-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2025; 15(4): 1285-1290
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20251504.92
Received: Apr. 6, 2025; Accepted: Apr. 22, 2025; Published: Apr. 30, 2025

Inflammatory Biomarkers in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Comprehensive Evaluation of Their Prognostic Value for Disease Severity and Outcomes
M. Sh. Karimov , Sh. Х. Mirzayeva , A. A. Eshmurzaeva , A. G. Isroilov
Tashkent Medical Academy, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
Copyright © 2025 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease marked by inflamed joints, systemic complications, and progressive disability. The early diagnosis of the disease followed by targeted treatment is essential to avert joint damage and to improve treatment outcomes. C-reactive protein (CRP), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), rheumatoid factor (RF), anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPAs), and cytokines like TNF-α and IL-6 are so far known to be important inflammatory markers that indicate the diagnosis of RA, severity of the disease, and monitoring of treatment response. The role of toll-like receptors (TLRs), especially TLR-2 and TLR-4, is emerging in inducing synovial inflammation and causes for joint destruction through the enhancement of pro-inflammatory pathways. In this regard, other emerging biomarkers include calprotectin and miRNAs, which may well hold promise in predicting disease clicks and efficacy of treatment. The present review highlights the relevance of both the old and new biomarkers in progressing RA diagnosis, personalized therapy, and patient management by reiterating that these should be combined to achieve better clinical outcomes.
Keywords: Rheumatoid arthritis, Inflammatory biomarkers, Autoimmune disease, TLR-2, TLR-4, CRP, ESR, ACPA, Cytokines, TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1, Autoantibodies, Personalized therapy, Prognostic markers
Cite this paper: M. Sh. Karimov , Sh. Х. Mirzayeva , A. A. Eshmurzaeva , A. G. Isroilov , Inflammatory Biomarkers in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Comprehensive Evaluation of Their Prognostic Value for Disease Severity and Outcomes, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 15 No. 4, 2025, pp. 1285-1290. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20251504.92.
1. Introduction
- Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic autoimmune disease that has adverse effects on people and healthcare systems worldwide. In the U.S., there are about 1.3 million adults with rheumatoid arthritis [12,47], whereas globally, it is between 0.5% and 1% of adults with rheumatoid arthritis. Women are 2-3 times more likely than men to have rheumatoid arthritis, with the common age range of onset being 30-60 years [12,17]. According to statistics about 35% of the patients become disabled within 10 years, and life expectancy is reduced further, up to five to ten years, that arises from complications of cardiovascular diseases [33,8]. The Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumatoid arthritis is characterized by synovial inflammation and hyperplasia ("swelling"), production of autoantibodies, including rheumatoid factor and anti-citrullinated protein antibodies, and progressive destruction of cartilage and bone leading to joint deformities. Systemic manifestations of RA include effects on the cardiovascular, pulmonary, psychiatric, and musculoskeletal systems [31].Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease involving genetic factors such as HLA-DRB1 in association with environmental risk factors: smoking and infections. These factors lead to citrullination of proteins, production of autoantibodies such as rheumatoid factors and anti-citrullinated protein antibodies. The formation of immune complexes caused by these autoantibodies activates the immune system, resulting in much chronic inflammation. The respectively inflamed joint synovial tissues cause a pannus, an invasive structure that erodes cartilage and bone. This activity is provoked by proinflammatory cytokines such as TNF-, IL-1, IL-6, and IL-17, as well as by enzymes such as matrix metalloproteinases and osteoclasts activated by RANKL. Chronic inflammation relates to its impact on concurrent cardiovascular disease and osteoporosis as systemic complications of directional immuno-dysregulation [14,46].The role of Inflammation Biomarkers in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Early diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis is of utmost importance to hinder the damage to joints and disease progression. Identification of these biomarkers will facilitate earlier diagnosis of RA, including circulating markers such as anti-CCP antibodies, RF, anti-MCV antibodies, and 14–3-3η proteins [43]. Biomarkers of inflammation are important in the diagnosis, target progress, and management of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Non-specific markers, including C-reactive protein (CRP) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), are routinely used to assess inflammation and treatment efficacy. Pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1, are responsible for joint destruction and placebo markers for RA therapy. Autoantibodies, including rheumatoid factor (RF) and anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP), are important in the early diagnosis of RA and identifying the potential for aggression. The 14-3-3η protein has also become an important predictor of disease progression. Together, these biomarkers have propelled personalized therapeutic strategies which have led to improved clinical outcomes in RA [1,32,30].
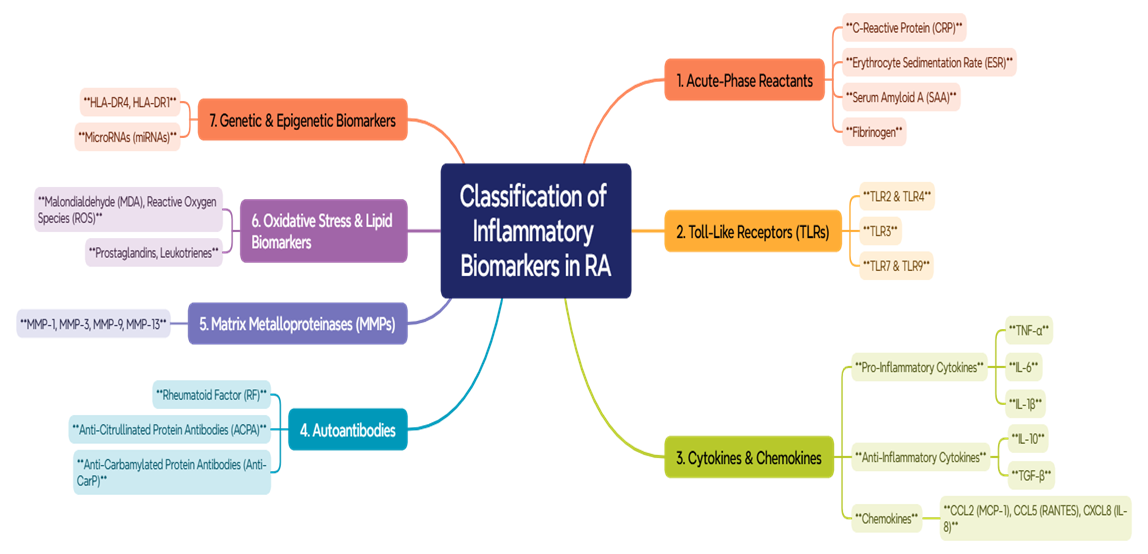 | Figure 1. Classification of Inflammatory Biomarkers in RA |
2. Conclusions
- Biomarkers of inflammation such as CRP, ESR, RF, ACPAs, TNF-α, and IL-6 are an essential part of the diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic management of rheumatoid arthritis. Toll-like receptors primarily TLR-2 and TLR-4 have furthered the understanding of mechanisms responsible for the inflammation of the synovium and subsequent joint destruction. Newer biomarkers namely calprotectin and miRNAs show promise in predicting disease progression and response to treatment. The combined efforts of these above parameters provide an enabling framework for early diagnosis, targeted therapy, and treatment approval enhanced by improved patient outcomes, thus highlighting their critical roles in providing better care for RA. Further studies of new biomarkers and their roles in clinical practice are expected to inform better management for RA.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML