-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2025; 15(7): 2183-2191
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20251507.20
Received: May 28, 2025; Accepted: Jul. 3, 2025; Published: Jul. 11, 2025

Clinical Approach to the Treatment of Chronic Non-Healing Wounds in Diabetes Mellitus: Efficacy of Cold Atmospheric Plasma and Modern Wound Dressings
Bobokulova Shokhista Abdualimovna1, Safiullina Marina Sergeevna2, Rempel Lyubov Anatolevna2, Mavlyanova Nigina Shavkatovna2
1PhD, Senior Lecturer, Department of General and Pediatric Surgery, Tashkent State Medical University, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
2Student, Faculty of Medicine, Tashkent State Medical University, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
Correspondence to: Bobokulova Shokhista Abdualimovna, PhD, Senior Lecturer, Department of General and Pediatric Surgery, Tashkent State Medical University, Tashkent, Uzbekistan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Diabetic foot (DF) is one of the most severe and socially significant complications of diabetes mellitus, associated with a high risk of infection, chronic ulceration, amputations, and subsequent disability. The prevalence of trophic ulcers in diabetes reaches 15–25%, and the risk of recurrence within 12 months exceeds 40%. The treatment of plantar ulcers remains a particularly complex clinical challenge due to their prolonged course, pronounced pain syndrome, and frequent biofilm formation. This study presents a clinical and experimental analysis of the effectiveness of a comprehensive approach to the treatment of trophic ulcers in 30 patients with DF. The treatment involved the use of cold atmospheric plasma (CAP) generated by the Plasma Skin device with the plasma shower nozzle in combination with modern wound dressings manufactured by HARTMANN (Atrauman Ag, Branolind N, Sorbalgon, Zetuvit Plus). The main group received CAP therapy combined with dressings, while the control group received only local dressing treatment. A phase-based selection of wound care products was employed, along with mechanical debridement, and for plantar ulcers, offloading systems by Fresco were used. The results showed that incorporating CAP into the treatment algorithm significantly accelerated granulation, reduced microbial contamination, stimulated angiogenesis (including via VEGF mediation), and decreased inflammation. These findings confirm the rationale for a comprehensive approach to treating trophic ulcers in patients with DF.
Keywords: Diabetic foot, Trophic ulcer, Cold atmospheric plasma, Atrauman Ag, Foot offloading, HARTMANN, Sorbalgon, Biofilm, VEGF, Plasma shower
Cite this paper: Bobokulova Shokhista Abdualimovna, Safiullina Marina Sergeevna, Rempel Lyubov Anatolevna, Mavlyanova Nigina Shavkatovna, Clinical Approach to the Treatment of Chronic Non-Healing Wounds in Diabetes Mellitus: Efficacy of Cold Atmospheric Plasma and Modern Wound Dressings, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 15 No. 7, 2025, pp. 2183-2191. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20251507.20.
1. Introduction
- Diabetic foot (DF) is one of the most serious and complex complications of diabetes mellitus, resulting from a combination of neuropathy, ischemia, and immunological disorders. This condition is characterized by the development of chronic wound defects that are often complicated by infection and lead to severe consequences, including lower limb amputations and reduced quality of life. According to the International Diabetes Federation (IDF), up to 25% of patients with diabetes develop foot ulcers during their lifetime, and up to 85% of all non-traumatic lower limb amputations are associated with infected trophic ulcers [1,2].The formation of trophic ulcers in DF is a complex interplay of multiple factors. The main mechanisms include diabetic neuropathy, which leads to loss of sensation and repetitive microtrauma; peripheral arterial disease with resulting ischemia and impaired tissue perfusion; and an immunodeficient state due to impaired leukocyte function and reduced immune response [3,4]. These changes disrupt the normal wound healing process—prolonging the inflammatory phase, reducing angiogenesis, increasing oxidative stress, and altering tissue metabolism—which contribute to the chronicity of the wound defect.One of the key factors complicating the treatment of chronic ulcers is the formation of bacterial biofilms.Biofilms not only sustain chronic inflammation but also hinder normal tissue repair processes, significantly reducing the effectiveness of conventional therapies [5,6].In this context, modern methods for treating trophic ulcers in diabetic foot syndrome involve not only systemic and local pharmacological treatments but also innovative physical therapeutic modalities. One of the most promising approaches is the use of cold atmospheric plasma (CAP)—an ionized gas with a temperature below 40°C, which possesses strong antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and regenerative properties [7-10]. CAP disrupts bacterial biofilms, reduces the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, stimulates angiogenesis, and activates regeneration of the cellular matrix. This contributes to accelerated wound healing and a reduced risk of infectious complications.In addition to CAP, the use of modern wound dressings tailored to the phase of the wound healing process plays a crucial role in the treatment of chronic wounds in diabetic foot syndrome. Phase-oriented wound dressings maintain an optimal moist environment, regulate exudate levels, provide antimicrobial protection, and stimulate tissue repair. A wide variety of advanced dressings—ranging from alginate and hydrofiber to antimicrobial silver-impregnated dressings—have proven effective in managing trophic ulcers [11,12].Another essential component of comprehensive treatment is adequate offloading of the affected area, especially in ulcers located on the plantar surface of the foot. Offloading reduces pressure on damaged tissues, prevents recurrent trauma, and creates favorable conditions for healing. The use of individually selected orthopedic insoles and specialized offloading devices significantly improves clinical outcomes and reduces recurrence rates [13,14].The objective of this study was to provide clinical justification for the effectiveness of using cold atmospheric plasma in combination with HARTMANN wound dressings and mandatory offloading of the plantar surface in the treatment of trophic ulcers in patients with diabetic foot syndrome.Pathophysiology of Trophic UlcersIn diabetic patients, the wound healing process is impaired at all stages, resulting in chronic, hard-to-treat wounds. A key pathophysiological factor is suppressed fibroblast activity—cells responsible for synthesizing collagen and extracellular matrix components essential for granulation tissue formation. There is also a disruption in the expression of growth factors, particularly vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), which plays a central role in angiogenesis and microcirculation restoration at the site of injury. As a result, the reparative potential of tissues is reduced, and the formation of new blood vessels is slowed, critically impairing oxygen and nutrient delivery to the wound bed [15,16,17].Chronic inflammation is another significant aspect of the pathophysiology of diabetic ulcers. In diabetes, there is a hyperexpression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α). These cytokines sustain the inflammatory process by activating the transcription factor NF-κB and other signaling pathways, which prevents the wound from transitioning from the inflammatory to the reparative phase. This dysregulation results in the prolonged presence of inflammatory cells in the wound, damage to surrounding tissues, and delayed epithelialization [18,19].A particularly important factor in the chronicity of trophic ulcers is the formation of bacterial biofilms—structured communities of microorganisms encased in an extracellular polymeric substance. Biofilms protect bacteria from antibiotics and immune defenses, promote persistent inflammation, and enhance resistance to treatment. They significantly reduce the effectiveness of conventional therapies and are among the leading causes of recurrence and complications in diabetic foot syndrome [20,21,22].Additionally, various external and local factors further worsen wound conditions and impede healing. Maceration of the wound edges, caused by excessive or improperly managed exudate, leads to tissue softening and an increased risk of microtrauma. Repetitive trauma due to improper pressure distribution on the foot and hyperkeratosis—excessive thickening of the stratum corneum—cause mechanical damage to tissues and disrupt normal regenerative processes. The lack of adequate offloading of the affected area significantly increases pressure on the ulcerative defect, impeding healing and contributing to chronicity [19,20,21].Thus, the pathophysiological cascade leading to the formation and chronicity of trophic ulcers in diabetic patients is multifactorial and requires a comprehensive treatment approach aimed at addressing both intrinsic (microcirculatory and immune disorders) and extrinsic (infectious and mechanical) factors.
2. Methods
- This study was conducted at the Podiatric Center (Diabetic Foot Clinic). A total of 30 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus of more than 5 years’ duration were included. Inclusion criteria comprised the presence of trophic foot ulcers persisting for at least four weeks, indicating a chronic wound process. Patients with clinical signs of osteomyelitis, critical limb ischemia, gangrene, systemic infections, or severe somatic diseases that could influence wound healing were excluded in order to avoid bias in the results [3,23].Patients were randomized into two equal groups using computer-generated random numbers. The main group (n = 15) received cold atmospheric plasma (CAP) therapy three times per week, in combination with HARTMANN wound dressings, selected based on the phase-oriented approach—i.e., choosing dressings appropriate to the wound phase (inflammation, exudation, granulation, epithelialization). The control group (n = 15) underwent standard wound care using HARTMANN dressings tailored to wound phase but without CAP therapy [24,25].To objectively assess the effectiveness of therapy, the following methods were employed:• Clinical examination and photographic documentation of the ulcers to monitor visible changes and healing dynamics;• Planimetry — measurement of ulcer surface area to objectively evaluate wound contraction over time [26];• Microbiological culture to identify pathogenic microflora and assess the efficacy of antimicrobial therapy;• Biochemical markers of inflammation and repair, including C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukin-6 (IL-6)—a key pro-inflammatory cytokine, and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), which reflects angiogenic activity [27,28];• A general clinical inflammation marker — erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR).Wound assessment was conducted every 3 days, allowing timely adjustments to therapeutic measures, reassessment of dressing types, and optimization of cold atmospheric plasma (CAP) parameters. Frequent monitoring helped in early detection of complications and improved the overall effectiveness of the treatment protocol.In addition to the above methods, the study also included cytological analysis of cellular changes in the wound, enabling a deeper morphological assessment of tissue state and therapy efficacy. Cytological material was obtained by gently scraping the wound edges using a sterile spatula or soft brush. Specimens were fixed and stained using standard techniques (Papanicolaou, Romanowsky–Giemsa), followed by microscopic evaluation of cell composition, the number of inflammatory cells (neutrophils, macrophages), presence of fibroblasts, signs of epithelial cell proliferation, as well as bacterial flora and inflammatory features [29].Cytological analysis provided additional insight into the dynamics of inflammatory and reparative processes at the cellular level, offering further evidence of CAP’s ability to reduce inflammation and stimulate tissue regeneration, corroborating clinical and laboratory findings.The use of these diagnostic tools complies with current clinical research standards in the treatment of diabetic ulcers, ensuring reliable and reproducible data that are essential for evaluating the effectiveness of emerging therapeutic technologies [30].Debridement and Wound Condition MonitoringDebridement is one of the most important and integral stages in the comprehensive treatment of chronic trophic ulcers, including diabetic wounds. The primary objective of this procedure is the removal of all non-viable tissue, such as necrotic material, fibrin deposits, hyperkeratosis, and bacterial biofilms, which contribute to sustained inflammation and obstruct normal wound healing [30]. Eliminating these barriers enables the wound to transition from chronic inflammation to the active phases of granulation and epithelialization, significantly accelerating tissue repair [31].In the study conducted at the Podiatric Center’s specialized Diabetic Foot Care Unit, debridement was primarily performed using mechanical methods with sterile surgical instruments — scalpels, curettes, and scissors. The procedure was carried out on an outpatient basis 1–2 times per week, depending on the extent of necrotic tissue and the stage of the wound healing process. Prior to debridement, the wound underwent superficial antiseptic treatment using octenidine-based solutions, which offer a broad spectrum of antibacterial activity without significant cytotoxic effects on granulation tissue [32,33].Special attention was given to the choice of antiseptics based on the wound healing phase. During the granulation and epithelialization stages, the use of aggressive and drying agents (e.g., Betadine, iodophores, hydrogen peroxide) was avoided, as modern research suggests that such agents may inhibit angiogenesis, impede keratinocyte migration, and increase cell apoptosis, thereby delaying regeneration [34,35]. Instead, preference was given to gentle, hydrophilic dressings and low-cytotoxicity antiseptics that support a moist wound microenvironment conducive to healing.Wound condition monitoring was conducted every 3 days, with systematic assessment of the following parameters:• The volume and nature of wound exudate (serous, purulent, hemorrhagic), serving as indicators of inflammatory activity and potential infection;• The color, texture, and density of granulation tissue, reflecting the quality and speed of new connective tissue and blood vessel formation;• The presence of fibrinous plaque, hyperkeratosis, and signs of infection (edema, erythema, local hyperthermia);• The degree of epithelialization at the wound edges, indicating wound closure progress and epithelial cell migration;• Visual inspection with photographic documentation, providing objective records of wound dynamics and allowing for planimetric analysis.This process is clearly illustrated by a series of clinical photographs showing the same patient’s foot at different stages of treatment and healing — starting from the initial examination and surgical necrectomy, through sequential wound care procedures and dressings involving cold atmospheric plasma therapy, to the final stage of epithelialization (Figures 1–5).
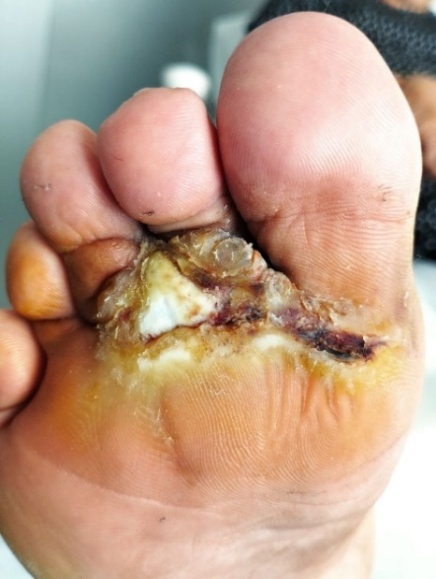 | Figure 1. A trophic ulcer developed in the area of scar tissue that had formed following surgical drainage of a phlegmon |
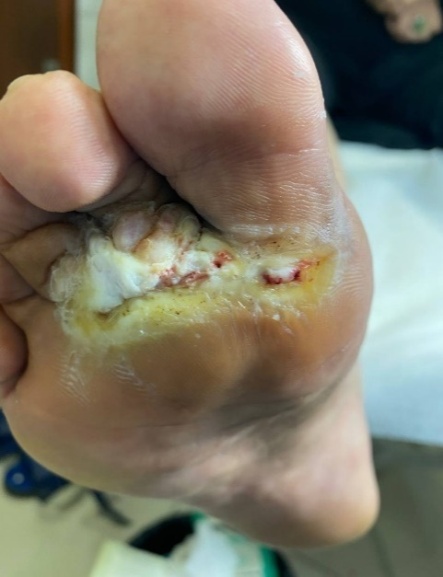 | Figure 2. Condition of the trophic ulcer after surgical necrectomy. Treatment included the use of Hartmann wound dressings and cold atmospheric plasma therapy |
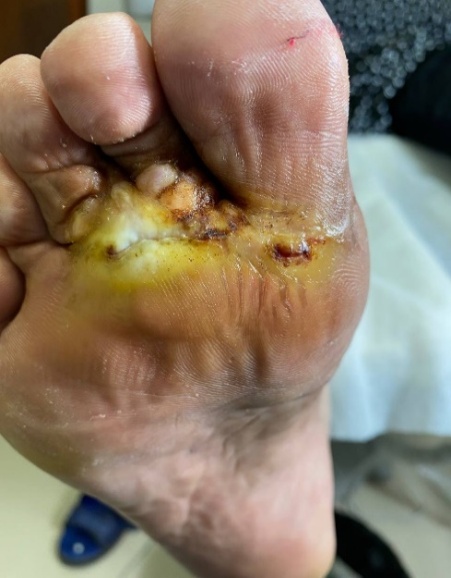 | Figure 3. Trophic ulcer: staged wound care and dressing changes throughout healing |
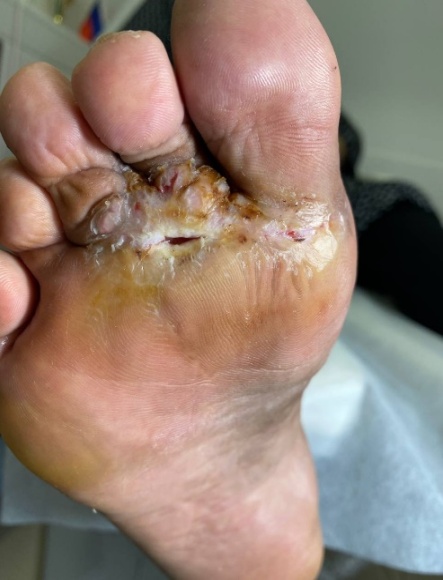 | Figure 4. Trophic ulcer: staged wound care and dressing changes throughout healing |
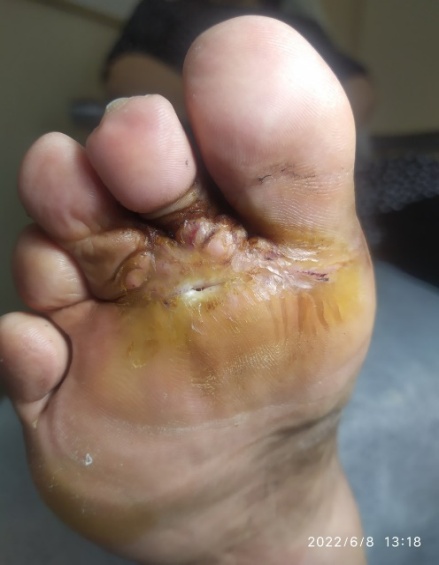 | Figure 5. Trophic ulcer: staged wound care and dressing changes throughout healing |
3. Results
- Upon completion of the 4-week treatment course, statistically and clinically significant differences were observed between the main group (CAP + HARTMANN dressings) and the control group:• The average reduction in ulcer area in the main group was 62.4%, compared to 32.8% in the control group (p < 0.01), indicating a marked acceleration of reparative processes with combination therapy. Wound size began to decrease as early as day 10–12 of treatment.• The formation of mature granulation tissue (visually and based on cytological criteria) was observed in 86% of patients in the main group, versus 40% in the control group, confirming the role of CAP and appropriately selected dressings in promoting the transition from inflammation to proliferation.• C-reactive protein (CRP) levels decreased from 28 to 10 mg/L in the main group, compared to a reduction to 19 mg/L in the control group, reflecting a more pronounced anti-inflammatory effect of CAP therapy.• Interleukin-6 (IL-6), a key mediator of chronic inflammation, decreased from 18.4 to 9.6 pg/mL in the main group, while in the control group, the average level remained at 13.1 pg/mL.• Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), which promotes angiogenesis, increased from 57 to 104 pg/mL in the main group, demonstrating enhanced microcirculation and vascularization at the ulcer site.• Microbiological cultures on day 21 remained positive in only 33% of patients in the main group, versus 73% in the control group, confirming the antiseptic efficacy of the combined approach (CAP + Atrauman Ag).Additional confirmation was provided by cytological analysis, which revealed a reduction in neutrophils and the emergence of active fibroblasts.
4. Discussion
- The integration of cold atmospheric plasma (CAP) and a phase-oriented selection of wound dressings demonstrated significant advantages in the treatment of trophic ulcers in patients with diabetic foot syndrome. The findings confirm that this combination produces multifactorial therapeutic effects: it accelerates wound debridement, stimulates granulation tissue formation, reduces microbial load, and lowers inflammatory background.The clinically significant reduction in ulcer size, improvement in inflammatory biomarkers (CRP, IL-6), and increase in VEGF levels in the main group indicate activation of reparative and angiogenic processes under the influence of CAP. One of the key factors in the success of combination therapy was the proper organization of the wound dressing process. The use of HARTMANN dressings in accordance with the phases of the wound healing process ensured not only optimal moisture balance but also fulfilled a number of additional functions—antimicrobial protection (Atrauman Ag), effective exudate management (Sorbalgon, Zetuvit Plus Silicone Border), and stimulation of epithelialization (Branolind N). This individualized approach to dressing selection significantly increased treatment efficacy, minimized the risk of maceration and secondary infection, and shortened ulcer healing time.Particular attention should be paid to offloading the foot, which is critically important in the presence of plantar ulcers. The use of offloading materials eliminated pressure on the wound surface, reduced the risk of progression of soft tissue damage, and improved microcirculation in the affected area. This confirms that without adequate offloading, even the most advanced technologies and dressings lose their effectiveness.Thus, the presented approach combines elements of both innovative and evidence-based medicine, providing comprehensive targeting of the key pathophysiological mechanisms of chronic wounds. It has strong potential for clinical implementation, especially in specialized diabetic foot clinics and outpatient chronic wound treatment centers.
5. Conclusions
- Based on the conducted study, it can be concluded that the use of cold atmospheric plasma (CAP) as part of combination therapy for trophic ulcers in diabetic foot syndrome significantly increases clinical efficacy. In combination with phase-oriented HARTMANN dressings and mandatory offloading of the plantar surface, CAP therapy provides pronounced antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and regenerative effects, initiates active tissue recovery, shortens healing time, reduces the risk of infectious complications, and improves the overall condition of patients.This therapeutic approach affects not only the symptoms, but also the pathogenetic mechanisms of the chronic wound process. Biochemical and cytological data confirm reduced inflammation, angiogenesis activation, and enhanced tissue repair. Practical implementation of this method in an outpatient or day-hospital setting does not require complex equipment and can be easily adopted by most healthcare facilities.The safety and tolerability of CAP therapy, along with the convenience and effectiveness of modern dressings, make this treatment scheme widely applicable. The method aligns with the principles of personalized medicine and holds high potential for inclusion in clinical guidelines for the treatment of chronic ulcers in patients with diabetic foot syndrome.In summary, comprehensive therapy incorporating CAP, phase-specific dressings, and plantar offloading can be considered a promising direction in modern wound management, fully aligned with evidence-based standards and aimed at improving the quality of life for patients with diabetic complications. The method is safe, suitable for outpatient practice, and can be recommended for inclusion in clinical guidelines.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML