-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2025; 15(5): 1589-1592
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20251505.61
Received: May 2, 2025; Accepted: May 28, 2025; Published: May 30, 2025

Effectiveness of Irreversible Electroporation (IRE) in Children with Adenoid Vegetations
U. S. Khasanov, U. R. Khudayberganov
Tashkent Medical Academy, Uzbekistan
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Adenoidal hypertrophy (AH) and adenotonsillar hypertrophy are common disorders in the pediatric population and can cause symptoms such as mouth breathing, nasal congestion, hyponasal speech, snoring, and obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), as well as chronic sinusitis and recurrent otitis media. More serious long-term sequelae, typically secondary to OSA, include neurocognitive abnormalities (e.g. behavioral and learning difficulties, poor attention span, hyperactivity, below average intelligence quotient); cardiovascular morbidity (e.g. decreased right ventricular ejection fraction, left ventricular hypertrophy, elevated diastolic blood pressure); and growth failure. Adenoidectomy (with tonsillectomy in cases of adenotonsillar hypertrophy) is the typical management strategy for patients with AH. Objective: To evaluate the safety and efficacy of irreversible electroporation (IRE) technology for the treatment of pediatric adenotonsillar hypertrophy. Discussion: This study is the first to describe the use of IRE technology for non-thermal adenotonsillar tissue ablation in pediatric patients. The procedure was short and relatively less painful than standard treatment. No bleeding occurred and in the short-term tonsillar size was reduced and clinical scoring of obstructive symptoms improved. Further clinical trials with long-term follow up are underway.
Keywords: Adenoidal hypertrophy, Children, Irreversible electroporation, Diagnose, Lymphadenoid tissue, Treatment
Cite this paper: U. S. Khasanov, U. R. Khudayberganov, Effectiveness of Irreversible Electroporation (IRE) in Children with Adenoid Vegetations, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 15 No. 5, 2025, pp. 1589-1592. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20251505.61.
1. Introduction
- Adenoidal hypertrophy (AH) is a prevalent condition in pediatric populations, often associated with upper airway obstruction and a spectrum of clinical symptoms, including mouth breathing, snoring, hyponasal speech, recurrent otitis media, and sleep disturbances such as obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). Left untreated, AH can lead to significant long-term complications, including neurocognitive delays, craniofacial deformities, hearing impairment, and cardiopulmonary dysfunction. Traditional surgical management, typically adenoidectomy or adenotonsillectomy, remains the mainstay of treatment; however, these procedures are not without risks and complications, particularly related to bleeding, postoperative pain, and long recovery periods.In recent years, there has been growing interest in minimally invasive technologies that offer effective tissue ablation with reduced morbidity. Irreversible electroporation (IRE), a novel non-thermal technique, has emerged as a potential alternative to conventional surgery for various soft-tissue pathologies. Unlike traditional surgical methods, IRE induces controlled cell death through high-voltage electrical pulses without damaging surrounding connective tissues, vessels, or nerves. Although IRE has shown promising outcomes in adult oncology and urological applications, its use in pediatric otolaryngology remains largely unexplored.This study aims to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of IRE in children with adenotonsillar hypertrophy. By assessing clinical outcomes, postoperative pain levels, and improvements in quality of life indicators, the research seeks to determine whether IRE could serve as a viable, less invasive therapeutic option for managing AH in children.
2. Methods of Research
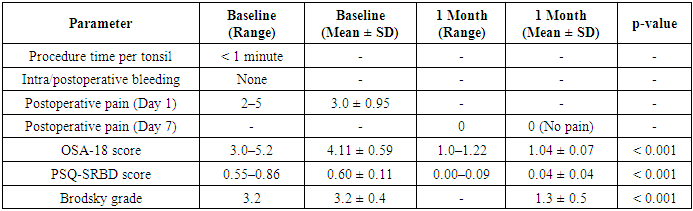
- A new technology of non-thermal tissue ablation IRE (ENTireTM) was evaluated for adenotonsillar hypertrophy in 12 children aged 5 to 13 years with upper airway obstruction. Six patients underwent adenotonsillar reduction and 6 underwent adenoid reduction. The procedure was performed under general anesthesia. Postoperative pain was assessed daily for one week using the Wong-Baker Faces Pain Scale. Improvement in quality-of-life parameters were evaluated using the Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA-18) questionnaire and the Pediatric Sleep Questionnaire - Sleep-Related Breathing Disorder (PSQ-SRBD) questionnaire at baseline and 1-month post-procedure. Tonsillar size was assessed using the Brodsky grading scale.
3. Results
- Adenoid is a lymphoid tissue located in the roof and posterior wall of the nasopharynx. Normally being a resistance center against upper respiratory infections, it may become a source of recurrent and chronic infection itself.Adenoid hypertrophy is a common childhood disease. An enlarged adenoid can occlude the choana, especially when sleeping in a supine position. Symptoms due to airway obstruction like mouth breathing, hyponasal speech and snoring in children are observed. It may also cause otitis media with effusion and accompanying conductive hearing loss and in the most serious cases, obstructive sleeping apnea and accompanying growth retardation and cor pulmonale.According to the opinion, the combination of increased antigen loads with imperfect immune responses in childhood can cause pathological changes in the pharyngeal tonsil. At the same time, under the condition of approximately the same antigen aggression, pathology of the pharyngeal tonsil with pronounced clinical manifestations occurs only in 20-30% of children. It is believed that the analysis of the perinatal period can contribute to the prediction of the development of pathology of the pharyngeal tonsil in children at different ages.A number of local and general disorders are associated with hypertrophy of the pharyngeal tonsil. Among the local manifestations are difficulty in nasal breathing, impaired growth of the facial skull, hearing and speech disorders.Impaired nasal breathing leads to a decrease in the protective function of the nasal mucosa, inhibition of the motor activity of the ciliated epithelium, alkalosis of nasal mucus, an increase in bacterial contamination of the nasal mucosa, a decrease in the activity of the lysosomal enzyme. This pathogenetic chain leads to damage to the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx, nasal cavity, and paranasal sinuses. The frequency of combinations of sinusitis with hypertrophy of the pharyngeal tonsil, in 2/3 of children with adenoid vegetations and radiographic changes in the transparency of the paranasal sinuses, sinusitis, as such, is absent. The existing radiographic changes are due to the presence of adenoids, which disrupt the aeration and vascular tone of the mucous membrane of the nose and paranasal sinuses. The presence of adenoid vegetations also has a noticeable negative effect on the course of chronic sinusitis. Disorders of the formation of the maxillofacial skeleton include pronounced dentofacial deformations (high hard palate, narrowing of the upper jaw, lack of space for teeth in the alveolar processes of the jaws), which occur in 65.9% of cases and appear already in the first period of the primary bite, i.e. before 4 years. As a consequence of the disorder of the formation of the maxillofacial skeleton, a curvature of the nasal septum develops due to a violation of the development of the hard palate.Closed nasal speech is explained by the fact that adenoids, limiting the mobility of the soft palate, cause disturbances in phonation and articulation of speech.Common symptoms include headache, dizziness, sleep disorders, absent-mindedness and forgetfulness. Sometimes noted: nocturnal enuresis (in 15% of patients); epileptic seizures; laryngospasm: visual impairment, cardiovascular and bronchopulmonary system dysfunction.Symptoms of dysfunction of distant organs and systems that are observed with adenoids are caused not only by difficulty in nasal breathing - they are often based on a neuroreflex mechanism. The cause of pathological reflexes leading to dysfunction of the central nervous system (nervous tic, laryngospasm attacks, stuttering, nocturnal enuresis, etc.) is the presence of infected areas of hyperplastic lymphadenoid tissue. The first subjective and objective clinical manifestations of autonomic dysfunctions should be treated with extreme caution, remembering that most often they are signs not of the onset of the disease, but in fact of an already advanced phase of decompensation.Symptoms from the central nervous system in a child with adenoids can be regarded as a manifestation of a significant adverse effect on it of pathologically altered lymphoid tissue of the nasopharynx. In children with adenotonsillar pathology, a statistically significant increase in the prevalence of neurotic tendencies is observed, and signs of emotional lability are more often detected. More than half of the children have intelligence indicators below the age norm, which is assessed as a delay in mental development. In 80% of children with hyperplasia of the pharyngeal tonsil, signs of autonomic dystonia were detected as a consequence of pathological adaptation.In an EEG study of children with pathology of the pharyngeal tonsil, general cerebral disorders of varying degrees of severity were found in all of them. Moderate forms prevail in 58.7% of subjects, mild general cerebral disorders - in 34.9% of patients, and pronounced changes occur only in 6.3% of cases. EEG symptoms indicating predominant damage to stem structures were detected in 31.7% of children. Signs of hypothalamic dysfunction were recorded in 22.2% of cases, and mediobasal structures - only in 6.3% of people. It is noteworthy that 42.9% of patients had epileptiform syndrome.Breathing predominantly through the mouth reflexively leads to a decrease in the depth of respiratory movements and a decrease in pulmonary ventilation. Therefore, such children have insufficient blood oxygenation, which negatively affects the functioning of all organs and systems.Also, the negative impact of chronic inflammation of the lymphadenoid tissue of the nasopharynx on the child's body is undeniable, one of the manifestations of which can be endogenous intoxication.Constant nasal discharge irritates the skin of the vestibule of the nose and upper lip, and frequent swallowing of discharge - disorders of the gastrointestinal tract. Adenoid growths, like adenoiditis, reduce the resistance of the child's body, are risk factors for bronchopulmonary pathology.Snoring and sleep apnea syndrome can be attributed to disorders of both general and local nature. Difficulty in nasal breathing is one of the main factors contributing to the development of snoring. Snoring is often perceived as an unfavorable but safe sound phenomenon. However, the so-called "powerful" snoring is a harbinger and one of the main manifestations of a serious disease - sleep apnea syndrome (SAS). The first witnesses of this terrible disease are waking relatives who watch as breathing stops, then the sleeping child snores loudly, sometimes tosses and turns, moves his arms or legs and starts breathing again. Children with a severe form of SAS are at risk for sudden death syndrome. The mortality rate of patients with sleep apnea syndrome is on average 6-8%. If we take into account the consequences of various complications directly or indirectly related to this pathology, then the total mortality rate from SAS reaches 37%. The results of the studies give reason to believe that to eliminate snoring during sleep, the first stage is indicated complex surgical intervention aimed at restoring normal nasal breathing.
|
4. Discussion
- This study represents an initial clinical evaluation of irreversible electroporation (IRE) as a treatment modality for adenotonsillar hypertrophy in children. The results indicate that IRE is a safe and effective alternative to traditional surgical interventions. The procedure was short in duration, caused minimal postoperative discomfort, and resulted in a measurable reduction in tonsillar size and improvement in obstructive symptoms within one month post-treatment.The absence of intraoperative and postoperative bleeding, along with the rapid resolution of pain by the seventh day, highlights the minimally invasive nature of IRE. Compared to conventional adenotonsillectomy, which often involves a longer recovery period and higher complication rates, IRE appears to offer a gentler therapeutic approach for pediatric patients.The findings are particularly significant in the context of the broader health impact of adenoidal hypertrophy in children. Obstructive symptoms associated with this condition can negatively affect sleep quality, craniofacial development, cognitive performance, and overall quality of life. Effective and timely treatment is therefore essential not only for symptomatic relief but also for preventing long-term complications.IRE's non-thermal mechanism, which selectively disrupts cell membranes without damaging surrounding tissues, presents a notable advantage in pediatric applications. This precision makes it especially suitable for delicate anatomical areas such as the nasopharynx, where preservation of healthy structures is critical.However, the present study is not without limitations. The small sample size and short follow-up period restrict the generalizability of the results. Long-term outcomes, including the potential for tissue regrowth or delayed complications, remain unknown. Additionally, while no adverse events were recorded, further investigations with larger cohorts are necessary to confirm the safety profile of this technique.In summary, the positive short-term outcomes observed in this pilot study support the potential of IRE as an innovative treatment option for children with adenotonsillar hypertrophy. Continued research, including multicenter trials with extended follow-up, will be vital to establishing its place in clinical practice.
5. Conclusions
- This study is the first to describe the use of IRE technology for non-thermal adenotonsillar tissue ablation in pediatric patients. The procedure was short and relatively less painful than standard treatment. No bleeding occurred and in the short-term tonsillar size was reduced and clinical scoring of obstructive symptoms improved. Further clinical trials with long-term follow up are underway.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML