Teshaev Sh. J., Negmatullayeva M. N., Sultonova N. A.
Bukhara State Medical Institute, Bukhara, Uzbekistan
Correspondence to: Teshaev Sh. J., Bukhara State Medical Institute, Bukhara, Uzbekistan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Abstract
The problems of miscarriage and other medical and social aspects related to this pathology are still acute and are waiting for an adequate solution. The approach to solving this problem from a clinical and immunological point of view is promising. In this regard, immunological studies were conducted, including the determination and assessment of the cytokine status of the examined women. In addition, the hematological and biochemical parameters of the blood were determined, which are somehow related to the activity of the immune system.
Keywords:
Habitual miscarriage, Pathology, Markers
Cite this paper: Teshaev Sh. J., Negmatullayeva M. N., Sultonova N. A., The Most Important Parameters of Spontaneous Miscarriages in the Early Gestational Period, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 15 No. 6, 2025, pp. 1687-1692. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20251506.12.
1. Introduction
Habitual miscarriage, defined as the loss of three or more consecutive pregnancies before 20 weeks of gestation, remains a significant clinical and public health concern worldwide [1,4,10,11]. Despite advances in reproductive medicine, its etiology often remains unexplained in nearly 50% of cases, making diagnosis and treatment challenging. The condition has profound emotional, psychological, and social impacts on affected women and couples, highlighting the need for timely identification of risk factors, including anatomical, genetic, endocrine, immunological, and infectious causes [2,3,6]. The increasing prevalence of infertility, delayed childbearing, and autoimmune disorders further emphasizes the importance of focused research and the development of effective management protocols [5,7,8]. Therefore, habitual miscarriage continues to be a relevant topic in modern gynecology and reproductive science, demanding comprehensive interdisciplinary approaches for improved outcomes.The purpose of this study was to determine and evaluate the cytokine status in pregnant women, their relationship with hematological and biochemical parameters, as well as to establish the degree of interrelation of these parameters with each other.
2. Materials and Methods of Research
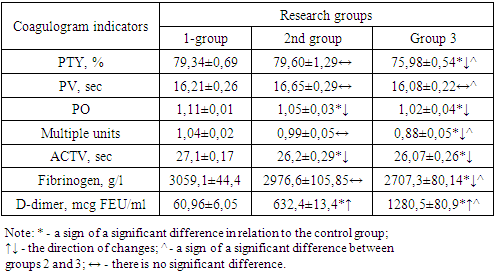
To achieve this research goal, the blood and blood serum of the examined pregnant women were studied, which were divided into 3 groups of equal number and representative of other parameters: - Group 1 (control group)-pregnant women with a physiological course of pregnancy, n=53;- Group 2 (main group)-pregnant women with OAL due to pregnancy loss, women who had pre-pregnancy preparation and registration for pregnancy in the early stages of gestation-4-9- weeks, n=47;- Group 3 (comparison group)-pregnant women with OAL due to pregnancy loss, who did not have pre-pregnancy preparation and registration for pregnancy at a later stage of gestation-9-14 weeks, n=51.It is known that a coagulogram is a blood test to assess the condition of the coagulation and anticoagulation system of the blood. The prothrombin index (PTI), prothrombin time (PV), (PO), international normalized ratio (INR), activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT), fibrinogen, and the protein fragment D-dimer were determined. The results are shown in the table 1. It should be noted that the coagulogram is a part of the hemostasiogram, which is mandatory during pregnancy.Table 1. Comparative coagulogram parameters in pregnant women by study group
 |
| |
|
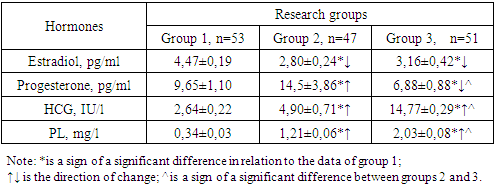
It was found that the PTI is a number that reflects the percentage ratio of the PV of standard blood to the PV of the subject and indicates the state of the blood coagulation system. In our studies, the PTI in group 2 (79.60±1.29%) practically did not differ from the control data (79.34±0.69%, P>0.05), whereas in group 3 (the comparison group) this indicator was reduced compared to groups 1 and 2 (75.98±0.54%, P<0.05). This means that the pre-gravidar preparation had a positive effect on the PTI, which rose to the level of the control group.But you can't tell this from the PV indicator, since this parameter did not significantly differ in all the compared groups (P>0.05). If we consider that PV is the time in seconds during which a blood clot forms, and is responsible for assessing the state of the blood, it becomes clear that during pregnancy, regardless of pre-pregnancy preparation, these parameters in all groups do not significantly differ from each other (P>0.05)) in addition, it is established that the indicator decreases in relation to in the control group in group 1- 1.06 times, in group 2 - 1.09 times (P<0.05).The same imbalance of parameters was noted for INR, where the parameters of the main group (0.99±0.05 units) were at the control level (1.04±0.02 units), and the parameters of the comparison group (0.88±0.05 units) remained 1.18 times lower than normal values (P<0.05). This indicates that there are changes in the degree of blood clotting, which is a more sensitive parameter than PTI. However, the imbalance of the INR parameter in our case does not deviate from these reference values (1.8-2.0 units), which allows us to indicate the absence of a pre-pathological condition in the blood coagulation system in the examined pregnant women with and without pre-pregnancy preparation.The above 4 indicators (PTI, PV, PO, INR) changed unidirectionally in the comparison group (group 3) and the main group (group 2), but no noticeable deviations from normal indicators (group 1) were found, although some significant differences were noted between the compared groups. I would like to emphasize that some other parameters of the coagulogram, such as APTT and D-dimer, changed in different directions, so that APTT in groups 2 and 3 (26.2±0.29 sec and 26.07±0.26 sec, respectively) were significantly reduced by 1.3 and 1.04 times (P<0.05) compared to the data of group 1. However, the parameters of the D-dimer were, on the contrary, significantly increased in the compared groups, in particular, in group 2 10.37 times (632.4±13.49 micrograms of FEU/ml) in group 3 21.01 times (12,805±80.9 micrograms of FEU/ml) compared to the data of group 1 (60.96±6.05 micrograms FEU/ml)-P<0.001.It is known that APTT shows the effectiveness of the internal mechanism of blood clotting at the stage of formation of the fibrin network, which allows for effective monitoring of this process in the human body. A decrease in this parameter indicates a violation of the formation of the fibrin network in the blood. But if you look at the figures obtained in comparison with the reference values (25.1-36.5 seconds) but it becomes clear that, therefore, the coagulogram indicator also showed no serious signs of pathology. Considering that a d-dimer is a protein fragment that is formed when a blood clot dissolves during blood clotting. This indicator is used to assess the formation of blood clots and their dissolution. An increased level of D-dimer in the blood indicates the activity of ongoing thrombosis processes. This parameter is necessary for monitoring anticoagulant therapy (Negmatullayeva M.N. et al., 2022; www.invitro.ru, 2024). We note that the sharply increased parameters of the D-dimer in pregnant women in group 3, where no pre-gravidar preparation was performed, the increase in this group was not 21.01 times (P<0.0001) relative to the control, but in group 2, where pre-gravidar preparation was performed, the parameters were also significantly increased by 10.37 times (P<0.001), compared to the data of the control group, but noticeably lower (by 2.02 times , P<0.001) compared to the data of the 2nd group. The obtained results show that the pre-gravidar preparation allowed a noticeable decrease in D-dimer in the blood of the examined pregnant women (P<0.001), which indicates the high effectiveness of the proposed treatment method. The absence of a decrease in this parameter to normal values (group 1) is due to the short follow-up period. Thus, D-dimer is recommended as a diagnostic marker and prognostic predictor for determining disorders of the coagulation and anticoagulation systems in pregnant women, as well as for determining the effectiveness of treatment in pregnant women with pre-pathological conditions.Another important parameter of the coagulogram is the fibrinogen content in the blood of the subjects. Fibrinogen is a colorless protein that is one of the main factors of human blood clotting. It is produced in the liver and is constantly present in a certain concentration in the blood. In addition to its hemostatic function, it participates in the processes of tissue regeneration, fibrinolysis, angiogenesis and vascular wall strengthening. In addition, fibrinogen is a protein of the acute phase of inflammation. In our studies, fibrinogen was reduced in group 3 by 1.13 times (P<0.05), and in group 2 by 1.03 times (P>0.05). A decrease in fibrinogen in the subjects indicates that pregnancy is occurring in the body with a deterioration in blood clotting. It can be seen that the pre-gravidar preparation helps to increase blood fibrinogen to almost normal values (P>0.05), which indicates the effectiveness of the therapy.Thus, the comparative parameters of the coagulogram in pregnant women with and without pre-pregnancy preparation (group 3) out of 7 parameters of the coagulogram at the time of the study, 6 indicators (85.71%) turned out to be significantly changed relative to the control, however, 5 of them seemed significantly reduced, and 1 increased (P<0.05-P<0.001). Other results were obtained for pregnant women with pre-pregnancy preparation, where 3 parameters out of 7 (42.86%) of the control group (P<0.05-P<0.001) turned out to be significantly different, and 2 of them were reduced and one was increased. These figures clearly show the effect of pre-gravid preparation in normalizing the coagulogram in the examined pregnant women. The changes were most pronounced in terms of APTT, D-dimer, and fibrinogen, which changed in different directions relative to the control. APTT was significantly reduced by 1.03 and 1.04 times, respectively, compared to the control data (P<0.05), and D-dimer was, on the contrary, increased by 10.37 and 21.01 times, respectively, compared with normal values (P<0.001). A decrease in fibrinogen in pregnant women in the subjects indicates that pregnancy is taking place in the body with a deterioration in blood clotting. It can be seen that the pre-gravidar preparation helps to increase blood fibrinogen to almost normal values (P>0.05), which indicates the effectiveness of the therapy.Thus, comparatively, the coagulogram parameters in pregnant women with and without pre-gravid preparation showed that in pregnant women without pre-gravid preparation (group 3) and 7 coagulogram parameters at the time of the study, 6 readings (85.71%) turned out to be significantly changed relative to the control, however, 5 of them turned out to be significantly reduced, and 1 increased (P<0.05-P<0.001). Other results were obtained for pregnant women with pre-pregnancy preparation, where 3 out of 7 parameters (42.86%) turned out to be significantly different from the data of the control group (P<0.05-P<0.001), and one of them was reduced and one was increased. These figures clearly show the effect of pre-gravid preparation in normalizing the coagulogram in the examined pregnant women. The changes were most pronounced in terms of APTT, D-dimer, and fibrinogen, which changed in different directions relative to the control. APTT, D-dimer, and fibrinogen, which have changed in different directions relative to the control. The APTT was significantly reduced by 1.03 and 1.04 times, respectively, relative to the control data (P<0.05), and the D-dimer was, on the contrary, increased by 10.37 and 21.01 times, respectively, compared with normal values (P<0.001). The decrease in fibrinogen in pregnant women with pre-gravid preparation was minimal up to 1.03 times (P>0.05), and in pregnant women without pre-gravid preparation it was maximal up to 1.13 times (P<0.005). It was found that pre-gravidar preparation led to normalization or close to normalization of coagulogram parameters in the examined pregnant women, which indicates the high effectiveness of the therapy. D-dimer, fibrinogen content, APTT (coagulogram parameters) are recommended as a diagnostic marker and prognostic predictor for determining disorders of the coagulation and anticoagulation system in pregnant women, as well as for determining the effectiveness of pre-pregnancy preparation in pregnant women with pre-pathological and pathological conditions.Subsequently, along with the hemostasis and coagulogram parameters, the hormone content in the blood of the examined pregnant women was determined, estradiol, human chorinonic gonadotronin (hCG) and sugar lactogen (PL) in the blood of the examined were determined. The results were presented in the form of a table 2.Table 2. Comparative parameters of hormone levels in the blood of pregnant women with and without pre-pregnancy preparation
 |
| |
|
It is known that estradiol is a sex steroid hormone, the main function of which is to prepare the female reproductive system for reproduction, participates in maintaining the normal course of pregnancy and hormonal regulation of childbirth and lactation. Determination of estradiol concentration is necessary to assess ovarian function. If we take into account that the concentration of estradiol in the blood decreases during pregnancy, then in our cases, this pattern was revealed, in all three groups the estradiol content was lower than the reference parameters (19.5-356.7 ng/ml). So, in the 1st group, if the indicator was 4.47±0.19 ng/ml, then in the 2nd group the parameters were 1.60 and 1.41 times significantly lower (P<0.05) than in the control group, respectively.However, different results were obtained in terms of progesterone levels; in group 2 (pregnant women with pre-pregnancy preparation) and in group 3 (pregnant women without pre-pregnancy preparation), the indicators changed in different directions relative to the control group (P<0.05). If we consider that progesterone is an endogenous steroid that affects the menstrual cycle, pregnancy and human embryonic development, then its constant monitoring during pregnancy becomes important. The normal parameters for women during pregnancy, depending on the trimester of pregnancy, are; I-trimester-10-90 pg/ml; II trimester -30-150 pg/ml; III trimester - 40-450 pg/ml. It has been found that as the trimester of pregnancy increases, the level of progesterone in the blood of pregnant women also increases.In our studies, the progesterone level in group 1 was 9.65±1.10 pg/ml, which corresponds to the reference value (P>0.05). However, in pregnant women without pre-pregnancy preparation (group 3, comparison group), this parameter was 6.88±0.88 pg/ml and was reduced by 1.40 times compared to the control (P<0.05), but in pregnant women with pre-pregnancy preparation (group 2, main group), this indicator was at the level of 14.5±3.86 pg/ml, which is 150 times higher than normal values (P<0.05). It was revealed that such an imbalance in progesterone concentration in pregnant women is the effect of pre-pregnancy preparation. If we consider that all the parameters of this sex hormone were within the boundaries of the reference values, then no serious pathological changes associated with this sex hormone were detected.HCG is known to be a pregnancy recognition hormone produced by trophoblast cells that surround the growing embryo. The reference values of this parameter increase with increasing gestation period from 5.8-71.2 IU/l to 13950-62530 IU/l. In our studies, this hormone was detected in low concentrations, respectively, in group 1, 2.64±0.22 IU/l, in group 2, 4.90±0.71 IU/l, and in group 3, 14.77±0.29 IU/l. The imbalance of the identified parameters indicates the presence of a pre-pathological condition in the examined pregnant women.PL is a peptide hormone produced by only a percentage of the fetus during pregnancy. The content of this hormone in the blood depends on the duration of pregnancy and ranges from 0.06-1.7 mg /l to 4.5-11.8 mg/l (reference values). In our studies, the PL in group 1 was 0.34±0.03 mg/l, which is at the boundary of the reference values. In groups 2 and 3, there was a significant increase in this parameter (P<0.05) g, by 3.56 and 5.97 times, respectively (P<0.001). Thus, comparative parameters of the level of sex hormones in the blood of pregnant women with and without pre-pregnancy preparation showed that the trend of quantitative changes in all 4 hormones studied was similar in groups 2 and 3, but the intensity of changes differed between the compared groups. If estradiol decreases in the comparison group and the main group (P<0.005), then the levels of progesterone, hCG, and PL were elevated relative to the control (P<0.05). The imbalance of indicators and the single direction of changes in the parameters of these hormones indicates the presence of a pathological process and the effectiveness of pre-pregnancy preparation. It is known that the lipid composition of the blood also varies depending on the pre-pathological and pathological state of the body. In addition, pregnancy also makes adjustments to the lipid composition of the blood, in this regard, we studied low-density lipoproteins (LDL) and high-density lipoproteins (HDL) in the examined pregnant women. The results obtained in the comparative aspect are shown in Figure 1.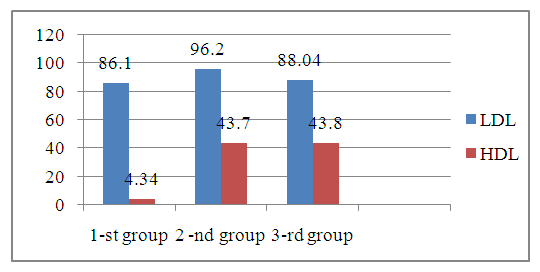 | Figure 1. Comparative LDL and HDL values in the blood of pregnant women with and without pre-pregnancy preparation, mg/dl |
It has been established that LDL is the main carrier of cholesterol in the blood. High LDL levels increase the risk of atherosclerosis. LDL is the final stage of the metabolism of endogenous lipids synthesized in the liver in the body. The recommended LDL level was developed by the American Heart Association, NJH and NCEP in 2003 and is less than 100 mg/dl (less than 2.6 mmol/L). Figure 1 shows that LDL in all the compared groups is below 100 mg/dl, that is, it corresponds to a normal value, although there is a slight increase in group 2 (the main group is up to 96.2±7.15 mg/dl, but the result is lower than the control (P>0.05).The picture is almost the same in terms of HDL content in the blood of the examined patients. There are practically no significant differences between the compared groups (P>0.05). If we consider that HDL has antiatherogenic properties and reduces the risk of the formation and development of atherosclerosis and CVD, in addition, it simulates inflammatory reactions, it becomes clear that low HDL levels can lead to an increased risk of CVD in the examined. The reference values are in the range of 40-100 mg/dl for women. In our cases, the HDL levels were 43.4±1.25 mg/dl, 437±1.06 mg/dl and 43.8±0.86 mg/dl, respectively. It can be seen that HDL is at a low level of the norm and there is also no significant difference between the groups (P>0.05). In addition, the positive effect of pre-gravid preparation was also not noted.Thus, the analysis of comparative LDL and HDL values in the blood of pregnant women with and without pre-pregnancy preparation showed that these parameters were at the upper and lower limits of normal values, respectively. In both cases, there was no significant difference between the compared groups (P>0.05). In both cases (pregnant women with and without pre-pregnancy preparation), the positive effect of pre-pregnancy preparation was not noted. The revealed facts indicate that the content of LDL and HDL in the blood of pregnant women cannot be diagnostic and prognostic criteria for the course and outcome of this pathology, as well as for assessing the effect of pre-pregnancy preparation.Another important factor during a normal pregnancy is vitamin D (cholecalceferol). It is known that vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that is necessary for the effective absorption of phosphorus and calcium in the body. Its connection with the favorable course of pregnancy and fetal development has been proven by numerous studies. The optimal level of this vitamin for pregnant women (reference values) does not differ from other people's data and amounts to 30-50 ng/ml (75-125 nmol/l) in blood serum.In our studies, the level of vitamin D in the blood serum of the examined pregnant women differed between the compared groups.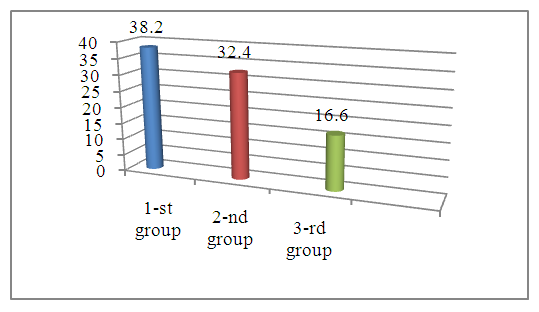 | Figure 2. Comparative indicators of vitamin D in the blood serum of pregnant women with and without pre-pregnancy preparation, ng/ml |
We found that the concentration of vitamin D in the control group (group 1) was 38.2±0.8 ng/ml, which corresponded to the reference value (P>0.05), these parameters of the main group (group 2 -32.4±1.20 ng/ml) were also at the level of reference values. However, these indicators were 1.18 times significantly lower than in the control group (P<0.05). Separately, I would like to emphasize that the parameters of the comparison group (group 3) were sharply, significantly reduced by 2.30 times compared to the control (P<0.001). This decrease in the level of vitamin D in the blood serum was also observed in relation to the main group (1.95-fold decrease, P<0.001). This fact indicates the high efficiency of pre-gravid preparation for pregnant women, since in the group of pregnant women with pre-gravid preparation, the content of the studied indicator reaches normal values, and in pregnant women who did not receive pre-gravid preparation, the vitamin D content remained at a sharply low level.Thus, an analysis of the comparative parameters of vitamin D in the blood serum of pregnant women with and without pre-gravid preparation showed that the level of vitamin D in pregnant women with a physiological course (group 1) and pregnant women with pre-gravid preparation were at the lower limits of the reference values, although the content of this vitamin was 1.18 times significantly low in pregnant women with pre-gravid preparation. compared to the control group (P<0.05). However, the rates of pregnant women without pre-pregnancy preparation were significantly low in relation to the above-mentioned two groups - 2.30 and 1.95 times, respectively (P<0.001). This fact indicates the high efficiency of pre-pregnancy preparation for pregnant women. In this regard, the determination of vitamin D in the blood serum during pregnancy is recommended as a marker for monitoring the course of pregnancy and evaluating the effectiveness of pre-pregnancy preparation for this category of women.Considering the role of cytokines in the human body, in particular in the activity of the immune system, as well as their pathogenetic significance for pre-pathological and pathological human conditions, we considered it advisable to determine and evaluate the cytokine status in the examined pregnant women. Although the trend of changes was almost the same (with the exception of the IL-1ß content in group 2), the intensity of changes differed between the compared groups and between cytokines. It has been established that IL-1ß is a pro-inflammatory cytokine that is a mediator of inflammation and immunity synthesized by stimulated B lymphocytes, macrophages, fibroblasts and creatinocytes. Participates in the regulation of immunological processes-the immune response (reference values 0-11 ng/ml). In connection with the above, the definition of IL-1ß is important. Our studies have established that during the physiological course of pregnancy, the content of this cytokine was 6.97±0.18 ng/ml, which is at the boundary of the reference values. However, in women of group 2, the IL-1ß content was slightly reduced compared to those of group 1, 3.80±0.47 ng/ml (1.83 fold decrease, P<0.001). But it should be noted that this parameter was also at the boundary of the reference values. The decrease in this parameter in group 2 is a consequence of effective complex treatment.The results of studies in group 3, 8.83±0.84 ng/ml, were 1.27 times higher than in group 1 (P<0.05), and 2.32 times higher than in group 2 (P<0.001). Such an imbalance in IL-1ß concentration is a consequence of the treatment, where timely treatment (group 2) leads to a decrease in this indicator to a minimum, and the absence of such treatment leads to the fact that the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-1ß does not decrease, supporting the inflammatory process in the body of the examined pregnant women. Other results were obtained from the concentration of IL-2 in the blood serum of the examined. Considering that IL-2 is a peptide that is a mediator of inflammation and immunity (a pro-inflammatory cytokine). This cytokine is produced by T cells in response to antigenic and mitogenic stimulation, and has bactericidal activity against gram-negative bacteria, including E.Col. In addition, this cytokine is involved in the development of septic shock. As sepsis progresses, the level of IL-2 in the blood decreases, which requires its correction.Our studies showed that the IL-2 content in the blood serum of patients in group 2 was increased by 3.94 times compared to those in group 1, respectively, 85.9±17.6 ng/ml versus 21.81±0.59 ng/ml (P<0.001). This fact indicates that the level of this cytokine increases sharply due to the presence of a pathological process, the etiological agents of which are pathogenic microorganisms, including gram-negative microorganisms. However, this indicates that the inflammatory process not only attenuates, but is also supported by pro-inflammatory cytokines, including IL-2.Almost the same results were obtained when analyzing the results of the 3rd group. The average levels of this cytokine in the blood serum of the patients were 4.14 times significantly higher than those of women with physiological pregnancy (group 1)– respectively, 90.2±3.42 ng/ml versus 21.81±0.59 ng/ml (P<0.001). In both cases, the pre-gravidar preparation, regardless of the time, did not contribute to a decrease in IL-2 in the blood serum. After treatment, the level of this cytokine was elevated in patients of both study groups (group 2 and 3).Thus, the determination and assessment of the content of IL-1ß and IL-2 (proinflammatory cytokines) in the blood serum of the examined shows that their contents have changed in different directions depending on the study group. If IL-2 was increased in both groups almost equally by 3.94 and 4.14 times compared to the data of group 1 (P<0.001), then IL-1ß was increased in group 3 by 1.27 times (P<0.05) and was reduced in group 2 by 1.83 times (P<0.001). It should be emphasized that there were no significant differences in IL-2 between the compared 2 and 3 groups, while significant differences were found in IL-1ß (a 2.32-fold increase in group 3). The multidirectional changes are explained by the level of involvement of these cytokines in the inflammatory process in the examined women, as well as their diagnostic and prognostic value in this pathology in women with and without pre-pregnancy training.The same studies were conducted to study the level of IL-6 in the blood serum of the examined women with and without pre-pregnancy preparation with OAA. It has been established that IL-6 is a pro-inflammatory cytokine that is synthesized by activated macrophages and T cells, stimulates the immune response, and is an important mediator of the acute phase of inflammation. The determination of this cytokine makes it possible to more accurately assess the immune status of the examined. In this regard, we determined IL-6 in the blood serum of the examined patients. The content of this cytokine in pregnant women with a physiological course was 7.49±0.21 ng/ml, which was at the level of reference values. However, in group 2 patients, this cytokine was sharply elevated to 146.5±18.3 ng/ml, which is 19.56 times higher than the parameters of group 1 (P<0.001). This elevated condition indicates the absence of attenuation of the inflammatory process, regardless of the complex treatment. The same studies to determine IL-6 were conducted with group 3 patients. It was found that the average parameter of this cytokine in the examined patients was 249.0±10.01 ng/ml, which is 33.24 times significantly higher than in group 1 patients (P<0.001).
3. Conclusions
Thus, a study of the quantitative composition of IL-6 in the blood serum of patients with OAA with and without pre-treatment showed that in both groups compared, the level of this cytokine was significantly 19.56 and 33.24 times higher, respectively, than in patients in the control group (P<0.001).This fact indicates a high IL-6 parameter in the examined women of groups 2 and 3, due to the absence of a decrease in the activity of the inflammatory process in the body. The identification of statistically significant differences between the main group (group 2) and the comparison group (group 3) in terms of IL–6 content (a 1.70-fold difference in favor of group 3 patients) indicates the effectiveness of timely pre-gravidar preparation, which was manifested by a decrease in the activity of this indicator of the inflammatory process. The same changes were detected in the level of IL-1ß and IL-2 in the blood serum of the patients, only with a reduced intensity of changes. In this case, the IL-6 content is recommended not only as a diagnostic criterion, but also as a prognostic marker indicating the outcome of the pathological condition and a marker for determining the effectiveness of the complex treatment of pre-pregnancy preparation.
References
| [1] | Andersen LB, Dechend R, Karumanchi SA, Nielen J, Joergensen JS, Jensen TK, et al. Early pregnancy angiogenic markers and spontaneous abortion: an Odense Child Cohort study. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2016; 215(5): 594. e1–594.e11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2016.06.007. |
| [2] | Jarylkasinova, G. J., Mavlyanov, I. R., & Yuldashova, R. U. (2020). Pharmacoeconomic efficacy of ferrous and ferriciron supplements in the territory of the republic of Uzbekistan. European Journal of Molecular and Clinical Medicine, 7(8), 1310-1315. Retrieved from www.scopus.com. |
| [3] | Negmatullaeva M.N., Tuksanova D.I., Zaripova D.Ya. Structural-optical properties of blood serum and their role in predicting the development of osteoporosis in perimenopause. Russian Bulletin of Obstetrician-Gynecologist. 2024; 24(3): 71‑76. (In Russ.) https://doi.org/10.17116/rosakush20242403171. |
| [4] | Rakhmonkulova, Nargiza & Nematilllaeva, Mastura & Tuksanova, Dilbar & Kholova, Nodira & Solieva, Nozima. (2024). Comparative characterization of liver morphometric parameters during pregnancy in experimental chronic renal failure. BIO Web of Conferences. 121. 04004. 10.1051/bioconf/202412104004. |
| [5] | Rovner P., Stickrath E., Alston M., Lund K. An early pregnancy unit in the United States: an effective method for evaluating first trimester pregnancy complications // J. Ultrasound Med. 2018. Vol. 37. Р. 1533–1538. |
| [6] | Sultonova N.A. Rol' patologii endometriya pri reproduktivnyh poteryah v rannih srokah beremennosti. Tibbiyotda yangi kun№4 (34) 2020 392-395 str. |
| [7] | Tilloeva, S. S. (2020). Study of psychoemotional status and life quality of patients with bronchial asthma in combination of arterial hypertension, effects of complex therapy. European Journal of Molecular and Clinical Medicine, 7(3), 3786-3790. Retrieved from www.scopus.com. |
| [8] | Yuldashova, R., Tilloeva, S., Djuraeva, N., Adizova, D., Sultanova, N., & Asrorov, A. (2024). Efficiency of ferrotherapy when using different groups of iron drugs in patients with Helicobacter pylori. In BIO Web of Conferences (Vol. 121, p. 03004). EDP Sciences. |
| [9] | Yuldashova, R.U. (2022) Ways To Increase The Efficiency Of Ferrotherapy In Iron Deficiency Anemia Taking Into Account The Presence Of Helicobacteriosis. Journal of Pharmaceutical Negative Results, 13, DOI: 10.47750/pnr.2022.13.S09.576. |
| [10] | Zaripova D.Ya., Abdullaeva M.A., Sultonova N.A., Ahmedov F.K., Nasirova Z.S., Umurov E.U., Shukrullaeva G.Zh. Optimizaciya mer diagnostiki rannej menopauzy i prezhdevremennoj menopauzy. Zhuranl Reproduktivnoe zdorov'e vo stochnaya Evropa. 2024; 14 (5). S. 617-628. |
| [11] | Zaripova D.Ya. Diagnosticheskie kriterii vyyavleniya osteoporoza v perimenopauzal'nom periode. Reproduktivnoe zdorov'e vo stochnaya Evropa. 2024; 14 (5). S. 590-598. https://doi.org/10.34883/PI.2024.14.5.004. |


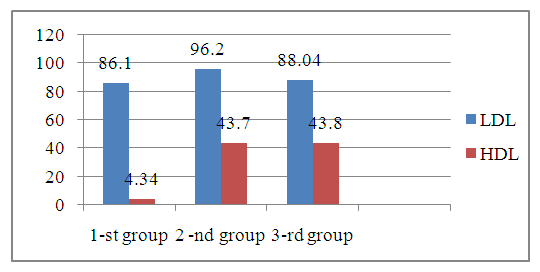

 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML
