Radjabov Alisher Islomovich1, Saidov Akbar Ahadovich1, Shayakhmetova Meiramkul Kojavmetovna2
1Bukhara State Medical Institute, Bukhara, Uzbekistan
2National Medical University of Kazakhstan named after J. Asfendiyarov, Kazakhstan
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Abstract
During 2022-2025, in our study, we conducted dental examinations among 120 patients aged 25 to -74 who had orthopedic dental treatment, partially with secondary adentia. When using an acetal prosthesis, the number of complications in the oral cavity was proven to have decreased convincingly by 1.7 times, it was found that the quality of orthopedic treatment of patients increased. Acetal prostheses have been found to convincingly reduce the colonization of pathogenic and conditionally-pathogenic microorganisms and candida fungi in the oral cavity by 1.2 times compared to acrylic and nylon prostheses, and to increase the quality of orthopedic treatment in partial toothlessness.
Keywords:
Partial toothlessness, Dentures, Acetate prosthesis, Oral cavity
Cite this paper: Radjabov Alisher Islomovich, Saidov Akbar Ahadovich, Shayakhmetova Meiramkul Kojavmetovna, Taking into Account the Anatomical Position of the Oral Cavity in the Treatment of Partial Toothlessness, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 15 No. 5, 2025, pp. 1491-1497. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20251505.41.
1. Introduction
Orthopedic treatment of patients with partial teeth and restoration of lost functions of the tooth-jaw system is an urgent task of Dentistry.One of the main causes of complications in the use of partially removable plate prostheses is damage to the underlying tissue and its mechanical overpressure, leading to the development of prosthetic stomatitis and atrophy of the alveolar tumor [1,3]. Partially removable plate prostheses, an uneven distribution of chewing pressure on the underlying tissue leads to an increase in atrophy processes in areas where excess pressure falls [2,7].Despite the fact that the quality of orthopedic dental care for patients has significantly improved, the problem of restoring the lost functions of the tooth-jaw system in the absence of teeth is still unresolved [4,6]. Factors that provoke the development of pathological reactions of the body for removable dentures include: the influence of microorganisms, the allergic and toxic effect of the substances that make up the composition of the prosthesis, the thermal insulation effect of the prosthetic base on the sub – denture tissue, a decrease in the tone of blood vessels, a slowdown in blood and lymph flow [5].Due to the high need for orthopedic treatment with removable dental prostheses, improving orthopedic treatments with an individual approach to each patient, taking into account the anatomical-functional conditions of the oral cavity, increases the accuracy and effectiveness of the study [8].The purpose of the study is to improve the selection of prosthetic types in orthopedic treatment, taking into account the anatomical-functional state of the oral cavity in partial toothlessness.
2. Material and Research Methods
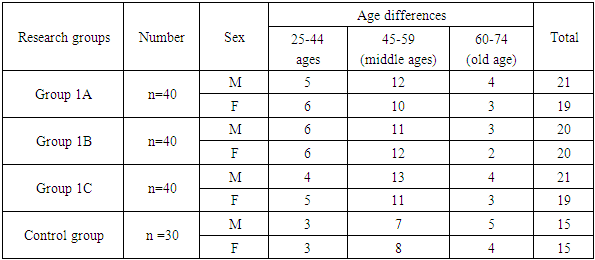
In our scientific study, we conducted dental examinations among 120 patients aged 25 to -74 who had orthopedic dental treatment, with partial secondary adentia.In the process of asking patients, attention was paid to the fact that all patients lost their teeth as a result of caries complications and paradont diseases. Dental examination and examination was carried out with a generally accepted standard set of dental equipment: survey, patient complaints, objective examination, oral mucosa, teeth and tooth rows, periodont tissue, examination of the chewing muscles and chakka-lower jaw, what complaints the patient had.At the time of the request for a clinical examination, Anamnesis was collected, we also paid attention to whether there are diseases of the local and general organism, salivation.We divided the main group patients into three groups for research purposes. The main first group of patients consisted of patients with Acetal dentures, the second group of patients consisted of patients with “Phthorax” acrylic dentures, and the third group of patients with elastic nylon dentures.In the control group, the tooth rows and oral tissue are made up of healthy individuals. The patients and healthy individuals that make up all groups are made up of individuals who do not have additional disease and burn disease.Data on the clinical formation of groups by us are presented in Table 1.Table 1. Clinical groups of patients
 |
| |
|
Patients were found to have discomfort in working conditions, compliance with the conditions of oral cleansing, harmful habits and consumption of carbonated-colored drinks; predisposition to allergic diseases, experience in the use of removable dental prostheses.In order for the distribution of those in the study to give accurate data from the abstract, men and women were distributed in almost the same number. After placing removable dental prostheses in patients, patients underwent a complete clarification of the procedure for its use and use, cleaning and maintenance of the prosthesis.When examining patients, attention was paid to the external expression of the face, whether there is asymmetry or not, the tightness of wrinkles, the size of the nasomaxillary area, the presence of changes in the facial skin, and the condition of the oral corridor, oral diaphragm, palate dome and tongue, as well as the condition of the dental arch and parodontine were assessed (Figure 1). In general, the necessary clinical and diagnostic work in patients was carried out perfectly and the necessary practices were carried out. In the course of clinical studies, 120 patients were examined and orthopedic treatment was carried out. Removable dental prostheses were carried out on the basis of the necessary methods and raw materials. A day after the removable dental prosthesis was installed and fixed, examinations were carried out in patients, and subsequent attendance periods were appointed for observation.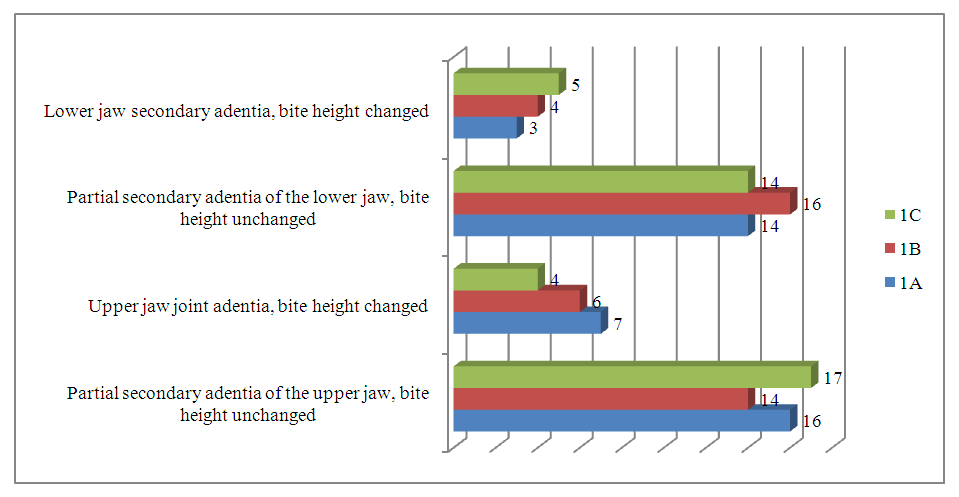 | Figure 1. Partial secondary adentia manifestations in research groups |
A special serum therapy developed by A. N.Akbarov and A. H. Zhumaev (2021) was used to treat patients. During the examination, it turned out that the prosthesis was custom-made, and the results of the orthopedic examination confirmed its authenticity. Various questions were asked about the duration of the patients' adaptation to the prosthesis after wearing removable dentures, their attitude towards the raw material used for the denture base, complaints about the design of the prosthesis, the aesthetic appearance of the dentures, their opinions on the quality and hygienic quality of the dentures, storage conditions, the ease of care for removable dentures, the effect of removable dentures on patients' taste preferences, whether they interfere with the pronunciation of letters when speaking, and similar questions.The method for determining the hygienic condition of removable dental prostheses is a for this study.N. Akbarov and A.A special technique has been developed to determine the hygienic condition of the surface of dental prostheses, which are taken away by H Jumaevs. After orthopedic treatment of patients with partial absence of teeth, this method can be performed hygienic treatment of the oral cavity.The method of assessing the condition of the oral mucosa is partially obtained dental prostheses all the time show different visual effects on the tissue in the prosthetic position. As a result, the use of a removable dental prosthesis is caused by the response of the oral mucosa to new conditions formed in the place of the prosthesis. Partial and complete removable dental prostheses call for signs of inflammation of different manifestations caused by exposure to the tissues of the prosthetic seat, which does not adversely affect the effectiveness of orthopedic treatment. One of the main causative factors of this negative effect is the pressure of the chewing, which falls from the prosthesis instead of the prosthesis. As a result, the blood vessels are steamed, which serves as a direct barrier to the base of the prosthesis to such functions as protection of the mucous membrane, nutrition, separation of mucous membranes. Thanks to this, the process of atrophy in bone tissue can be observed in the alveolar tumor and hard palate, that is, in place of a prosthesis. Since the atrophy process does not go smoothly in the jaws, the position of the prosthetic position remains much different from the previous one, and as a result of a violation of the stagnation of the prosthesis instead of the prosthesis at the time of performing the Fuchsia, foci of inflammation of various manifestations also appear and cause discomfort to the patient. In addition, inflammations also arise due to the fact that the monomer contained in acrylic prostheses calls various allergic processes to the mucous membrane. The condition of the affected tissue of the prosthetic seat was explained by its color changes, dryness or moisture, and the scale of the dispersion of the process. To assess these signs, to diagnose in the ham A.K. Iordanishvili used the classification of stomatitis after orthopedic prostheses, proposed by 2007. Determination of the pH value of the oral cavity fluid by performing the following actions, the pH value of the oral cavity fluid of patients was determined by collecting it. It was noted from the patient that without swallowing, without moving the tongue and lips, the head was lowered forward. Thus, the oral fluid was collected for 120 seconds, all the collected oral fluid was taken into a special container. To determine the pH of the fluid from the oral cavity (pH-meter) was used. since there are special devices in the composition of the pH -meter, it allows you to get the result in a matter of seconds.Microbiological examination methods microbiological studies were carried out before and after prosthetics in the groups of patients we studied. To do this, patients were offered to rinse their mouth with distilled water 2 hours after eating, and then collect their oral liquid in a sterile container. From the resulting material, a series of sequential dilutions was prepared in the laboratory, after which a certain volume of them was placed on the surface of differential diagnostic nutrient media: agar for anaerobes, Endo environment, milk-saline agar, Kalina environment, bloody agar, MRS-4 environment, Saburo environment, etc. were used. In the study, bacteria were grown in bloody agar, Endo environment, milk-salty, Saburo-like environments under normal conditions for 18-24 hours, at a temperature of 37°C. The method of growing anaerobic microbes in sealed plastic bags filled with natural gas was used when planting to separate them. After the expiration of the specified periods, the containers in which the microbes were planted were removed from the thermostat, and the overgrown colonies were counted. On the basis of microscopic data of smeared greases per gram, the group and types of isolated microorganisms were determined; the nature of the properties of microbial cultures was determined in selective differential diagnostic feed environments.
3. Results and Their Discussions
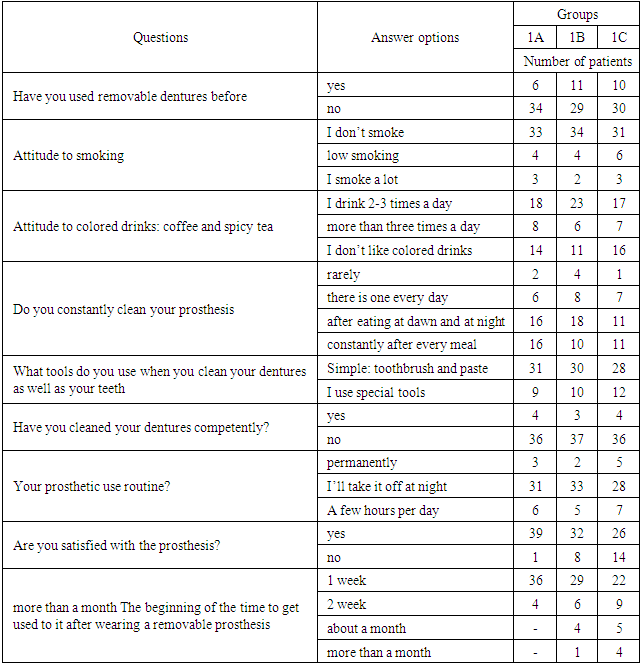
Statistical processing of the results was carried out on the package of the Statistica personal computer software for Windows 7.0, as well as using the computer program “EXCEL-2007”. The parameters for the distribution of the symptoms being analyzed are shown in terms of the mean value of the mean square deviation (m±m). Many comparison techniques have been used to compare more than a pair of averages (Newman-Cayles); a Styudent criterion has been calculated for many comparisons. The correlation coefficient was calculated on Spirmen. The difference between the groups in the symptoms being compared was considered statistically significant at р <0,05.120 patients with partial secondary adentia in the main group were divided into 3 groups during the treatment process: 1A-the main group, patients in this group were prepared with Acetal dentures. Nylon prosthesis “Valplast” was prepared for group 1B. Dental prostheses from acrylic polymer “Phthorax” were prepared for group 1С.In the process of examination, the examiners paid attention to the appearance of the facial part, the absence of asymmetry, to what extent their natural folds on the face became smooth, when the face was divided into three parts, changes in the lower part, and similar signs of importance on the face. The examination was then carried out in the mouth and examined the condition of the oral corridor, the floor of the mouth, the palate dome and soft palate tissue, the teeth retained in the oral cavity, the toothless alveolar tumor.The preparation stages were carried out on the basis of selected technologies and materials. Partial retractable dentures were scheduled a day after the wear of the patients, and patients were assigned follow-up examination times for follow-up. Partial withdrawal assessment of the clinical condition of dentures the duration of the period for which patients get used to it after wearing dentures indicates the effectiveness of orthopedic treatment. The adaptation of oral tissue to a foreign body and new conditions can greatly affect the human psyche. This is a complex and long-term physiological test. Data from the survey showed that patients wearing the first-time Acetal prosthesis in Group 1A, compared to groups 1B and 1С, found that the prosthesis did not take much space in the oral cavity and that the prosthesis was not much noticeable in the oral cavity, i.e. aesthetically comfortable. Since the base of the prosthesis is made monolithically with Acetal polymers, the fixation elements of the Acetal prostheses have a significant aesthetic advantage. The presence of clammers, whose colors are well chosen, restrained in high quality, is almost invisible. The Acetal prostheses are constructively very comfortable-this is in the small area of the base of the prosthesis. When upper jawprotezing with an acetal prosthesis, the base of the prosthesis can be placed in the front, back or central area of the hard palate, depending on the topography of the defect, while in acrylic and nylon prostheses it is less possible. It was easy for patients to get used to their Acetal prostheses.Patients using dentures made of acetal, nylon, and copper should be able to optimally adjust to the prosthetics. Patients using an acetaldehyde prosthesis may experience hypersensitivity to changes in the prosthesis design and hypersensitivity to the effects of the prosthesis. Structurally, the acetal prosthesis consists of an acrylic prosthesis with high strength and elasticity. Such a prosthesis allows patients with disabilities to move independently around the body, and also allows the doctor to move painlessly around the body.The most interesting indicators of the results of the survey were organized by the cleanliness aspects of the prostheses. In accordance with it, the majority of patients, 45% (54 individuals), mentioned that they cleaned the prosthesis once a day, while those who cleaned 2 times a day were 24.1% (29 individuals). Those who constantly cleaned after receiving each meal were 20% (24 people). A total of 19 patients (15.8%) were found to use special tools in dental prosthetic cleaning. Most of the patients, 81 (67.5%), use the usual paste and brush when cleaning dentures. During the 6-month follow-up period, only 11 people applied for qualified prosthetic cleaning, which was 9.1%.Table 2. Survey data
 |
| |
|
It should be borne in mind that 98 out of all patients (81.6%) do not smoke. Based on these data, we can conclude that the aesthetic properties of dentures may vary to one degree or another.Hygienic cleaning of dental prostheses obtained by patients was assessed for their changes in quality over a period of 1, 3, 6 months. As a result of the fact that some of the removable dental prostheses touch the mucous membrane directly and the inflammations caused by the accumulated microorganisms in it to the mucous membrane, the maxillary circulatory system is not affected, and as a result of this, the current that arises in the jaw surfaces the processes of atrophy. Uneven atrophy in the jaws affects the stabilization of the prosthesis, and the failure of the prosthesis, that is, its fracture extimole, increases. At the same time uneven atrophy causes discomfort to the patient by preventing the denture from stagnating in the oral cavity while performing the function, causing patients to wake up negative feedback on the prosthesis.According to the data on the purity index of dentures obtained in all patients in all three main groups, the use of Whole dentures did not determine the worst result during the period - a “very poor level of cleanliness”, which corresponds to 5.0-5.5. After the 1st month of evaluating the use of prostheses and their level of cleanliness, the rates changed dramatically among 1A patients and the following data were obtained: 35% satisfactory, 45% good level, and the remaining 20% had poor condition.Alternatively, the hygienic condition indicators of dental prostheses obtained after a month of patients in Group 1B (27%)-were at a good level, 39.4% – at a satisfactory level, the rest - at a bad level.The effect of orthopedic treatment when treated by dental prostheses taken to patients can be assessed by the short length of time patients get used to removable dental prostheses, that is, how quickly the patient gets used to the oral prosthesis. As a result of a study of the condition of the oral mucosa of patients of all three groups, it was found that there are foci of various degrees of colored inflammation in the place of the prosthesis.After a period of more than seven days, in both groups of Examiners, there was a decrease in the inflammatory dimensions of the prosthetic leg. It was also observed that during chewing on the mucous membrane, the level of inflammation produced by the pressure from the prosthesis decreases. In individuals who began to use partially removable dental prostheses, the 1st was calculated as the days of adaptation of the oral mucosa to the prosthesis in the 1st decade. From the following days, there was a decrease in the average size of the foci of inflammation.In all patients, after 90 days, the mucous membrane of the prosthetic leg has adapted to the prosthesis, and its inflammatory response has significantly decreased. From the sixth month of the analysis of the observations, it was found that in patients using dentures with Acetal extraction, the foci of inflammation changed for the better, that is, the Centers of inflammation were not detected at all in the first group, while in the 1B group it was 23 mm. But inversely to these results, none of the patients had any complaints about the adaptation of prostheses.An assessment conducted by us can observe that the inflammatory process of the denture tissue in patients wearing Acetal dentures is decreasing, this is confirmed by the structure of the surface of the removable denture base and indicates the advantage of using dentures made of acetal polymers. Monitoring the mucous membrane of the oral cavity in dynamics after prosthetics is a necessary and objective condition for assessing the hygienic and functional state of mucous membranes and dentures for the Prevention of dental diseases, the appearance of soft and hard caraches on prostheses, the appearance of foci of inflammation and pathogenic microflora in the parodont.An important factor in the development of changes in the oral cavity and dentures is the decrease in the resistance of the mucous membrane as a result of the accumulation of microorganisms and pathogenic flora. At the same time, the reaction of oral fluid plays an important role in the violation of the hygiene of the surface of the partially removable dentures, the appearance of caraches in them.Even 10 days after prosthetics, there were no clear changes in the pH value of oral fluid. After 90 days, the pH level of oral fluid shifted to the alkaline side and reached rn - 7.35, and 180 and 360 days after prosthetics, the pH value was 7.63 and 7.61, respectively. Therefore, in the formation of soft and hard caraches, a violation of hygienic conditions and an important condition in the mechanism of storage and use of partially removable dentures is that the oral fluid is alkaline in the pH environment.The long-term interaction of dental prostheses with the environment of the oral cavity and the tissues of the place of the prosthesis is one of the unresolved and difficult problems of modern orthopedic dentistry to the end. Prosthetic materials interact with the tissues of the prosthetic limb and often negatively affect the condition of the oral cavity. Obviously, this prosthesis depends on the material from which it is made, the specificity of its structure, the state of oral hygiene and the individual characteristics of the body. The use of dental prostheses is an intervention that changes biological balance and microflora in the tissues of the oral cavity, as a result of which it plays an important role in the formation of soft and hard caraches on the surface of dental prostheses and the organization of the structure of damage in it. In patients using partially removable acrylic dental prostheses, dysbacteriosis is noted in the oral cavity, which is accompanied by attenuation of non-specific protective factors and inhibition of the immune response. Advanced dysbacteriosis, removable dentures as the causative agent of immunodeficitis, and impaired oral hygiene can be shown. Because it can be assumed that important causes of the formation of deformable soft and hard caraches of the surface of removable dentures. In the resulting caraches, the ground is laid for the proliferation of bacteria and microbes of different types, and this naturally leads to a decrease in the local immune response of the oral cavity, as well as the formation of foci of various inflammations. The above refers to the need for morphological control on the surface of removable dentures. Caraches with such damaging plasticity are mainly formed in hard dental caraches on the subgingual surface, again the lunge has been found to accumulate in large numbers in supragingual areas on the surface as well. Morphologically, parietal microorganisms settle on the inner and outer surfaces of dentures. Especially in large quantities, they are abundant in the hard tooth Carache in the subgingival area, as well as in the tooth Carache in the lunge (supragingival) area. In optical Studies, a significant amount of detritus and microorganisms is detected on the smooth surface of dentures. At the same time, according to electron microscopy data, Special discrete caraches are detected, consisting of detritus and dental Carache residues with various microorganisms. These compounds are located directly on the surface of the dentures of the teeth, which are perceived as the formers of damaged-looking prosthetic Carache.Table 3. Functional features of the right and left original chewing muscles in patients of the main group
 |
| |
|
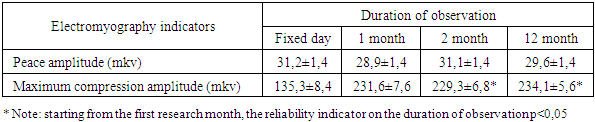
It follows from the 3 tables that on the day of prosthetics, patients with lamellar prostheses have maximum sensitivity to the bioelectric phase, the amplitude of biopotentials in muscles is 135.3±8.4 mkv -127.6±8.1 mkv. In the muscles under study, the optimal compressive strength was recorded by US after 1 month after the insertion of partially removable plate prostheses, which in the original chewing muscles - 231.6±7.6 mkv, and in the temporalis muscles - 197.1±10.6 mkv.The results of the observation show that in patients who use removable dental prostheses, despite compliance with hygiene, preventive measures, there are some conditions in the oral cavity aimed at microbiocenosis, immune resistance and violation of the reactivity of the mucous membrane, which is manifested by the appearance of soft and hard tooth decay on the surface of dentures, which are partially. The above justifies the search for effective means for oral care, such as disinfection, deodorization, hygienic elixirs, in individuals who use partially removable dental prostheses. To clean dentures, which are made up of special cleaning solutions and hygienic means, there are tablets “Corega tabs” that are soluble in front. To apply the tablet, it is placed in a clean container and placed over it with water, the dental prosthesis, which is obtained after the tablet dissolves, is ivified in this water for fifteen to twenty minutes, then it is washed under running water and worn again. Before carrying out general clinical and orthopedic examinations, we carried out targeted, in-depth examinations in patients.From microbiological examinations, the indicators presented below were obtained: the microflora of the oral mucosa was also detected in the sown greases, taking it from the inner surface of the removable dental prosthetic base.In the analysis of lubricants, it is often possible to see representatives of normal and less conditional-pathogenic microflora. Quantitative indicators of bacteria and fungi in the oral cavity fluid are presented in Table 4.Table 4. Indications of microflora from the oral cavity
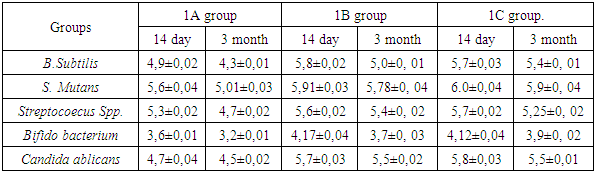 |
| |
|
4. Conclusions
Conclusion the study showed that the Acetal prosthesis does not change its position in the oral cavity environment and is less likely to accumulate microorganisms in it, so it has the advantage of alveolar tumor unevenness in partial toothlessness and application of preserved teeth in cases of convergence and divergence. When using an acetal prosthesis, the number of complications in the oral cavity was proven to have decreased convincingly by 1.7 times, it was found that the quality of orthopedic treatment of patients increased. Acetal prostheses have been found to convincingly reduce the colonization of pathogenic and conditionally-pathogenic microorganisms and candida fungi in the oral cavity by 1.2 times compared to acrylic and nylon prostheses, and to increase the quality of orthopedic treatment in partial toothlessness.
References
| [1] | Adamchik A.A. Improving the effectiveness of treatment of patients with dental defects with combined denture structures in periodontitis // Scientific review. Medical sciences. - 2014. – No. 1. – p. 25. |
| [2] | Arsenina, O.I. The significance of occlusive disorders in temporomandibular joint dysfunction // O.I. Arsenina, A.V. Popova, A.A. Gus // Dentistry. – 2014. – N 6. – pp. 64-67. |
| [3] | Barkan I.Yu., Stafeev A.A., Repin V.S. Features of adaptation of persons to full removable dentures in the aspect of assessment of psychoemotional status // Dentistry. - 2015. - Vol. 94, No. 5. - pp. 44-47. |
| [4] | Borunov A.S., Pryalkin S.V. The possibilities of patient adaptation in the complex treatment of dental deformities // Modern dentistry. - 2012. - No. 2. - pp. 75-79. |
| [5] | Dzansolova, D.E. The use of removable dentures in elderly and senile patients with partial loss of teeth in the lower jaw: abstract of the dissertation of the Candidate of Medical Sciences / D.E. Dzansolova. - M., 2014. - 21 p. |
| [6] | American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry. Management of the developing dentition and occlusion in pediatric dentistry // Reference Manual, 2014. – Vol. 40. – № 6, 18/19. – P. 352-365. |
| [7] | Albaker A. M. The oral health related quality of life in edentulous patients treated with Convhyentional complete dentures // Gerodontology, vol. 30, no. 1, pp. 61-66, 2013. |
| [8] | Elani HW, Harper S, Allison PJ, Bedos C, Kaufman JS. Socio-economic inequalities and oral health in Canada and the United States. J Dent Res. 2012; 91(9): 865-70. |



 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML


