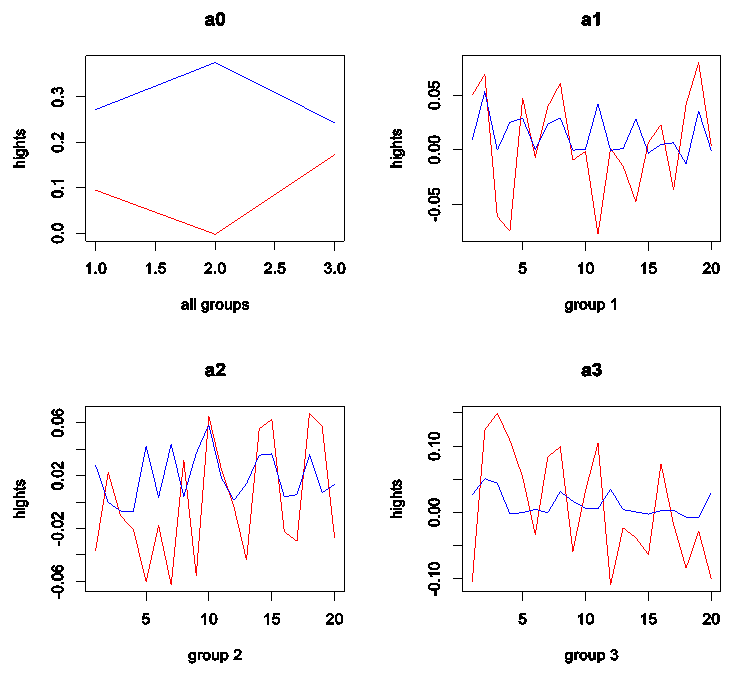 | Figure 1. ANOMD plot for simulated data from N(10,1): (a0) all groups and (a1), (a2) and (a3) for each group and G = 3, n = 60. Red line is treatment and blue line is within |
 | Figure 3. ANOMD plot for simulated four groups N(10,1) and one group N(12,1): (a0) all groups and (a1), (a2), and (a3) for each group and G = 3, n = 60 . Red line is treatment and blue line is within |
6. Test for Mean and Median
- For mean the null hypothesis
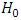 is that Blocks
is that Blocks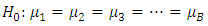 Treatments
Treatments For median the null hypothesis is that Blocks
For median the null hypothesis is that Blocks Treatments
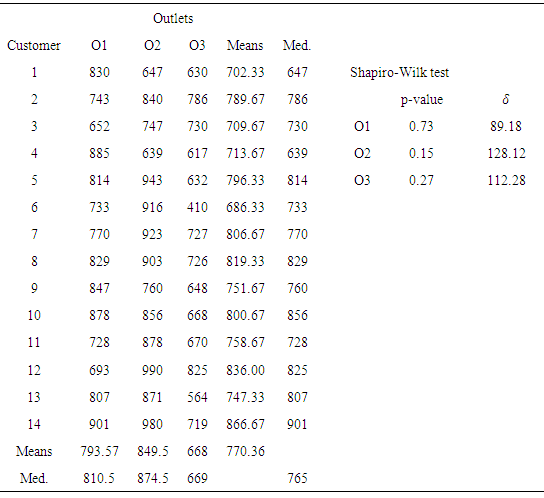
Treatments Fresh & fun is a food chain with three outlets; see, [12]. The owner is interested in testing the average service quality at the three outlets. Fourteen people are selected and they asked to eat at each of the three outlets. The order of visits to the three outlets was randomized, but each customer visited each outlet one time. After each visit, each customer rated the service on a scale of 1 to 100. The data is given in Table 7.To test for the assumption of normal distribution, the function shapiro.test() in R-software is used. Table 7 gives the sample data with means, medians, MD and Shapiro-wilk test for normal distribution. The results for the three groups are given in Table 7 where
Fresh & fun is a food chain with three outlets; see, [12]. The owner is interested in testing the average service quality at the three outlets. Fourteen people are selected and they asked to eat at each of the three outlets. The order of visits to the three outlets was randomized, but each customer visited each outlet one time. After each visit, each customer rated the service on a scale of 1 to 100. The data is given in Table 7.To test for the assumption of normal distribution, the function shapiro.test() in R-software is used. Table 7 gives the sample data with means, medians, MD and Shapiro-wilk test for normal distribution. The results for the three groups are given in Table 7 where  more than 0.01, 0.05 and 0.10, therefore, the assumption of normal cannot be rejected. Because the maximum MD to minimum MD is 1.4, the assumption of homogeneity of
more than 0.01, 0.05 and 0.10, therefore, the assumption of normal cannot be rejected. Because the maximum MD to minimum MD is 1.4, the assumption of homogeneity of  may not be rejected.
may not be rejected.
|
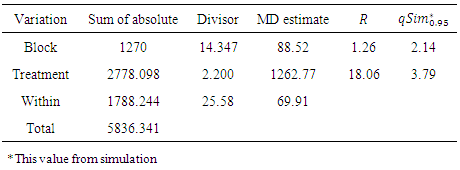
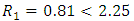 the null hypothesis could not be reject, .i.e., blocking is not effective while
the null hypothesis could not be reject, .i.e., blocking is not effective while 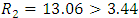 , therefore, the outlets are different in averages.
, therefore, the outlets are different in averages.
|
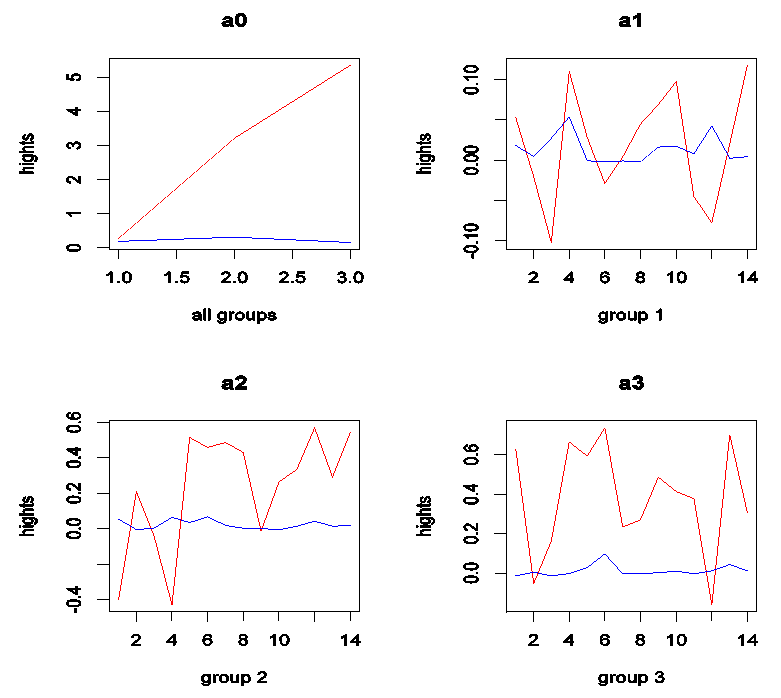 | Figure 4. ANOMD plots for the service quality data for three outlets |
|
|
6.1. Effect Sizes
- Effect sizes (ES) provide another measure of the magnitude of the difference expressed in standard variation units in the original measurement. Thus, with the test of statistical significance and the interpretation of the effect size (ES), the researcher can address issues of both statistical significance and practical importance. The most direct one is
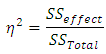 where
where 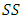 is the sum of squares.
is the sum of squares. 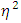 measures the proportion of the variation in
measures the proportion of the variation in 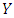 that is associated with membership of the different groups defined by
that is associated with membership of the different groups defined by  .
. 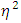 is an uncorrected effect size estimate that estimates the amount of variance explained based on the sample, and not based on the entire population.
is an uncorrected effect size estimate that estimates the amount of variance explained based on the sample, and not based on the entire population. 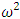 has been suggested to correct for this bias as
has been suggested to correct for this bias as 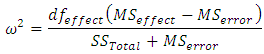 See; for example, [13], [14], [15], [16] and [17]. These two measures could be extended to ANOMD as
See; for example, [13], [14], [15], [16] and [17]. These two measures could be extended to ANOMD as 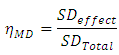 and
and Where
Where 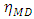 measures the proportion of mean differences in
measures the proportion of mean differences in  that is associated with membership of the different groups defined by
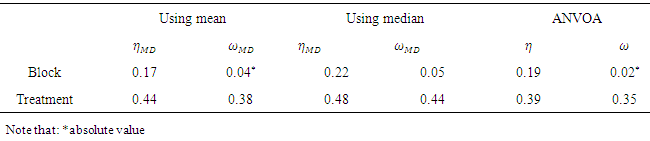
that is associated with membership of the different groups defined by . For the above data, Table 11 gives the computations of these measures.
. For the above data, Table 11 gives the computations of these measures.
|
- From Table 11, it is interesting to note that the percentage of explained variation using ANOMD for treatment is 44%
 and 38%
and 38% 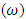 while the percentage of explained variation using ANOVA for treatment is 39% and 35%, respectively.
while the percentage of explained variation using ANOVA for treatment is 39% and 35%, respectively.7. Conclusions
- The ANOMD for a randomized complete block was derived by partition the total sum of differences into exact between sum of differences and exact within sum of differences. It had been shown that the TSD had been expressed as a linear combination of the data instead of square. The ANOMD had important information about the shifts in means and medians that studied by finding the ratios
 and tested for equal means or medians. Also, it offered a very effective way to find out the shifts in means and medians graphically. Actually, the graph is a very strong point if one can obtain the right conclusion from it. Two effect size measures are extended to ANOMD. These measures are showed that the percentage of explained variation based on ANOMD is more than the percentage of explained variation based on ANOVA. Also, it is shown that the TSD had not depended on any fixed location and this may make basis for comparisons between more than location measures.
and tested for equal means or medians. Also, it offered a very effective way to find out the shifts in means and medians graphically. Actually, the graph is a very strong point if one can obtain the right conclusion from it. Two effect size measures are extended to ANOMD. These measures are showed that the percentage of explained variation based on ANOMD is more than the percentage of explained variation based on ANOVA. Also, it is shown that the TSD had not depended on any fixed location and this may make basis for comparisons between more than location measures. Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML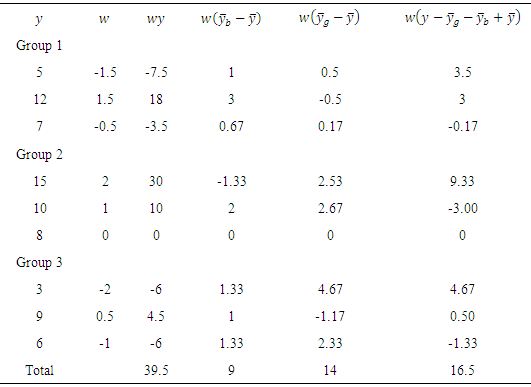
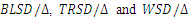 with different values of G and B from normal distribution and the number of replications is 10000
with different values of G and B from normal distribution and the number of replications is 10000