-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2025; 15(6): 2028-2031
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20251506.89
Received: May 20, 2025; Accepted: Jun. 15, 2025; Published: Jun. 23, 2025

A Modern View on the Problem of Non-Developing Pregnancy
Akhmadalieva N. Zh.1, Akhmadzhonova G. M.1, Mamazhonova S. O.1, Akhmedov F. K.2
1Andijan State Medical Institute, Andijan, Uzbekistan
2Bukhara State Medical Institute, Bukhara, Uzbekistan
Correspondence to: Akhmedov F. K., Bukhara State Medical Institute, Bukhara, Uzbekistan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Background. The problem of miscarriage, especially in the early stages, is of great importance both from a medical and social point of view. Approximately 80% of cases of spontaneous miscarriages occur in the first trimester. Among the various types of miscarriage, non-developing pregnancy attracts special attention, the multifactorial nature of which is beyond doubt. Aim. to study the expression of interleukin-2 (IL-2) in pregnant women with fetal growth retardation and spontaneous abortion. Materials and methods. We studied the pregnant women involved in the study, dividing them into 3 groups: Group 1 - complicated by fetal failure (n=50); II group - complicated by spontaneous miscarriage (n=54). control group - group of pregnant women with physiological pregnancy (n=30). Results. The results of our studies showed that the concentration of interleukin-2 (IL-2) in the blood of pregnant women with complications of fetal malformations in group I was 51.4±0.32 pg/ml, and in women included in group II, its level was 41.2±0.30 pg/ml. In pregnant women in the control group, this indicator was 18.2±0.22 pg/ml (P<0.001). ROC curve for the indicator “Interleukin-2 (IL-2) pg/ml”. The area under the curve was 0.92±0.12 (95% CI (confidence interval) 0.645.... 0.920), p=0.08, indicating that IL-2 can be used as a predictor of fetal growth retardation. In our study, the plasma IL-2 level in women with fetal growth retardation was 51.4±0.32 pg/ml (specificity 64%, sensitivity 92%). Conclusions. Thus, our study found a positive correlation between interleukin-2 (IL-2) and fetal growth retardation. It also showed that IL-2 is a reliable marker for fetal growth retardation alone.
Keywords: Interleukin-2, Pregnant women, Non-developing pregnancy, Cytokines
Cite this paper: Akhmadalieva N. Zh., Akhmadzhonova G. M., Mamazhonova S. O., Akhmedov F. K., A Modern View on the Problem of Non-Developing Pregnancy, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 15 No. 6, 2025, pp. 2028-2031. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20251506.89.
1. Introduction
- A missed abortion (DI), also known as a missed abortion, is defined by the World Health Organization as the death of an embryo within the uterus without its spontaneous removal (miscarriage), in which the fertilized egg remains in the uterine cavity. Obstetricians and gynecologists identify key risk factors for this condition, including anatomical, endocrine, infectious, immunological, and genetic causes [1,2].Pregnancy is a complex physiological process that is under the strict control of the body. Immune factors, including inflammatory and anti-inflammatory mechanisms, play an important role in all its stages: from fertilization to birth. Inflammatory processes play an important role in embryo implantation, and immune tolerance provides protection and development of the fetus, which is semi-allogeneic to the mother's organism [3,5].Pregnancy is divided into three immunological phases, which are determined by the influence of different groups of cytokines. In the first trimester, the inflammatory processes necessary for the introduction of trophoblast cells into the endometrium during implantation begin. The second phase is characterized by the predominance of an anti-inflammatory state, which ensures the symbiosis between the mother and the fetus. This state plays a key role in creating a favorable environment for the development of the fetus in the womb, ensuring the harmonious coexistence of the mother and the fetus, and ensuring normal growth and development of the fetus [6,8].Inflammatory substances and processes that cause inflammation play an important role in immune defense. Inflammatory cytokines help the body resist microbial attacks and tissue damage, which is especially important in protecting the fetus from infections during pregnancy. Cytokines take part in the reconstruction of the tissues of the uterus and egg cells, creating conditions for the development of the fetus [4,7]. The endometrium of women who have not had recurrent miscarriages produces Th2 cytokines (such as IL-2 and IL-6), whereas in women with recurrent unexplained miscarriages, the endometrium is dominated by Th1 cytokines (e.g., IL-2, IL-12, and IFNγ). Approximately 25% of women with unexplained recurrent miscarriages have an enhanced immune and inflammatory response to trophoblast antigens, as well as increased secretion of embryotoxic Th1 cytokines.The aim of the study was to study the expression of interleukin-2 (IL-2) in pregnant women with fetal growth retardation and spontaneous abortion.
2. Materials and Methods
- This study examined 134 pregnant women who applied to the department of pregnancy pathology and the hygiology departments of the Andijan City Maternity Complex during 2022-2023, including 104 pregnant women in the main group and 30 pregnant women in the control group whose pregnancy proceeded without complications. We studied the pregnant women involved in the study, dividing them into 3 groups: Group 1 - complicated by fetal failure (n=50); II group - complicated by spontaneous miscarriage (n=54). control group - group of pregnant women with physiological pregnancy (n=30);The data obtained as a result of the study were subjected to statistical processing on a personal computer using the Microsoft Office Excel-2012 software package.
3. Results
- Non-developing pregnancy remains one of the key problems of modern obstetrics, having both clinical and social significance, since its share in the structure of reproductive losses is quite significant (10-20%). The retention of a dead fetus in the uterus creates a serious danger to the health and life of a woman. The most noticeable disturbances occur in the hemostasis system, which increases the likelihood of bleeding regardless of the method of termination of such a pregnancy.
|
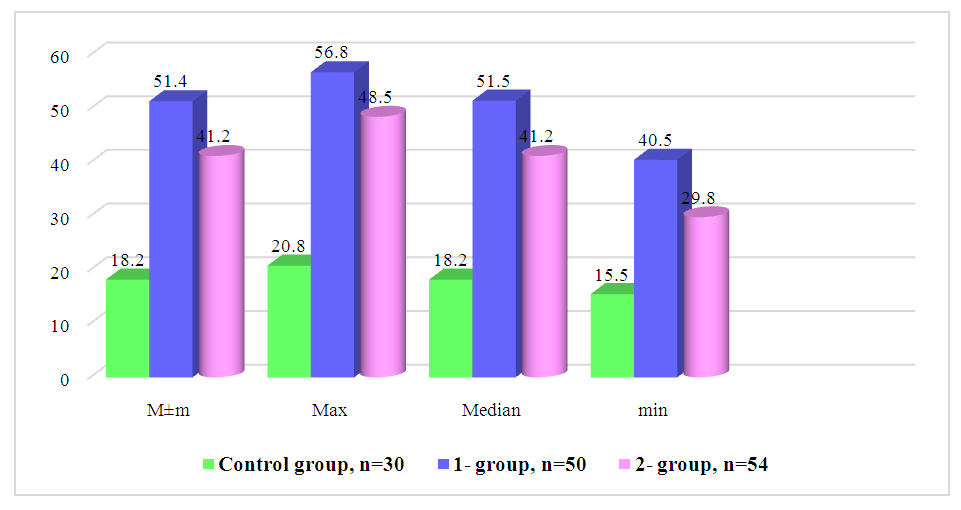 | Figure 1. IL-2 cytokine concentrations in pregnant women complicated by spontaneous abortions and fetal growth retardation |
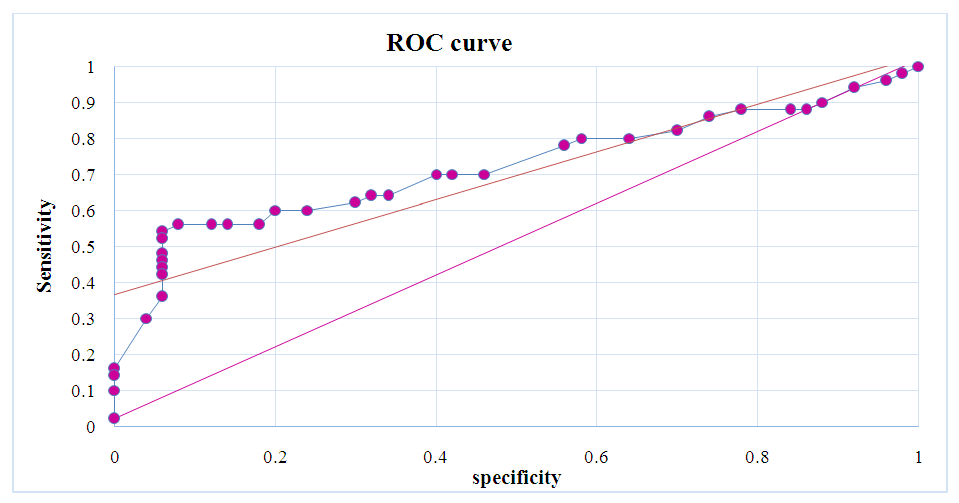 | Figure 2. ROC curve for the indicator “Interleukin-2 (IL-2) pg/ml” in fetal growth retardation |
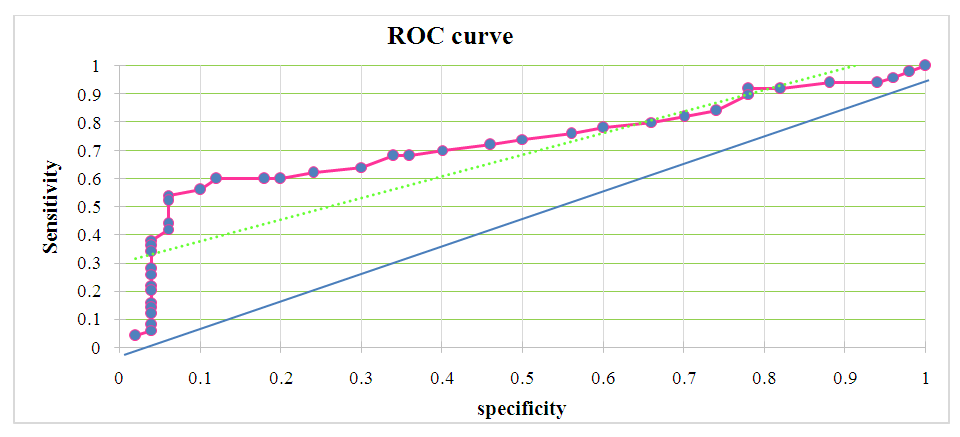 | Figure 3. ROC curve for the indicator “Interleukin-2 (IL-2) pg/ml” in spontaneous abortion |
4. Discussion
- The persistence of opportunistic microorganisms and viruses in the endometrium causes chronic inflammation, attracting mononuclear phagocytes and natural killer’s Th to the site, which produce proinflammatory cytokines such as TNF, IL-1β and IL-2. Changes in the endometrium disrupt the formation of local immunosuppression in the preimplantation period, which is necessary to create a protective barrier and prevent rejection of a partially foreign organism. An increase in the level of proinflammatory cytokines activates prothrombinase, which leads to the formation of hematomas and thromboses in the placenta, causing termination of pregnancy [5]. The area under the curve was 0.92±0.12 (95% CI (confidence interval) 0.645.... 0.920), p=0.08, indicating that IL-2 can be used as a predictor of fetal growth retardation. In our study, the plasma IL-2 level in women with fetal growth retardation was 51.4±0.32 pg/ml (specificity 64%, sensitivity 92%).The Th1 cytokines tested included IL-2, TNF α and β, and INF-γ, while the Th2 cytokines included IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, and IL-10. Despite the use of similar methods (ELISA and flow cytometry), the data from these studies contradict the hypothesis of a generalized inflammatory response in women with early pregnancy loss. It is important to consider that cytokines are produced not only by Th cell subtypes, but also by APCs and other immune cell groups [8]. Thus, measuring cytokine levels in peripheral blood serum is probably the most accurate way to assess the immune status of the body. In addition, complex interactions between cytokines and their synergistic or antagonistic effects may complicate the analysis of the obtained data [3,7].In conclusion, it should be emphasized that the presented data did not confirm the prevalence of any type of immune response in women with a missed miscarriage compared to women with a normal pregnancy. Elevated levels of IL-2 as well as positive correlations between most of the Th1 and Th2 cytokines studied may indicate a general activation of the immune response after fetal death in the first trimester. This aspect requires further research.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML