-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2025; 15(6): 1969-1974
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20251506.74
Received: May 22, 2025; Accepted: Jun. 13, 2025; Published: Jun. 21, 2025

Differentiated Immunotherapy for Acute Adhesive Small Bowel Obstruction
Khamdamov Bakhtiyor Zarifovich, Eshchanov Alisher Atabaevich, Khaidarov Farrukh Nuriddinovich
Bukhara State Medical Institute, Bukhara, Uzbekistan
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

The proposed treatment and diagnostic algorithm allowed to implement the concept of clinical and immunological management of patients with acute adhesive small intestinal obstruction, to ensure early detection of prognostically unfavorable signs, timely decision-making on surgical intervention and rational inclusion of immunotherapy. The stratified approach has proven its clinical, immunological and prognostic effectiveness.
Keywords: Acute adhesive small intestinal obstruction, Differentiated immunotherapy, Treatment and diagnostic algorithm
Cite this paper: Khamdamov Bakhtiyor Zarifovich, Eshchanov Alisher Atabaevich, Khaidarov Farrukh Nuriddinovich, Differentiated Immunotherapy for Acute Adhesive Small Bowel Obstruction, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 15 No. 6, 2025, pp. 1969-1974. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20251506.74.
1. Introduction
- Acute adhesive small bowel obstruction (ASBO) remains one of the most common causes of emergency surgical interventions in abdominal surgery, accounting for up to 75% of all cases of mechanical intestinal obstruction [1,6,9]. The incidence of morbidity associated with this pathology is steadily increasing, and the frequency of repeated operations and relapses reaches 30-35% [3,15,18]. At the same time, mortality in complicated cases can exceed 20-25%, especially in patients with an initial somatic burden and immune homeostasis disorders [2,13,19].Modern approaches to the treatment of OSTKI are focused primarily on eliminating the mechanical obstacle and sanitizing the lesion, but they do not take into account the depth of systemic inflammation and individual immunological characteristics of the patient [5,11,13]. Meanwhile, it is the immune response that determines the severity of complications, the course of the postoperative period and the risk of repeated interventions. According to modern studies, patients with severe OSTKI have significant disturbances in cellular and humoral immunity - a decrease in CD4⁺ and HLA-DR⁺, hyperexpression of IL-6 and TNF-α, an increase in the level of circulating immune complexes [5,8,11,18].To date, there are no universal algorithms for risk stratification based on immunological markers. Standard scales (e.g., APACHE II, qSOFA) are not adapted to the specific features of surgical inflammatory diseases of the abdominal cavity (2,8,10). Thus, the development of an integrated clinical and immunological model that allows predicting the outcome of the disease and individualizing treatment seems to be a relevant and timely task.The introduction of immunotherapy as a component of pathogenetic treatment is of additional importance. Drugs with proven immunomodulatory action, including polyoxidonium, galavit and interferonogenesis inducers, are able to reduce the severity of the systemic inflammatory response, restore immune reactivity and reduce the incidence of postoperative complications [7,12,20,21,22]. However, their use requires preliminary stratification and accurate assessment of the immune status. Thus, the relevance of this technique is due to the need to systematize approaches to clinical and immunological stratification of the severity of the course of OSTKN, the development of a prognostic scale and the introduction of immunocorrective therapy on a pathogenetic basis.Purpose of the study: development of a treatment and diagnostic algorithm for differentiated immunotherapy in acute adhesive small intestinal obstruction.
2. Material and Methods
- The work is based on the results of a comparative clinical and immunological study conducted in 2021-2024 at the Khorezm regional branch of the Republican Scientific and Practical Center for Emergency Medical Care. The study included 115 patients with an established diagnosis of acute adhesive small intestinal obstruction, hospitalized on an emergency basis with a characteristic clinical picture of intestinal obstruction. The entire diagnostic and treatment process was carried out in accordance with the approved protocols and in compliance with international ethical and legal standards. The study design met the criteria for cohort comparative observations with elements of stratification and control of prognostic factors, which ensured an appropriate level of reproducibility and internal validity of the data obtained.For comparison purposes, the entire sample of patients was divided into two groups. The control group included 56 patients treated according to the standard regimen without immunocorrective therapy and was used mainly for retrospective analysis of outcomes and assessment of the basic immune status in the absence of targeted intervention. The main group consisted of 59 patients who, along with basic therapy, were prescribed immunotherapy based on preliminary clinical and immunological assessment and risk stratification. In addition to the main cohort, the study included a group of healthy donors (n=20), matched by gender and age, with no history of acute or chronic inflammatory, autoimmune, or oncological diseases. This group was used as a reference to establish the range of physiological values of immunological parameters and calculate the degree of deviation from the norm in patients with OSTCN. The diagnostic package included a clinical and physical examination, standard laboratory tests, instrumental imaging methods, and an extended immunological study. The clinical assessment of the patient's condition was based on complaints, anamnesis, and objective examination data, including measurement of body temperature, respiratory rate, pulse, blood pressure, and assessment of the presence of peritoneal symptoms. Pain, bloating, nausea, lack of passage of intestinal contents, fever, and signs of intoxication were recorded with mandatory recording of the duration of pain syndrome and the time from the onset of the disease to admission.Laboratory diagnostics included determination of levels of leukocytes, neutrophils, lymphocytes, hemoglobin, hematocrit, platelets, as well as calculation of derived indices - neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), leukocyte intoxication index (LII) and hematological intoxication index (HPI). Biochemical parameters determined on the first day after hospitalization included levels of C-reactive protein (CRP), total protein, albumin, urea, creatinine and glucose. Coagulogram was performed according to indications and included activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT), international normalized ratio (INR) and fibrinogen level. All laboratory studies were performed on automatic analyzers in a certified laboratory of the health care institution, with observance of intralaboratory and interlaboratory quality control. Instrumental diagnostics was based on the step-by-step application of plain radiography of abdominal organs, ultrasound examination (US) and multispiral computed tomography (MSCT) with intravenous contrast. MSCT allowed to assess the degree of dilation of small intestinal loops, the presence of free fluid in the abdominal cavity, signs of ischemia, infiltration and thickness of the intestinal wall, as well as the transition zone and severity of the adhesion process. In some clinically unclear cases, diagnostic laparoscopy was used, which allowed to confirm the diagnosis and determine the scope of the upcoming surgical intervention. The immunological examination was carried out in two stages: upon admission (within the first 24 hours before the start of specific therapy) and again on the 5-7th day of treatment or in the early postoperative period. The study included an analysis of the cellular and humoral immunity, as well as the determination of proinflammatory cytokines and cell adhesion molecules. The flow cytofluorimetry method was used to assess the levels of CD3⁺, CD4⁺, CD8⁺, CD16⁺, CD25⁺, HLA-DR⁺ lymphocytes, as well as the CD4/CD8 index as an integral indicator of the regulatory balance of the T-cell link. Humoral parameters included IgA, IgM, IgG, circulating immune complexes (CIC) concentrations, as well as interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), ICAM-1, and VCAM-1 levels determined by ELISA using validated kits. All samples were analyzed on a BD FACSCalibur cytometer and enzyme immunoassay analyzers in compliance with the requirements for biomaterial, transportation times, and temperature conditions. As part of the study, an original integrated prognostic scale was developed, including 25 parameters combining clinical, laboratory, instrumental and immunological indicators. Each sign was assigned a certain point value depending on the degree of deviation and prognostic significance established on the basis of preliminary correlation analysis. As a result, the total score allowed classifying patients into three risk categories: low (up to 12 points), moderate (from 13 to 24 points) and high (25 points and more). Stratification determined the management tactics: at low risk, standard therapy with dynamic observation was carried out, at moderate risk, immunocorrective therapy with cytokine monitoring was prescribed, at high risk, emergency surgery was performed in combination with intensive immunotherapy and resuscitation observation. The effectiveness of the proposed algorithm was assessed based on clinical, immunological and prognostic criteria. The following outcomes were used: duration of hospital stay, incidence of grade III-V postoperative complications, mortality, number of repeated interventions and need for resuscitation support. Immunological parameters were analyzed dynamically, determining the degree of CD4⁺ population recovery, HLA-DR⁺ level, reduction of IL-6, TNF-α and CIC. The prognostic value of the scale was tested using ROC analysis: the area under the curve (AUC) for IL-6 and HLA-DR⁺ exceeded 0.91, the sensitivity of the model was 88.2%, specificity was 83.4%, Youden index was 0.716. Statistical data processing was performed using SPSS v.22 and Statistica v.12.5 packages. When comparing quantitative variables, the Student and Mann–Whitney tests were used, and for qualitative variables, the Pearson χ² test was used. The significance level in all calculations was taken at p <0.05. Thus, the applied methodology allowed us to objectively assess the relationship between immune imbalance and the severity of the clinical course of OSTCN, as well as reliably confirm the effectiveness of using a prognostic scale and immunotherapy regimens within the framework of a comprehensive treatment and diagnostic algorithm.
3. Results and Discussion
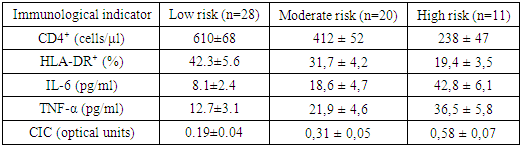
- The duration of pain syndrome, being one of the most accessible and objectively recorded parameters upon patient admission, showed high prognostic significance in the context of assessing the probability of complicated course of the disease and the need for surgical intervention. In the vast majority of patients treated conservatively, the pain syndrome was relatively short-term: 10 patients (28.6%) sought help within the first 6 hours from the onset of symptoms, and another 13 (37.1%) - in the interval from 6 to 12 hours. In total, 65.7% of non-operated patients were admitted in the first 12 hours from the onset of the disease. This fact indicates that early hospitalization correlates with a milder clinical course and a high chance of restoring intestinal patency without surgical intervention. In contrast, late admission was significantly more common among patients who required surgical treatment. Thus, only 1 patient out of 21 (4.8%) was admitted in the interval <6 hours, and only 2 (9.5%) - in the interval 6-12 hours. The majority of patients had experienced pain for more than 24 hours: 8 people (38.1%) were in the interval from 25 to 48 hours, and another 6 (28.6%) were in the subgroup >48 hours. Thus, two out of three operated patients (66.7%) were admitted after 24 hours of pain syndrome, which emphasizes the unfavorable prognostic value of delayed treatment. It is also important that all six patients who sought treatment after more than 48 hours were operated on. This indicates an absolute correlation between the duration of symptoms >48 hours and the need for surgical intervention, which allows us to consider this time limit as a threshold value when deciding on surgical tactics. The overall structure of the entire sample demonstrates that the majority of patients (67.8%) were admitted within the first 24 hours from the onset of symptoms. However, only 17.2% of those operated on sought help during this period. This disproportion emphasizes that early admission is a marker of a more favorable clinical outcome and a predictor of the success of conservative therapy, while late hospitalization statistically significantly increases the risk of complications, which is consistent with the data of other studies on OSTCH. Based on the identified patterns, the duration of pain syndrome was included in the clinical block of the prognostic scale with the appropriate gradation: <12 hours - 0 points, 13-24 hours - 1 point, 25-48 hours - 2 points, >48 hours - 3 points. In the final model, it occupied one of the key positions, along with the level of CD4⁺ and IL-6, which is confirmed by a high correlation with treatment outcomes. As expected, abdominal pain in OSTCN was a universal clinical symptom, registered in 100% of patients regardless of the subsequent treatment tactics. This confirms its mandatory role as a diagnostic criterion and a symptom determining urgent hospitalization. The second most common symptoms were bloating and lack of passage of intestinal contents. These complaints were noted in 83.9% and 85.7% of patients, respectively. However, their frequency was significantly higher in those patients who subsequently required surgical intervention: lack of stool and gases - in 95.2% of those operated on versus 77.1% in the conservative management group (p=0.019), indicating a more pronounced impairment of the motor-evacuation function of the intestine in this subgroup. Bloating was also more often observed in patients who underwent surgery (90.5% versus 82.9%), although the difference did not reach statistical significance. The most significant differences between the groups were noted in systemic manifestations of inflammation and intoxication. Thus, fever above 38°C was registered in more than half of the operated patients (11 of 21, or 52.4%), while in the subgroup treated without surgery, it was observed only in 17.1% of cases (p=0.002). This confirms that the presence of febrile temperature on admission is a significant predictor of a complicated course, reflecting the activation of the systemic inflammatory response and possible ischemia or inflammation of the intestinal wall. A similar trend is observed when assessing the symptoms of intoxication, such as severe thirst, dry mucous membranes, oliguria. These signs were recorded in 71.4% of operated patients and only in 34.3% of non-operated patients (p=0.008), which confirms their high predictive value and indicates systemic destabilization of water-electrolyte balance and the development of hypovolemia. Of interest is the frequency of repeated vomiting with bile, which occurred in 61.9% of patients who underwent surgery and in 28.6% of patients who were treated conservatively (p=0.015). Such symptoms apparently reflect irritation of the upper gastrointestinal tract against the background of a high level of obstruction and can serve as a clinical equivalent of severe adhesive syndrome with a functional disorder of the duodenogastric passage. A comprehensive assessment of these complaints showed that, on average, there were 6.2 complaints per patient in the group that underwent surgery, while in those who did not undergo surgery there were 4.8 (p=0.004). This reflects not only a more severe clinical condition, but also a more polymorphic and systemic symptomatic load. Taking into account the presented structure, six of the eight complaints listed in the table were included in the clinical block of the prognostic scale as independent variables, each of which received a weighted score depending on the frequency and strength of the relationship with the treatment outcomes. Thus, subjective symptoms in patients with TSCN, despite their apparent non-specificity, have a high prognostic value when properly systematized and quantitatively interpreted. Including complaints in the scoring system allowed not only to clarify the severity of the patient's condition, but also to form the basis for making tactical decisions. The obtained data demonstrate reliable positive changes in key immunological parameters against the background of immunotherapy in patients of the main group, stratified as patients with a high risk of severe TSCN. All the presented indicators are included in the final prognostic model and reflect both the severity of secondary immunodeficiency at the time of admission and the effectiveness of the immunocorrective therapy (Table 1).
|
4. Conclusions
- 1. The conducted clinical and immunological study showed that the course of acute adhesive small intestinal obstruction is accompanied by a pronounced immune-inflammatory imbalance, the degree of which directly correlates with the severity of the condition, the need for surgical intervention, the frequency of complications and mortality. Reliable changes were established both in the cellular link of immunity (decrease in CD4⁺, HLA-DR⁺, CD4/CD8 imbalance) and in the humoral profile (increase in IL-6, TNF-α, CIC), especially in patients with delayed admission and a history of multiple abdominal interventions. 2. Based on the data obtained, a prognostic scale was developed, including 25 clinical, laboratory, instrumental and immunological parameters. The scale allows for an early quantitative assessment (within the first 6-12 hours from the moment of hospitalization) of the degree of risk of complicated course and assigning the patient to one of three categories: low, moderate or high risk. According to the results of ROC analysis, the diagnostic accuracy of the model was AUC=0.91, sensitivity - 88.2%, specificity - 83.4%.3. A treatment and diagnostic algorithm for stratified management of patients with OSTKN has been developed, in which the risk level determines the scope of treatment measures. In the case of low risk, standard conservative tactics are implemented without immunotherapy; in the case of moderate risk, pathogenetically substantiated immunotherapy is carried out (polyoxidonium, thymogen, roferon-A); in the case of high risk, immediate surgical intervention is supplemented by intensive immunocorrection and dynamic monitoring of immunological parameters in the postoperative period. 4. Implementation of the algorithm in clinical practice has significantly improved treatment outcomes: reduced the incidence of grade III-V postoperative complications from 38.2% to 18.6% (p <0.01), reduced the number of reoperations by 3.2 times, reduced the average length of hospital stay by 26.9% and mortality by 3.3 times (from 30.4% to 9.1%). The proportion of patients with a favorable clinical outcome increased from 42.1% to 71.2%. 5. In addition to clinical effectiveness, the proposed approach demonstrated high social and economic viability. The level of rehabilitation in the early stages after discharge increased by 57.5%, and the estimated cost savings amounted to more than 9 million sums for each additional favorable outcome achieved.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML