-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2025; 15(6): 1898-1900
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20251506.56
Received: May 22, 2025; Accepted: Jun. 18, 2025; Published: Jun. 20, 2025

Assessment of Homocysteine Levels During in Vitro Fertilization Cycles: Diagnostic and Treatment Strategies
Okhunova Shakhnoza Botirjon qizi1, Sadikova Dilfuza Ravshanbekovna2, Maksudova Muhayyo Mansurovna3
1Doctoral Student, Tashkent Medical Academy, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
2PhD., Associate Professor, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology in Family Medicine, Tashkent Medical Academy, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
3PhD., Founder of the Clinic “Siz ona bo'lasiz”, Uzbekistan
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

This article evaluates the impact of blood homocysteine levels on the outcomes of in vitro fertilization (IVF) cycles in women with infertility. A total of 90 participants were divided into two groups, with one group undergoing pre-IVF homocysteine correction. The results revealed higher oocyte counts, improved embryo quality (class A), and increased clinical pregnancy rates in the group with normalized homocysteine. The findings highlight the clinical significance of monitoring and correcting homocysteine levels as part of individualized IVF preparation protocols.
Keywords: Homocysteine, IVF, Infertility, Oocyte quality, Embryo development, Pregnancy, Metabolic balance
Cite this paper: Okhunova Shakhnoza Botirjon qizi, Sadikova Dilfuza Ravshanbekovna, Maksudova Muhayyo Mansurovna, Assessment of Homocysteine Levels During in Vitro Fertilization Cycles: Diagnostic and Treatment Strategies, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 15 No. 6, 2025, pp. 1898-1900. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20251506.56.
1. Introduction
- Assistant reproductive technologies (Yort), especially extracorporeal insemination (IUI), today on the day barren couples for the most effective and wide being used from methods one is calculated. The ECU results different factors impact does, of these one in the body homocysteine level. [1] Homocysteine — methionine exchange as a result harvest to be amino acid is metabolic and immunological to processes impact shows. [2] Homocysteine level out of the norm high (hyperhomocysteinemia) or low (hypohomocysteinemia) in the body many systems, including reproductive to health negative impact shows. [3]In the world Despite the fact that IVF and IVF procedures have been performed for almost 40 years and are constantly being improved, it is still important to find ways to improve the effectiveness of these expensive programs. [4] One of these opportunities is to optimize the preparation of female patients for IVF and IVF treatment, an important part of which is to identify and correct factors that increase the risk of failure. In this regard, it is especially relevant to analyze how various conditions and diseases affect the effectiveness of the method. [5,6]Current in ECU protocols at the time embryo features with its "quality" It is believed to be related. A row research this showed that the embryo microscopic assessment genetic a relatively normal embryo when choosing information gives and implantation speed increases. [7] Embryo development stages classification modern systems blastomeres number of them one diversity, division speed and decomposition level such as features into account takes. Various diameter blastomeres existence embryo cell of mass uneven, asynchronous to the division take arrival possible.In recent years, scientific studies have been actively published in the literature on the increase or decrease in homocysteine in women of reproductive age during pregnancy and lactation, and the negative impact of this condition on pregnancy, childbirth and the neonatal period, as well as on the condition of the fetus and newborn [9].Take visited research this shows that homocysteine level height ovulator cycle to spoil, egg cell quality and number to decrease, embryo implantation level to decrease take [10] Therefore, the ECU cycle from the entrance before homocysteine amount determine, assess and normalization important importance has.
2. Material and Methods
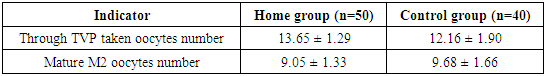
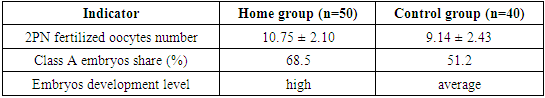
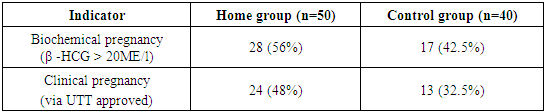
- The study will be conducted in Tashkent in 2022–2024. mother " You will be " at the EKU center take went. General 90 people on the account reproductive aged barren woman to check attraction Patients two to the group divided into: 50 people main per group, 40 people control to the group. Home in the group in women homocysteine level identified, high or lower in cases pharmacological and diet methods using normalized. Control in the group in women and this parameter not checked.In the study following stages and indicators rated: follicular through puncture (TVP) taken oocytes number of them morphological quality (M2), germination efficiency (2PN), embryos development level and quality, pregnancy determiner β -XGCH indicator and clinical pregnancy status.
3. Results
- To the study attraction 90 people were killed 50 of the women main group, 40 people and control group organization reached. Home to the group included of patients in all homocysteine level determined, out of the norm aside came out in cases (i.e. hyperhomocysteinemia or hypohomocysteinemia in cases of) treating and corrector measures applied. Control in the group women and the ECU cycle homocysteine level in advance without specifying Research during of patients age, infertility duration, oocytes and embryos quality, pregnancy results, as well as clinical and laboratory parameters was evaluated.
|
|
|
4. Discussion
- Research. during main in the group homocysteine level normalized after all indicators — oocytes number, fertility level, embryos quality and pregnancy to the surface arrival indicators control to the group than noticeable at the level high It was. This is homocysteine degree before EKU determination and need if correction through final the results improve possible shows.High homocysteine level endothelial dysfunction, oxidative stress and DNA damage take it comes, this and oocytes and embryos quality Reduces. Low homocysteine level and methylation processes enough to be absent take comes. Both reproductive in any case efficiency decreases.Research also, homocysteine in moderation to be implantation process success to increase service to do showed that homocysteine correction for folate acid, vitamins B6, B12 and diet therapy effective it has been.
5. Conclusions
- In the blood homocysteine level ECU cycle all stages — egg cell maturation, fertilization, embryo quality and to pregnancy noticeable impact shows. This is the case this parameter diagnostics algorithms input necessity Research shows. results based on following treatment algorithm working output.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML