-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2025; 15(7): 2199-2202
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20251507.23
Received: Jun. 16, 2025; Accepted: Jul. 3, 2025; Published: Jul. 11, 2025

Treatment of Immunological Disorders in the Acute Period of Hemorrhagic Stroke
Narzullaev Nuriddin, Shodmanov Jahongir, Makhmanazarov Orifjon
Bukhara State Medical Institute, Bukhara, Uzbekistan
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

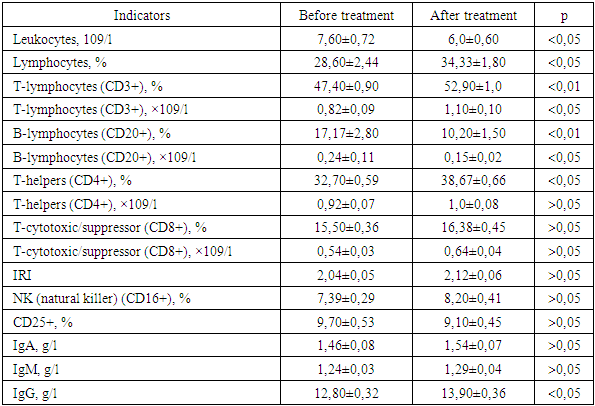
In order to study the effectiveness of reflexology in correcting immunological disorders in the acute period of hemorrhagic stroke, a clinical and immunological examination of 45 patients was performed (on the 2nd day of the patients' stay in the hospital and 15 days after the start of the early rehabilitation course). In the main group of patients (30 people), in whom the basic complex of rehabilitation measures was optimized by including reflexology, a reliable improvement in a number of indicators of cellular and humoral immunity was noted: a decrease in leukocytes in the peripheral blood (p<0.05), an increase in the content of lymphocytes (p<0.05), relative and absolute indicators of the content of T-lymphocytes (CD3+) (p<0.01 and p<0.05, respectively), immunoregulatory cells T-helpers (CD4+) (p<0.05), a decrease in the number of B-lymphocytes to normal values (p<0.01) and an increase in the level of IgG (p<0.05). In the control group (15 people), where standard treatment was carried out, such a pronounced dynamics of the indicators was not observed. Thus, the conducted complex clinical immunological study of the effectiveness of non-drug correction of immunological disorders in the acute period of ischemic stroke showed the high effectiveness of acupuncture, with the relative simplicity and safety of its use.
Keywords: Acute period of hemorrhagic stroke, Acupuncture, Reflexotherapy, Immune status, Cellular and humoral immunity
Cite this paper: Narzullaev Nuriddin, Shodmanov Jahongir, Makhmanazarov Orifjon, Treatment of Immunological Disorders in the Acute Period of Hemorrhagic Stroke, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 15 No. 7, 2025, pp. 2199-2202. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20251507.23.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Due to the high mortality rate after stroke, which remains one of the highest in the world [10], optimization of early rehabilitation of strokes has acquired particular importance in recent decades. Moreover, in 68% of cases, the cause of death in patients who have suffered a stroke at the age of over 60 years are complications that join the main pathological process, while the direct severity of the stroke is only 32% [2,3]. In the very near future after the onset of the most severe forms of stroke, complications develop that occur due to gross extensive damage to brain structures. Somatic complications caused by immobility of patients, autonomic dysfunction and infection develop at a relatively later time [2], therefore their prevention and treatment are of primary practical importance.In recent years, an important role in the pathogenesis of hemorrhagic stroke has been given to immunological mechanisms, since the interaction of the nervous and immune systems, carried out according to the principle of mutual regulation, determines the risk of dysfunction of one of them in the pathology of the other [6,8,11], aggravating the clinical picture and contributing to neurological deficit. One of the main autoimmune processes in the pathogenesis of stroke is damage to the endothelium of the vascular wall, which occurs with the participation of immune factors and is associated with the deposition of immune complexes on the inner surface of the vessels [1].The literature describes mainly various medicinal methods for correcting immunological disorders in patients who have suffered an ischemic stroke: recombinant IL-2 (roncoleukin) [5], cortexin [9], tactivin [7]. For effective rehabilitation of patients with arterial hypertension who have suffered a hemorrhagic stroke, a combined use of the standard hyperbaric oxygenation method and immunoprotection with actovegin according to the standard scheme in the basic complex of rehabilitation treatment has been proposed [4]. However, in addition to the high cost of immunomodulatory drugs, their use carries a risk of developing side effects, which can significantly limit their use. Centuries of experience in acupuncture allow it to be classified as a method that restores immune status.The aim of the study was to investigate the possible effectiveness of reflexology in correcting immunological disorders in the acute period of hemorrhagic stroke.
2. Materials and Methods of Research
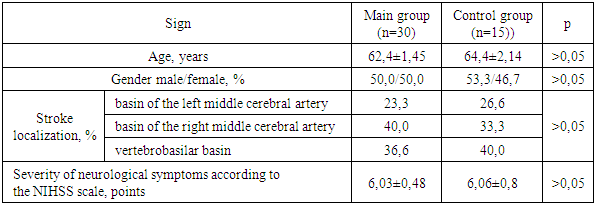
- A clinical and immunological examination of 45 patients (22 women and 23 men) in the acute period of hemorrhagic stroke, treated in the neuroreanimation department for patients with acute cerebrovascular accidents of the Bukhara branch of the Russian Scientific Center of Medical Care, was performed. The age of the patients ranged from 44 to 81 years (the average age was 64.3 ± 1.8 years). Stroke in the left middle cerebral artery basin was diagnosed in 12 patients, in the right middle cerebral artery basin in 18 patients, and in the vertebrobasilar basin in 15 patients. The clinical diagnosis was made on the basis of anamnestic information, the results of subjective and objective neurological symptoms, and data from additional research methods (computer tomography of the brain, duplex scanning of the main arteries of the head, cerebrospinal fluid analysis) in accordance with the ICD 10 revision. The severity of neurological symptoms, assessed using the NIHSS scale, averaged 6.05±0.42 points. To assess the possible impact of acupuncture on immune status indicators, a clinical and immunological study was conducted in two groups of patients, representative in terms of gender, age, and severity of neurological symptoms (Table 1).
|
3. Results of the Study and Their Discussion
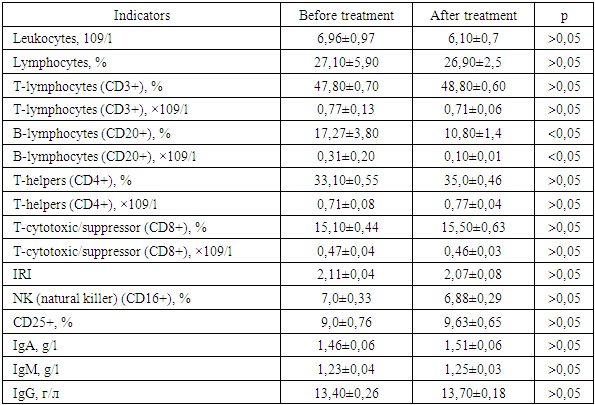
- In the control group, on the 15th day of the patients' stay in hospital, a tendency (p>0.05) towards a slight decrease in leukocytes and lymphocytes in the peripheral blood was noted, compared with the results obtained at the beginning of treatment (Table 2). An insignificant increase (p>0.05) in the content of the relative number of T-lymphocytes (CD3+) was also noted. The difference between the quantitative characteristics of the subpopulation indicators CD4+ and CD8+ before and after treatment was also not significant (p>0.05). A tendency towards an increase in the content of NK cells (CD16+) and CD25+ (p>0.05) was observed. The dynamics of the humoral immunity state is represented by a reliable (p<0.05) decrease to the norm of elevated B-lymphocytes (CD20+) and a slight tendency to increase IgA and IgG, the content of IgM remained virtually unchanged (p>0.05). Thus, a comparative analysis of the immunological examination in the control group showed that there were no significant changes in the immune status against the background of the generally accepted standard treatment of hemorrhagic stroke.
|
|
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML