-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Mathematics and Statistics
p-ISSN: 2162-948X e-ISSN: 2162-8475
2012; 2(6): 206-212
doi: 10.5923/j.ajms.20120206.07
Some Approaches to Symmetric Spaces
M-Alamin A. H. Ahmed
Departmemt of mathematics , Faculty of Science and Arts – Khulais , King Abdulaziz University , Saudi Arabia
Correspondence to: M-Alamin A. H. Ahmed , Departmemt of mathematics , Faculty of Science and Arts – Khulais , King Abdulaziz University , Saudi Arabia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
In this study we introduce some approaches , geometrical and algebraic which help to give further understanding of symmetric spaces and help scientists who are seeking for suitable spaces for their applications to carry on their job . One of the aims of this study is to put forward the close connection between different approaches to symmetric spaces , namely algebraic and geometrical features of these spaces with some results . Also giving some conclusions and remarks on the foundation of symmetric spaces with logical ordering of notions and consequences . We think that symmetric space is a very important field for understanding abstract and applied features of spaces , besides they are still need much effort to understand them because of the diversity of their approaches which mix between algebra and geometry , so this Paper is an attempt to disclose some of these features and helps in more understanding and put forward a base for future applications .
Keywords: Riemannian Manifold , Lie Groups, Lie Algebras , Homogeneous Spaces , Curvature Tensor
Cite this paper: M-Alamin A. H. Ahmed , "Some Approaches to Symmetric Spaces", American Journal of Mathematics and Statistics, Vol. 2 No. 6, 2012, pp. 206-212. doi: 10.5923/j.ajms.20120206.07.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- In studying spaces , one of the aims of this study is to introduce spaces that can suit some scientific applications . Many scientific problems in various fields may have their own conditions that might not agree with the geometric structure and properties of some spaces familiar to mathematicians and geometers . Historically the Euclidean space , then the Cartesian and so on have been serving the scientific needs and the solutions to many problems , but mathematicians always think of new spaces whenever it is crucial to do that , or also they introduce new spaces to be ready for future applications . In differential geometry , manifolds do their role to meet some scientific demands . This is due to some properties of manifolds , for instance manifolds need not be connected , or closed . They are never countable unless their dimension is zero . Differentiable manifolds for example lead to Lie groups, and these with their Lie algebras help to introduce some abstract spaces such as symmetric spaces . When we introduce symmetric spaces , this can be done through different approaches of algebraic and geometric nature .In this study we are going to discuss some of these approaches which lead to some invariant properties of symmetric spaces . We can look to these spaces from different aspects which unify some algebraic and geometric properties .
2. Preliminaries
2.1. Smooth Manifold
- Manifolds are topological spaces that are locally Euclidean and Hausdorff .A smooth manifold
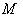 is a manifold endowed with a smooth structure , that is an atlas of charts satisfying smoothness conditions .Simple examples of smooth manifolds are the Euclidean n- space
is a manifold endowed with a smooth structure , that is an atlas of charts satisfying smoothness conditions .Simple examples of smooth manifolds are the Euclidean n- space 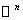 and unit sphere
and unit sphere 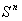 .
.2.2. Proposition
- A manifold is locally connected , locally compact , a union of a countable collection of compact sets , normal and meterizable .
2.3. A Smooth Tensor Field
- Let
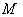 be a smooth manifold . A smooth tensor field
be a smooth manifold . A smooth tensor field 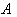 on the manifold
on the manifold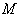 of type
of type 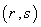 is the map
is the map 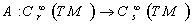 , which is multi- linear over
, which is multi- linear over 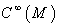 , that is , it satisfies the following :
, that is , it satisfies the following : 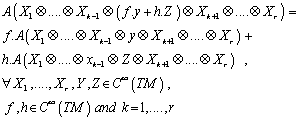 Shortly for the smooth tensor field
Shortly for the smooth tensor field 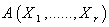 , We use the notation
, We use the notation 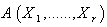 . Also
. Also 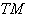 denotes the tangent bundle on
denotes the tangent bundle on 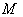 , that is the disjoint union of all tangent spaces on
, that is the disjoint union of all tangent spaces on 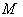 .
.2.4. Proposition
- Let
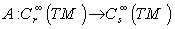 be a tensor field of type
be a tensor field of type 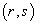 and the point
and the point 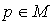 . Let
. Let 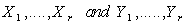 be smooth vector fields on
be smooth vector fields on 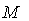 such that
such that 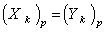 for each
for each 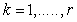 , then
, then 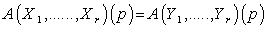
2.5. Definition ( Riemannian Metric )
- A Riemannian metric
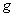 on a manifold
on a manifold 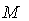 is a tensor field
is a tensor field 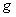 :
: 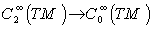 such that for each
such that for each 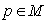 the restriction
the restriction 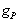 =
= 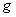
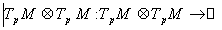 with
with 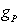 :
: 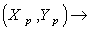
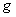
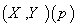 is an inner product on the Tangent space
is an inner product on the Tangent space 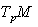 .
.2.6. Connections and Riemannian Connections
- In a smooth n – manifold
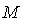 with a smooth Riemannian metric
with a smooth Riemannian metric 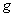 , let
, let 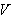 be the set of all smooth vector fields on
be the set of all smooth vector fields on 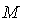 . A connection on
. A connection on 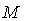 is the operator
is the operator 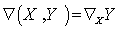 , satisfying the conditions :
, satisfying the conditions : 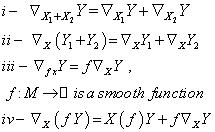 : If in addition to the above conditions we have
: If in addition to the above conditions we have 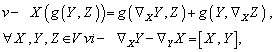 then the connection
then the connection 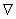 is called the Riemannian connection . We can use for a chart
is called the Riemannian connection . We can use for a chart 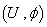 on n- manifold :
on n- manifold : 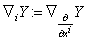 , then
, then 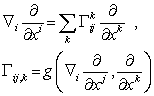 (The Chistoffel symbols ) . If
(The Chistoffel symbols ) . If 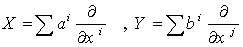 , then using
, then using 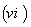 above we find the covariant derivative ( or the connection ) :
above we find the covariant derivative ( or the connection ) : 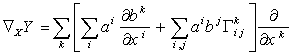
2.7. Parallel Vector Fields & Geodesics
- If
 is a smooth n – manifold with a smooth Riemannian metric
is a smooth n – manifold with a smooth Riemannian metric 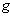 . Let
. Let 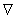 be the unique Riemannian connection on
be the unique Riemannian connection on 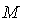 corresponding to
corresponding to 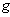 . Let
. Let 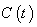 be a smooth regular curve in
be a smooth regular curve in 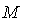 ,
, 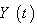 be a vector field along
be a vector field along 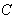 . Then
. Then 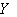 is parallel along
is parallel along 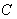 if
if 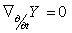 and
and 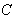 is a geodesic in
is a geodesic in 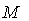 if
if 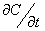 is parallel along
is parallel along 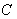 , that is , if
, that is , if 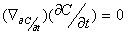 .
.2.8. Riemannian Manifold
- Let
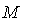 be a smooth manifold with a metric
be a smooth manifold with a metric 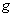 , the pair (
, the pair (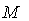 ,
, 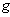 ) is called a Riemannian manifold . Geometric properties of (
) is called a Riemannian manifold . Geometric properties of (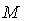 ,
, 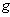 ) which only depend on the metric
) which only depend on the metric 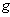 are called intrinisic or metric properties .
are called intrinisic or metric properties .2.9. Levi – Civita Connection
- In a Riemannian manifold with a metric
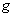 , a connection
, a connection 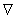 is called a Levi – Civita connection if it is torsion- free (
is called a Levi – Civita connection if it is torsion- free (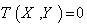 ) , and is compatible with
) , and is compatible with 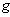 , Where :
, Where : 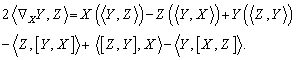
3. Lie groups and Lie algebras
- Lie groups and their Lie algebras are very useful and important tools when studying symmetric spaces , this results from the fact that their algebraic properties derive from the group axioms , and their geometric properties derive from the identification of group operation s with points in a topological spaces , and these are manifolds . We should note that every Lie group is a smooth manifold .
3.1. Definition( Lie group )
- A Lie group
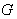 is a group satisfying two additional axioms :(i) The mapping of the group operation
is a group satisfying two additional axioms :(i) The mapping of the group operation 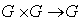 defined by
defined by 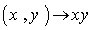 , and (ii) The inverse map
, and (ii) The inverse map 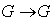 defined by
defined by 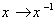 , are both smooth .Examples:
, are both smooth .Examples: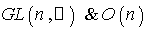 are examples of Lie groups .
are examples of Lie groups .3.2. Definition ( Lie Algebra of a Lie Group )
- The tangent space to a linear Lie group
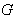 at the identity
at the identity 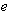 , denoted g=
, denoted g=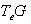 is its Lie algebra endowed with a ( non-associative ) multiplication , the Lie bracket satisfying the axioms of a Lie algebra as a vector space .
is its Lie algebra endowed with a ( non-associative ) multiplication , the Lie bracket satisfying the axioms of a Lie algebra as a vector space . 3.3. Homomorphisms of Lie Groups and Lie Algebras
- The homomorphism of the Lie groups
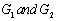 is a function
is a function 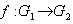 which is a homomorphism of groups and a smooth map between the manifolds
which is a homomorphism of groups and a smooth map between the manifolds 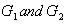 .If g1 and g2 are two Lie algebras , also the homomorphism of Lie algebras is a function
.If g1 and g2 are two Lie algebras , also the homomorphism of Lie algebras is a function 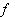 : g1
: g1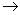 g2 which is a linear map between the vector spaces g1 and g2 preserving Lie brackets ,that is
g2 which is a linear map between the vector spaces g1 and g2 preserving Lie brackets ,that is 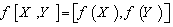 .
.3.4. Left and Right Translations
- If
 is a Lie group , for every
is a Lie group , for every 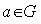 we define : (i ) Left translation as the map
we define : (i ) Left translation as the map 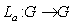 such that
such that 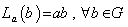 .(ii ) Right translation as
.(ii ) Right translation as 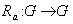 such that
such that 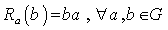 .
.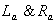 are both diffeomorphisms ,
are both diffeomorphisms , 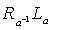 or
or 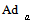 is given by
is given by 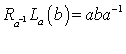 The derivative
The derivative 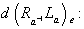 g
g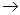 g is an isomorphism of Lie algebras , denoted by
g is an isomorphism of Lie algebras , denoted by 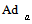 : g
: g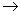 g .That is ,
g .That is , 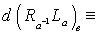
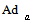 .
. 3.5. Adjoint Representation
- If we denote the Lie group of all bijective linear maps on g by GL(g) , then we call the map
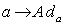 where
where 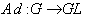 ( g) the adjoint representation of
( g) the adjoint representation of 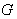 . g. If
. g. If 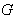 is a linear group we have
is a linear group we have 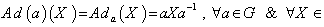 The derivative
The derivative 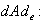 g
g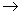 gL(g) denoted by
gL(g) denoted by 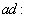 g
g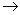 gL(g) is called the adjoint representation of g ( where gL(g) denotes the Lie algebra , End(g , g ) of all linear maps on g ) . In the case of linear group we have
gL(g) is called the adjoint representation of g ( where gL(g) denotes the Lie algebra , End(g , g ) of all linear maps on g ) . In the case of linear group we have 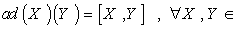 g , and
g , and 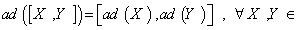 g . According to what is mentioned we can define the Lie algebra of the Lie group as :
g . According to what is mentioned we can define the Lie algebra of the Lie group as : 3.6. Definition ( Lie Bracket )
- Given a Lie group
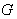 , g =
, g = 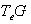 with the Lie bracket defined by :
with the Lie bracket defined by : 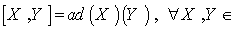 g , is the Lie algebra of the Lie group G .
g , is the Lie algebra of the Lie group G .3.7. Left and Right Invariant Vector Fields
- Given
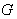 is a Lie group , we define a vector field
is a Lie group , we define a vector field 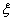 on
on 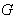 as : (i ) Left-invariant vector field if and only if
as : (i ) Left-invariant vector field if and only if 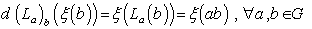 , and (i ) Right – invariant vector field if and only if
, and (i ) Right – invariant vector field if and only if 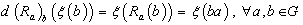 .If
.If 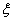 is a left – invariant vector field , putting
is a left – invariant vector field , putting 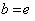 , we have :
, we have : 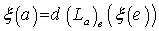 , that is
, that is 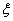 is determined by its value
is determined by its value 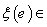 g , at the identity
g , at the identity 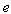 . The map
. The map 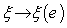 , establishes an isomorphism between the space of left – invariant vector fields on
, establishes an isomorphism between the space of left – invariant vector fields on 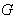 and g . In fact for
and g . In fact for 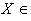 g , we define the vector field
g , we define the vector field 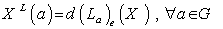 , then the map
, then the map 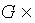 g
g 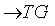 given by
given by 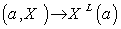 is an isomorphism between
is an isomorphism between 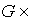 g and the tangent bundle
g and the tangent bundle 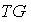 .
. 3.8. Definition ( Lie Subalgebra and The Ideal )
- If g is a Lie algebra , a subalgebra η of g is a subspace of g such that
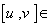 η ,
η , 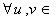 η . If η is a subspace of g such that
η . If η is a subspace of g such that 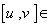 η ,
η , 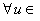 η and all
η and all 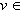 g , we call η an ideal in g . Note that many properties of Lie groups structure can be studied and derived through their Lie algebras , that is why they are important to be studied . A simple Lie algebra has no proper ideal . The semisimple algebras are constructed of simple ones .
g , we call η an ideal in g . Note that many properties of Lie groups structure can be studied and derived through their Lie algebras , that is why they are important to be studied . A simple Lie algebra has no proper ideal . The semisimple algebras are constructed of simple ones .3.9. The Exponential Map
- In a Riemannian manifold
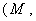 g ) with the point
g ) with the point 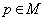 , the exponential map
, the exponential map 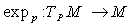 is defined by
is defined by 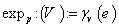 where
where 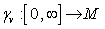 is the constant speed geodesic emanating from
is the constant speed geodesic emanating from 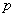 with
with 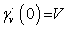 and
and 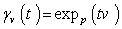 .The Lie algebra g generates a group through the exponential mapping . A general group element is
.The Lie algebra g generates a group through the exponential mapping . A general group element is 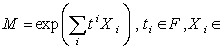 g . If we choose a basis
g . If we choose a basis 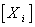 for g . Then
for g . Then 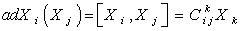 , we sum over k . The
, we sum over k . The 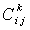 are real structure constants . The structure constants define the matrices
are real structure constants . The structure constants define the matrices 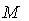 of the adjoint representation through
of the adjoint representation through 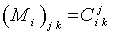 .
. 3.10. Cartan Subalgebra
- In a simple Lie algebra , we have two kinds of generators : (i) The Cartan subalgebra , which is a maximal abelian subagebra
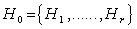 such that
such that 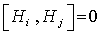 . On representing each of the Lie algebra by
. On representing each of the Lie algebra by 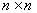 matrix , then
matrix , then 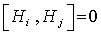 means the matrices
means the matrices 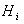 can all be diagonalized simultaneously . Their eigenvalues
can all be diagonalized simultaneously . Their eigenvalues 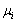 are given by
are given by 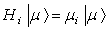 , where the eigenvectors are labeled by the weight vectors
, where the eigenvectors are labeled by the weight vectors 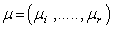 . (ii) There are raising and lowering operators denoted
. (ii) There are raising and lowering operators denoted 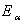 such that
such that 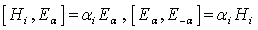 .
.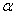 is an r – dimensional vector called a root ,
is an r – dimensional vector called a root , 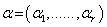 and r is the rank of the algebra . The roots form a lattice in the space dual to the Cartan subalgebra . They are useful in the problem of classification of symmetric spaces .
and r is the rank of the algebra . The roots form a lattice in the space dual to the Cartan subalgebra . They are useful in the problem of classification of symmetric spaces . 3.11. Killing Form
- If g is a Lie algebra , we define the Killing form
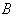 of g over afield
of g over afield 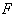 as the bilinear form :
as the bilinear form : 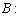 g
g 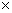 g
g 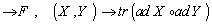 .The Lie group and its Lie algebra are called semisimple if the Killing form is nondegenerate .
.The Lie group and its Lie algebra are called semisimple if the Killing form is nondegenerate .4. Homogeneous Space
- To introduce homogeneous spaces we should remember the action of the group on a set .
4.1. The G-space
- A locally compact Hausdorff space equipped with a transitive action of the group
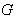 , is called a
, is called a 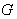 - space .
- space .4.2. Theorem
- Let
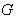 be a locally compact group and let
be a locally compact group and let 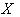 be a transitive
be a transitive 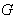 - space . Let
- space . Let 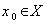 and
and 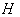 be the isotropy group of
be the isotropy group of 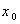 . If
. If 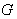 is compact , then
is compact , then 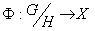 given by
given by 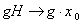 is a homomorphism .
is a homomorphism .4.3. Definition ( Homogeneous Space )
- A Homogeneous space
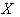 is a transitive G- space that is isomorphic to a quotient space
is a transitive G- space that is isomorphic to a quotient space 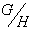 . That is , there is an isomorphism by the mapping
. That is , there is an isomorphism by the mapping 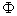 as in the previous theorem , making
as in the previous theorem , making 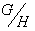 isomorphic to
isomorphic to 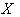 .In a homogeneous space every point looks exactly like every other point . We can also look at a homogeneous space as a space whose isometry group acts transitively on it .
.In a homogeneous space every point looks exactly like every other point . We can also look at a homogeneous space as a space whose isometry group acts transitively on it .4.4. Example
- As an example of a homogeneous space , the n-sphere
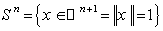 , its isometry group is the group of rotations given by
, its isometry group is the group of rotations given by 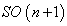 . For every two points
. For every two points 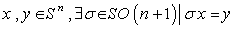 , so that there is a transitive action and
, so that there is a transitive action and 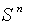 is a homogeneous space .
is a homogeneous space .5. Symmetric Spaces
- These are spaces which possess the properties of symmetry and homogeneousness,and they have many applications ,this is because they have mixed algebraic and geometric properties . The beginning for these spaces is that they are spaces with parallel curvature tensor , later they were introduced through different approaches . They have much in common . Any symmetric space has its own special geometry , Euclidean , elliptic and hyperbolic are some of these geometries . We give some approaches to symmetric spaces using some algebraic and geometric properties.
5.1. Some Approaches to Symmetric Spaces
- A symmetric space can be considered as : 1 - A Riemannian manifold with point reflection .2 - A Riemannian manifold with parallel curvature tensor .3 - A Lie group with certain involution . 4 - A homogeneous space with special isotropy group .5 - A Riemannian manifold with special holonomy .6 - A special Killing vector field .7 - A Lie triple system . These may be some of many other approaches to symmetric spaces , but we are interested in this work in some of these approaches to reach the required aims of this study .
6. Symmetric Spaces and Parallel Curvature Tensor
- The most famous approach to symmetric spaces is that related to Ellie Cartan , we introduce it here to complete the picture of our opinions :
6.1. Definition
- A Riemannian manifold
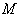 is called locally symmetric if its curvature tensor
is called locally symmetric if its curvature tensor 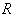 is parallel , that is
is parallel , that is 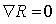 .
.6.2. Theorem ( E. Cartan )
- Let
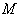 be a Riemannian manifold . Then
be a Riemannian manifold . Then 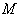 is locally symmetric
is locally symmetric 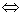
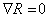 , where
, where 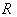 is the curvature tensor of
is the curvature tensor of 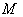 , and
, and 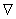 is the connection induced on 4-tensor on
is the connection induced on 4-tensor on 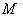 by the Levi – Civita connection of
by the Levi – Civita connection of 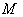 .
.6.3. Theorem ( Symmetric Space )
- A Complete , Locally symmetric , simply connected Riemannian manifold is a symmetric space . According to what is mentiond above we can give many examples of symmetric spaces , where we shall give some details on some of them when introducing other approaches to symmetric spaces . Briefly we can say that
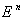 ( the Euclidean space ) ,
( the Euclidean space ) , 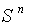 ( the unit sphere in
( the unit sphere in 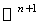 ) and
) and 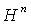 ( the hyperbolic space ) are all examples of symmetric spaces.
( the hyperbolic space ) are all examples of symmetric spaces. 7. Symmetric Spaces with Point Reflection
- Here we consider symmetric spaces as Riemannian manifolds with point reflections : Let
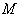 be a Riemannian manifold ,
be a Riemannian manifold , 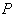 a point of
a point of 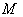 . If the geodesic reflection at any point
. If the geodesic reflection at any point 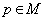 is an isometry of
is an isometry of 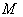 , that is
, that is 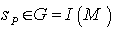 , the isometry group of
, the isometry group of 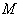 , such that
, such that 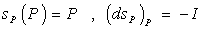 .The isometry
.The isometry 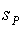 is called symmetry at
is called symmetry at 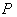 . From this definition ,
. From this definition , 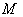 is geodesically complete and homogeneous . We can say that a Symmetric space
is geodesically complete and homogeneous . We can say that a Symmetric space 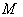 is precisely a homogeneous space with a symmetry at some point
is precisely a homogeneous space with a symmetry at some point 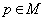 . We identify the homogeneous space
. We identify the homogeneous space 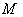 with the coset space
with the coset space 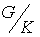 where
where 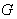 is the isometry group of
is the isometry group of 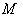 , and
, and 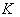 is the isotropy group
is the isotropy group 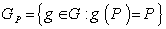 .
.7.1. Definition ( Locally Symmetric Space )
- A locally symmetric space is a Riemannian manifold in which the geodesic symmetry at each point is an isommetry in a normal neighbourhood of the point . Symmetric Spaces are locally symmetric too, the geodesic symmetries in this case are global isometries .
7.2. Example ( The Unit Sphere )
- Let
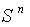 be the unit sphere in
be the unit sphere in 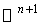 with the standard scalar product . On taking the symmetry at any point
with the standard scalar product . On taking the symmetry at any point 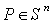 as the reflection at the line
as the reflection at the line 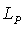 in
in 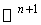 , that is
, that is 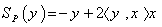 . This symmetries generate the full isometry group which is the orthogonal group
. This symmetries generate the full isometry group which is the orthogonal group 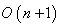 . The isotropy group of the last standard unit vector
. The isotropy group of the last standard unit vector 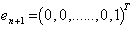 is
is 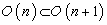 .
. 7.3. Example ( The Orthogonal Group ) ( Abstract )
- Let
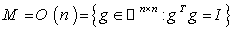 , a Submanifold of the matrix space
, a Submanifold of the matrix space 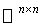 . The Riemannian metric on
. The Riemannian metric on 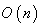 is induced from the trace scalar product on
is induced from the trace scalar product on 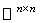 :
: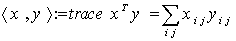 . For any
. For any 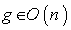 and
and 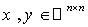 we have :
we have : 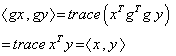 ,
, 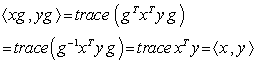 ( the inner product is preserved ) . Right and left multiplications with
( the inner product is preserved ) . Right and left multiplications with 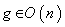 preserve the subset
preserve the subset 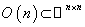 , so they act as isometry on
, so they act as isometry on 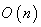 turning
turning 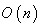 into a homogeneous space . The linear map
into a homogeneous space . The linear map 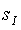 on
on 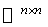 given by
given by 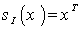 is an isometry of
is an isometry of 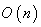 preserving
preserving 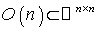 and the scalar product of
and the scalar product of 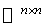 . This is the symmetry at the identity matrix
. This is the symmetry at the identity matrix 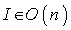 since it fixes
since it fixes 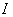 and acts as
and acts as 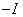 on the tangent space
on the tangent space 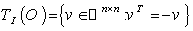 . The symmetry at an arbitrary element
. The symmetry at an arbitrary element 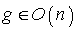 is given by
is given by 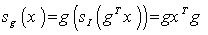 , noting that
, noting that 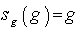 and for any
and for any 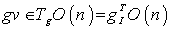 , we have
, we have 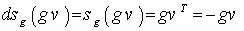 .
. 8. Symmetric Space as a Lie Group with Involutive Isometry
- This approach can be seen through point reflection , then we can introduce the notion of involution and symmetric pairs with involutive automorphism .
8.1. Definition ( Symmetric Space and Involution )
- Let
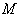 be a Riemannian manifold with the metric
be a Riemannian manifold with the metric 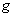 such that for every point
such that for every point 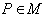 there exists an isometry
there exists an isometry 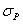 of
of 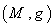 called an involution such that :
called an involution such that : 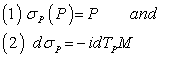 .Composition of involutions will get translations along geodesics which can be used to extend geodesics to the whole of
.Composition of involutions will get translations along geodesics which can be used to extend geodesics to the whole of 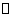 and this means
and this means 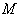 is geodesically complete .
is geodesically complete . 8.2. The Role of Lie Groups
- Again we consider Lie groups in this approach , this is through the fact that the group of isometries mentioned above is a Lie group .By Hopf – Rinow theorem any two points in a geodesically complete Riemannian manifold can be connected by a geodesic . We deduce that the translations along the geodesics make the isometry group
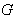 ( Lie group ) acting on
( Lie group ) acting on 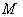 transitively . Here also we identify
transitively . Here also we identify 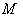 with
with 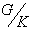 ( Homogeneous space ) , where
( Homogeneous space ) , where 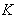 is the isotropy group at a point
is the isotropy group at a point 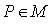 .
. 9. Characterization of Symmetric Spaces
- One of the most surprising features of symmetric spaces is that we can get their properties and information about them from their groups of isometry and this is another scope for more study .
9.1. The Triple ( g , η , ρ )
- In the symmetric space
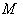 , let
, let 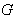 be its group of isometry and
be its group of isometry and 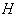 is the isotropy group at
is the isotropy group at 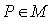 then
then 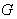 has a Lie group structure and
has a Lie group structure and 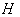 is a closed Lie subgroup of
is a closed Lie subgroup of 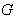 . The Lie algebra g of
. The Lie algebra g of 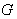 is the space of Killing vector fields on
is the space of Killing vector fields on 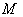 . The Lie algebra η of
. The Lie algebra η of 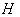 is a subalgebra of g and has a natural complementary subspace ρ such that :g = η
is a subalgebra of g and has a natural complementary subspace ρ such that :g = η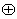 ρ , [η, η] η , [η, ρ ]
ρ , [η, η] η , [η, ρ ] 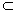 ρ and [ρ , ρ ]
ρ and [ρ , ρ ] 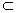 ρ . So the characterization of symmetric spaces is the same as characterization of such triples ( g , η , ρ ) .
ρ . So the characterization of symmetric spaces is the same as characterization of such triples ( g , η , ρ ) . 10. Results and Conclusions
- → The geometric and algebraic approaches to symmetric spaces can be modified to deduce each other .→ Most of features of symmetric spaces can be extracted from their Lie algebras or the triple ( g , η , ρ ) .→ The study of symmetric spaces and continuous research in their properties and classification can lead to most surprising results that can help in their applications .-The different approaches to symmetric spaces mentioned in this paper , lead to specifying two important features of symmetric spaces , that is homogeneousness and symmetry .Homogeneousness can be considered as algebraic property through the transitive action of the isometry group while symmetry is a geometric property which can be seen through point reflection in the Riemannian manifold . An important remark on symmetric spaces is that we can use them in describing some abstract and non- abstract spaces , and this unifies the theory and application of spaces which pave the way for future applications in many fields .
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML