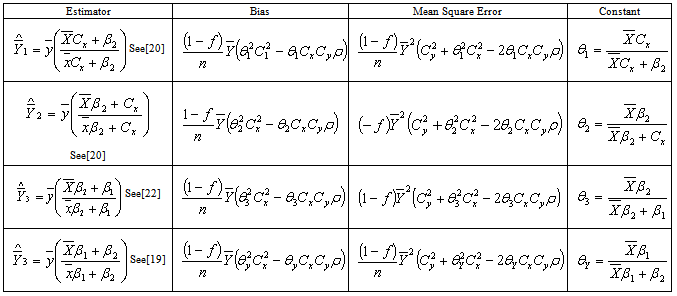-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Mathematics and Statistics
p-ISSN: 2162-948X e-ISSN: 2162-8475
2013; 3(3): 130-134
doi:10.5923/j.ajms.20130303.05
On the Efficiency of Ratio Estimator Based on Linear Combination of Median, Coefficients of Skewness and Kurtosis
Kazeem A. Adepoju, Olanrewaju I. Shittu
Department of Statistics University of Ibadan Ibadan, Nigeria
Correspondence to: Kazeem A. Adepoju, Department of Statistics University of Ibadan Ibadan, Nigeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
In this paper, an estimator which is robust in the present of outlier and Skewness is proposed. This is achieved by incorporating median, a good measure of location in this regard to the modified ratio estimator developed as in[22]. Using well analyzed data to illustrate the procedure for the Ratio estimator, its Mean square error was observed the minimum of the existing estimators considered. The proposed modified estimator is uniformly better than all other estimators and thus most preferred over the existing modified ratio estimators for the use in practical applications for certain population with peculiar characteristics
Keywords: Ratio, Product, Estimator, Parameter, Mean Square Error
Cite this paper: Kazeem A. Adepoju, Olanrewaju I. Shittu, On the Efficiency of Ratio Estimator Based on Linear Combination of Median, Coefficients of Skewness and Kurtosis, American Journal of Mathematics and Statistics, Vol. 3 No. 3, 2013, pp. 130-134. doi: 10.5923/j.ajms.20130303.05.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Ratio estimation involves the use of known population totals for auxiliary variables to improve the weighting from sample values to population estimates of interest. It operates by comparing the sample estimate for an auxiliary variable with the known population total for the same variable on the frame. The ratio of the sample estimate of the auxiliary variable to its population total on the frame is used to adjust the sample estimate for the variable of interest. The ratio weights are given by Xx (where X is the known population total for the auxiliary variable and x is the corresponding estimate of the total based on all responding units in the sample). These weights assume that the population for the variable of interest will be estimated by the sample equally as well (or poorly) as the population total for the auxiliary variable is estimated by the sample.Consider a finite population U = {U1, U2, .UN} of N distinct and identifiable units. Let Y is a study variable with value Yi measured on Ui, i = 1, 2, 3… N giving a vector Y= {Y1, Y2…, YN}. The problem is to estimate the population mean
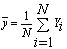 with some desirable properties on the basis of a random sample selected from the population U. The simplest estimator of population mean is the sample mean obtained by using simple random sampling without replacement, when there is no additional information on the auxiliary variable available. Sometimes in sample surveys, along with the study variable Y, information on auxiliary variable x correlated with Y is also collected. This information on auxiliary variable x, may be utilized to obtain a more efficient estimator of the population mean. The two broad categories of estimators using auxiliary information are the Ratio method and product method of estimation. Among those who have worked on these estimators see[15],[18],[19] and[22]. This study is motivated by the success recorded as in[18] on their respective works on “Modified ratio estimators using known median and coefficient of Kurtosis” and “Efficiency of some modified ratio and product Estimators using known value of some population parameters”.The essence of conducting research is to provide dependable solution to practical problems. This paper will uncover some estimators in the literature for better modeling potentials, therefore, the study is of high significance as it tends to improve on the existing ratio estimators thereby facilitate increase in precision of estimator.
with some desirable properties on the basis of a random sample selected from the population U. The simplest estimator of population mean is the sample mean obtained by using simple random sampling without replacement, when there is no additional information on the auxiliary variable available. Sometimes in sample surveys, along with the study variable Y, information on auxiliary variable x correlated with Y is also collected. This information on auxiliary variable x, may be utilized to obtain a more efficient estimator of the population mean. The two broad categories of estimators using auxiliary information are the Ratio method and product method of estimation. Among those who have worked on these estimators see[15],[18],[19] and[22]. This study is motivated by the success recorded as in[18] on their respective works on “Modified ratio estimators using known median and coefficient of Kurtosis” and “Efficiency of some modified ratio and product Estimators using known value of some population parameters”.The essence of conducting research is to provide dependable solution to practical problems. This paper will uncover some estimators in the literature for better modeling potentials, therefore, the study is of high significance as it tends to improve on the existing ratio estimators thereby facilitate increase in precision of estimator.2. Motivation
- The present work is motivated by recent works by statisticians on modified ratio estimators. Therefore further modification can be made to bring about gain in precision.
3. Literature Review
- The historical development of the ratio method of estimation began as far back as 1662. Auxiliary information is any information closely related to the study variable. The use of auxiliary information usually leads to the sampling strategy with higher efficiency compared to those in which no auxiliary information is used. Higher precision can also be achieved by using the auxiliary information for the dual purposes of selection and the estimation procedure. It is important to note that proper use of the knowledge of auxiliary information may result in appreciable gain in precision of the estimates. But indiscriminate use of auxiliary information might not provide the desired precision and in some extreme cases might even lead to loss in precision. Many authors since the discovery of ratio method of estimation have come up with various degree of modification of the conventional ratio estimations for better performance. See also[10],[11],[12] and[22] for more.
4. Methodology
- In this section, review will be made on the existing modified ratio estimators and the new class of modified ratio estimators. Consider a finite population U (U1, U2… UN) of N distinct and identifiable units. Let Y is a study variable with value Yi measured on Ui, i = 1, 2, 3… N giving a vector
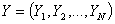 . The problem is to estimate the population mean
. The problem is to estimate the population mean 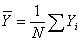 with some desirable properties on the basis of a random sample selected from population U. The simplest estimator of a population mean is the sample mean obtained by using random sampling without replacement, when there is no additional information on the auxiliary variable available. Sometimes in sample survey, along with study variable Y, information on auxiliary variable X correlated with Y is also collected. This information on auxiliary variable X may be utilized to obtain a more efficient estimator of the population mean. Ratio method of estimation, using auxiliary information is an attempt made in this direction. Before discussing further about the modified ratio estimators and the proposed modified ratio estimators of notations to be used are described.N - Population Sizen - Sample Sizef - n/N, Sampling fractionY - Study VariableX - Auxiliary Variable
with some desirable properties on the basis of a random sample selected from population U. The simplest estimator of a population mean is the sample mean obtained by using random sampling without replacement, when there is no additional information on the auxiliary variable available. Sometimes in sample survey, along with study variable Y, information on auxiliary variable X correlated with Y is also collected. This information on auxiliary variable X may be utilized to obtain a more efficient estimator of the population mean. Ratio method of estimation, using auxiliary information is an attempt made in this direction. Before discussing further about the modified ratio estimators and the proposed modified ratio estimators of notations to be used are described.N - Population Sizen - Sample Sizef - n/N, Sampling fractionY - Study VariableX - Auxiliary Variable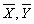 - Population means
- Population means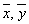 - Sample meansSX,SY - Population Standard deviationsCX,CY - Coefficient of Variationsρ - Coefficient of Correlation
- Sample meansSX,SY - Population Standard deviationsCX,CY - Coefficient of Variationsρ - Coefficient of Correlation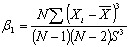 , coefficient of skewness of the auxiliary variable
, coefficient of skewness of the auxiliary variable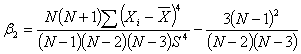 ,coefficient of the auxiliary variable Md – Median of the auxiliary variable B(.) – Bias of the estimatorMSE (.) – Mean squared error of the estimator
,coefficient of the auxiliary variable Md – Median of the auxiliary variable B(.) – Bias of the estimatorMSE (.) – Mean squared error of the estimator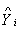 – Existing modified ratio estimator
– Existing modified ratio estimator4.1. Existing Modified Radio Estimators with Their Biases, Mean Squared Errors and Their Constants
|
4.2. Proposed Modified Ratio Estimators
- In this paper, the following modified ratio estimator is proposed
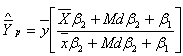 , the corresponding Bias, the Mean Square Error and constant are derived respectively as
, the corresponding Bias, the Mean Square Error and constant are derived respectively as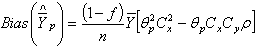
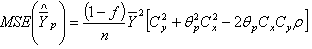 The constant
The constant 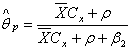
5. Computation of Constants, Bias and Mean Square Error
5.1. Overview
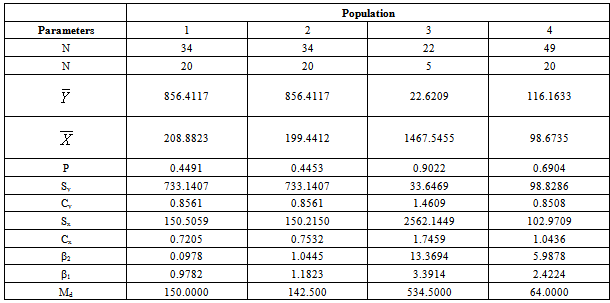
- For the sake of convenience to the readers and for the case of comparison, the computation will be made of the Bias, MSE and Constant of existing modified ratio estimators and the proposed ratio estimator. This is to enable the assessment to be made of the various estimators. The parameters from the natural populations stated earlier will be in use.This
|
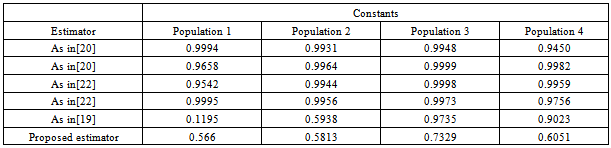
5.2. The Constants of the Existing and Proposed Modified Ratio Estimators
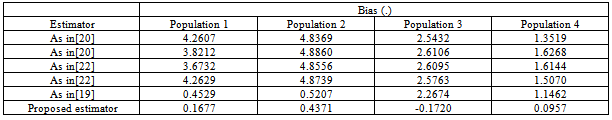
5.3. The Biases of the Existing and Proposed Modified Ratio Estimators
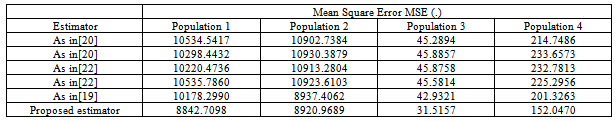
5.4. The Mean Square Errors of the Existing and Proposed Modified Ratio Estimators
6. Conclusions
- In this paper, a new ratio estimator has been proposed using linear combination of the Coefficient of Skewness, Coefficient of Kurtosis and Median of the auxiliary variable. We have reviewed the existing ratio estimators along with their properties such as Constants, Biases and Mean Square errors. The biases and mean squared errors of the proposed estimators are obtained and compared with that of existing modified ratio estimators.The performances of the proposed modified ratio estimators are assessed with that of existing modified ratio estimators for certain natural populations. In this direction, we have considered four natural populations for the assessment of the performances of the proposed modified ratio estimator with that of existing modified ratio estimators in statistics literature. The population 1, 2 and 3 are taken from[10], while population from[1].The constants biases and the mean square errors of the existing and the proposed modified ratio estimators for the above populations have been displayed in the table in the earlier section. It is observed that the biases and the mean square errors of the proposed estimator are less than the biases and mean square errors of the existing modified ratio estimators for most of the populations.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML