-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2025; 15(4): 969-971
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20251504.26
Received: Mar. 12, 2025; Accepted: Apr. 1, 2025; Published: Apr. 8, 2025

Onco-Epidemiological Characteristics of Oncological Diseases
Kholmamatova Larisa Khakberdievna
Independent Researcher, Military Medical Academy of the Armed Forces of the Republic of Uzbekistan
Correspondence to: Kholmamatova Larisa Khakberdievna, Independent Researcher, Military Medical Academy of the Armed Forces of the Republic of Uzbekistan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

According to statistical data, the number of new cases of oncological diseases among the population is increasing every year. Currently, identifying and eliminating risk factors for dangerous and benign tumors among the population is one of the most important problems of modern medicine. Among the diseases of the population, oncological diseases occupy a high place in terms of mortality at all ages and lead to a decrease in the average life expectancy of the population and significant economic losses. One of the most urgent problems in medicine is the early detection and early diagnosis of precancerous diseases that lead to the development of dangerous and benign tumors. Therefore, precancerous diseases of the female genital organs remain one of the most urgent problems among general gynecological diseases.
Keywords: Abortion, Intrauterine device, Genital inflammatory diseases, Menstrual cycle, Childbirth, Risk factors, Tumor, Breast cancer
Cite this paper: Kholmamatova Larisa Khakberdievna, Onco-Epidemiological Characteristics of Oncological Diseases, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 15 No. 4, 2025, pp. 969-971. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20251504.26.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Currently, one of the risk factors for oncological diseases among the population is the early detection and early treatment of precancerous diseases, which plays a key role in preventing the development of malignant tumors. Despite many achievements in the diagnosis and treatment of tumors and precancerous diseases in modern medicine, tumors and precancerous diseases remain one of the urgent problems [5]. According to the World Health Organization, “10 million people die from oncological diseases per year, which is 1/3 of the world's mortality rate. Scientists estimate that by 2040, new cases of oncological diseases will increase by 47% annually, reaching 28.4 million ...”. Among diseases in the world, oncological diseases occupy a high place in terms of mortality among women of all ages [10].In order to raise the level of medical services to the population to a new level in accordance with the seven priority areas of the Development Strategy of New Uzbekistan for 2022-2026, the Presidential Decrees No. PF60 dated January 28, 2022 “...improving the quality of qualified services to the population in primary medical and sanitary services....,” and No. PF-87 dated March 7, 2022 “On measures to further intensify work on systematic support for families and women” were developed. The resolutions of the President of the Republic of Uzbekistan are aimed at improving the quality of qualified medical services in remote and remote areas, as one of the main problems of medicine is the timely detection, early diagnosis and prevention of oncological diseases [1,2].Tumors and precancerous diseases of the female genital organs are also among the most common gynecological diseases [3,4]. Precancerous diseases of the female genital organs are characterized by a negative impact on reproductive and sexual function. Due to the rather mild course, patients do not always seek medical attention [6,7].Therefore, precancerous diseases of the female genital organs remain one of the most urgent problems among general gynecological diseases.According to numerous statistical studies conducted in recent years, the number of breast diseases is characterized by a rapid increase [5]. Fibrocystic disease, first of all, is associated with the most common pathology among breast diseases, the incidence of which is recorded at the age of 40-44. Risk factors for breast diseases are diverse. Scientists believe that genetic, reproductive, adaptive and energy homeostasis disorders are important risk factors [4,9].In this area, we can safely say that, given the current increase in cancer incidence and high mortality rates among cancer patients, the study of precancerous diseases and their relationship to the risk of cancer is of great interest in modern medicine. At the same time, the main problem of medicine remains the timely detection of the disease.Thus, the onset of the disease and mortality rate depend on the geographical characteristics of the population's permanent residence, and this indicator varies in the west and east of Eurasia.
2. Purpose of the Research
- The purpose of the work is to study the most important onco-epidemiological risk factors for oncological diseases.
3. Materials and Methods
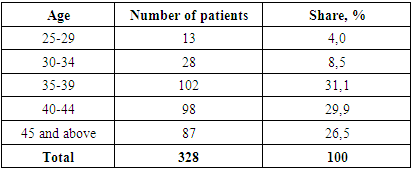
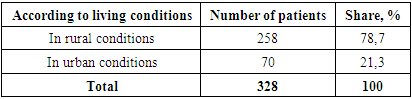
- In-depth medical examinations conducted by the Central Military Clinical Hospital among the population of Tashkent region from August to November 2024, patients who were being treated for tumors and precancerous diseases and were first detected among the population, and patients were examined using ultrasound examination, mammography and radiography, and vaginal smear examination methods, based on the information in the outpatient card. Complete anamnesis data and instrumental examinations of the population who underwent a medical examination allowed us to identify the population at risk of developing tumors and precancerous diseases.
4. Results and Discussion
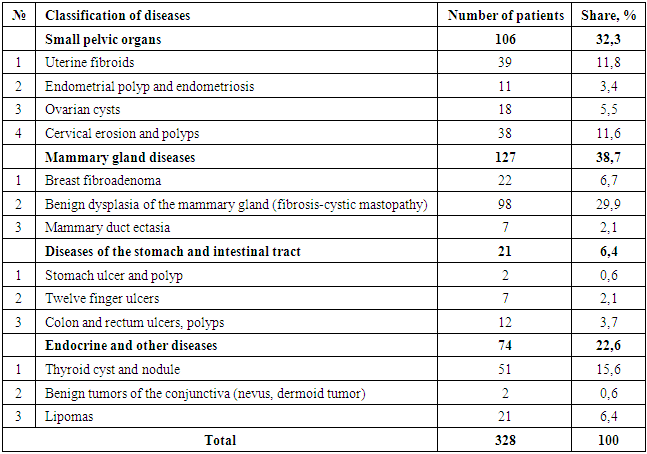
- A description of precancerous diseases and benign tumors detected among those in the study group is presented in Table 1.
|
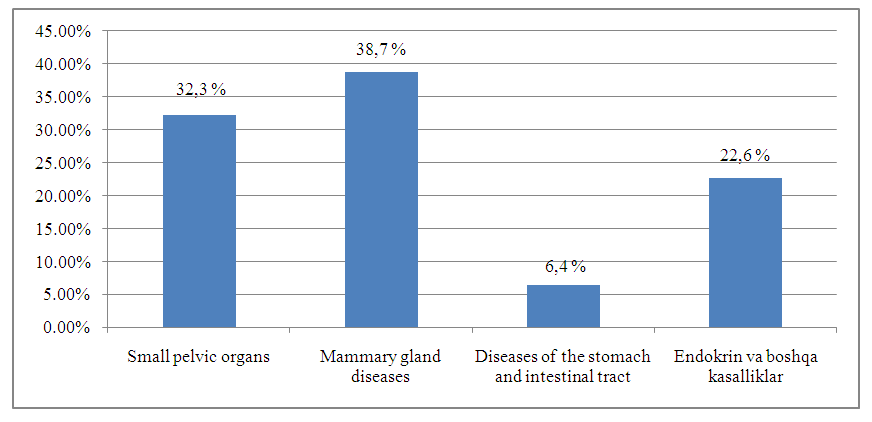 | Figure 1. Analysis of the classification of diseases identified among the population, (%) |
|
|
5. Conclusions
- Our analysis revealed that the following factors play a major role in the development of oncological diseases among the population: harmful habits, poor sexual life, colds, stress, and, most importantly, a decrease in the activity of the immune system. Regular medical examinations among the population are important in the prevention and early detection of oncological diseases. Therefore, when organizing medical examinations, it is necessary to ensure that they are composed of all specialists and undergo a complete medical examination.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML