Juraev Shakhzod Raimovich1, Khamdamov Alisherzhon Bakhtiyorovich1, Faizullaeva Nigora Yakhyaevna2, Khamdamov Bakhtiyor Zarifovich1
1Bukhara State Medical Institute, Uzbekistan
2Institute of Human Immunology and Genomics, Uzbekistan
Correspondence to: Juraev Shakhzod Raimovich, Bukhara State Medical Institute, Uzbekistan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Abstract
The article investigates immunological features of chronic prostatitis in young men depending on the presence of metabolic syndrome. Levels of pro-inflammatory (IL-2, TNF-α) and anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-4), as well as vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), were analyzed in blood serum and ejaculate. The data reveal significant differences between groups of patients with chronic prostatitis with and without metabolic syndrome. Metabolic syndrome was shown to amplify inflammation, angiogenesis, and cytokine imbalance, emphasizing the need for a personalized approach to treatment.
Keywords:
Chronic prostatitis, Metabolic syndrome, Cytokines, IL-2, TNF-α, IL-4, VEGF, Inflammation
Cite this paper: Juraev Shakhzod Raimovich, Khamdamov Alisherzhon Bakhtiyorovich, Faizullaeva Nigora Yakhyaevna, Khamdamov Bakhtiyor Zarifovich, Immunological Features of Chronic Prostatitis Depending on the Presence of Metabolic Syndrome in Young Men, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 15 No. 4, 2025, pp. 863-866. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20251504.02.
1. Introduction
The immune system is a key link in maintaining the body's health, providing protection against infections and controlling homeostasis. It is responsible for recognizing and neutralizing pathogens, as well as eliminating damaged or abnormal cells. One of the main mechanisms by which the immune system performs its functions are cytokines - small protein molecules that serve as signals between cells [2,5,8,15,16,17].Cytokines play a crucial role in regulating immune and inflammatory responses. They participate in the activation and differentiation of immune cells, coordinate interactions between them, and influence the intensity and duration of the immune response [1,6,9,11].Metabolic syndrome, characterized by conditions such as obesity and insulin resistance, contributes to changes in the cytokine profile in the body [3,7,12,14].Understanding the general importance of the immune system and the role of cytokines is important for developing new approaches to the diagnosis and treatment of chronic prostatitis, especially in combination with metabolic syndrome. The study of immune markers can provide valuable information on the pathogenesis of the disease and potential points of therapeutic intervention [4,10,13].Purpose of the study: The levels of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines and vascular growth factor in the blood serum and ejaculate of men with chronic prostatitis were studied depending on the presence of metabolic syndrome at a young age.
2. Materials and Methods of Research
To carry out this research work, 45 young men aged 27 to 44 years with chronic prostatitis who applied to the urology department of the Bukhara Regional Multidisciplinary Medical Center were examined in the period from 2023 to 2024. This cohort was divided into two subgroups: The main group (n = 20) - men with chronic prostatitis in combination with metabolic syndrome; the comparison group (n = 25) - men with chronic prostatitis without metabolic syndrome.The diagnosis was established based on clinical and functional data in accordance with the international consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of urological diseases (ICD-10). The diagnoses were verified based on a thorough collection of anamnesis, clinical, laboratory (general blood test, urine test) biochemical blood test, instrumental (ultrasound, CT, MRI). Particular attention was paid to the duration of the pathological process, previous and concomitant diseases.Interleukins were determined in blood serum and ejaculate using the solid-phase enzyme immunoassay method, according to the attached instructions. The set uses a "sandwich" version of the solid-phase enzyme immunoassay. The "Cytokine" test set was used to determine IL-2, 4 and TNFα, VEGF (St. Petersburg, Russia).
3. Research Results and Their Discussion
In the first stage of our study, we examined the level of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-2, IL-4, TNFa) and vascular growth factor (VEGF) in the blood serum of patients with chronic prostatitis without metabolic syndrome (comparison group, n = 25).IL-2 is a key cytokine that stimulates T-lymphocyte proliferation, which reflects the adaptive response of the body to the inflammatory process in the prostate. In the control group, this indicator was 13.2±0.17 pg/ml, while in patients with chronic prostatitis without metabolic syndrome (CP without MS) it was slightly higher - 14.4±0.09 pg/ml (Fig. 1). A slight increase in the IL-2 level in patients with CP without MS compared to the control group may indicate activation of the cellular component of immunity in conditions of chronic inflammation.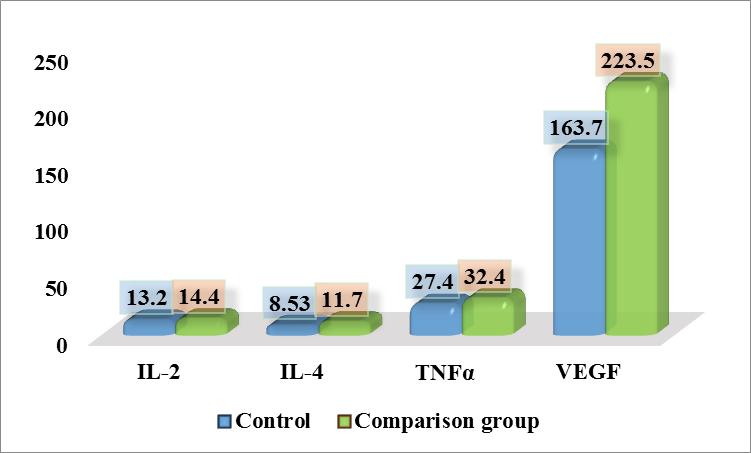 | Figure 1. Cytokine levels in patients with chronic prostatitis without metabolic syndrome (comparison group), (pg/ml, P≤0.05) |
IL-4 plays an important role in the differentiation of T-helpers of the second type (Th2) and stimulates the production of antibodies, which may indicate an adaptive immune response in conditions of chronic inflammation. In the control group, this indicator was 8.53±0.11 pg/ml, while in patients with chronic prostatitis without metabolic syndrome (CP without MS) it was significantly higher - 11.7±0.11 pg/ml (Fig. 1). An increase in the IL-4 level in patients with CP without MS may indicate increased activation of the humoral component of immunity.TNF-α is a key inflammatory mediator involved in maintaining chronic inflammation and activating immune cells. In the control group, this indicator was 27.4±0.09 pg/ml, while in patients with CP without metabolic syndrome it increased to 32.4±0.25 pg/ml. The difference between the groups was an increase of 1.18 times compared to the control group. This result reflects increased activation of the inflammatory response in patients with chronic prostatitis.VEGF is a key regulator of vascular permeability and growth of new vessels, which is important for maintaining the inflammatory process and tissue regeneration. In the control group, this indicator was 163.7±0.48 pg/ml, while in patients with CP without MS it was significantly higher - 223.5±1.05 pg/ml. The difference between the groups corresponds to an increase in the VEGF level by 1.37 times compared to the control group. Increased VEGF levels in patients with CP without MS may indicate activation of angiogenesis in response to chronic inflammation in the prostate tissue.Next, we studied the level of cytokines in a subgroup of men with chronic prostatitis in combination with metabolic syndrome (main group, n=20).In the control group, the IL-2 level was 13.2±0.17 pg/ml, and in patients with CP with MS it increased to 15.1±0.11 pg/ml, which corresponds to a 1.14-fold increase in the level compared to the control group.In patients with CP with MS, the level of interleukin-4 (IL-4) was 17.8±0.10 pg/ml, which is 2.09 times higher than in the control group (8.53±0.11 pg/ml) (p<0.05) (Fig. 2).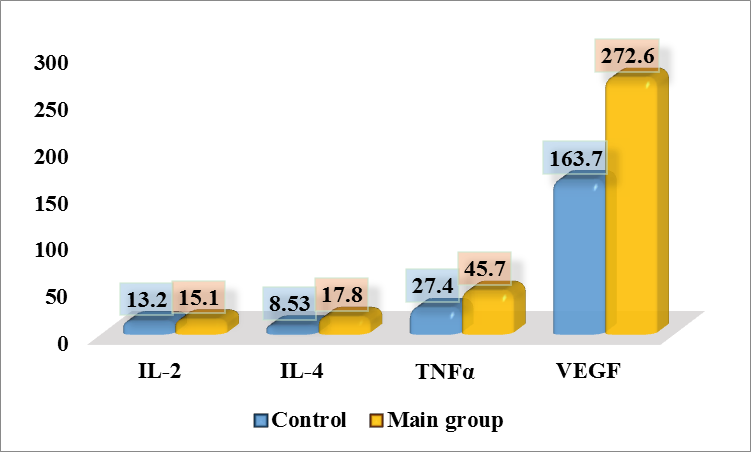 | Figure 2. Cytokine levels in patients with chronic prostatitis with metabolic syndrome (main group), (pg/ml, P≤0.05) |
The level of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) in patients with chronic prostatitis with metabolic syndrome (CP with m.s.) was 45.7±0.28 pg/ml, which is 1.67 times higher than in the control group (27.4±0.09 pg/ml) (p<0.05).When analyzing the level of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), it was found that in patients with chronic prostatitis with metabolic syndrome (CP with m.s.), it was significantly increased by 1.67 times and amounted to 272.6±2.65 pg/ml than in the control group (163.7±0.48 pg/ml) (p<0.05).Thus, a significant increase in the levels of the studied markers in groups of patients with chronic prostatitis, especially in the main group, is associated with increased inflammation and metabolic disorders. Increased IL-2 indicates activation of the cellular component of immunity and chronic inflammation. Increased IL-4 reflects activation of the humoral component of immunity and cytokine imbalance, which is more pronounced in patients with metabolic syndrome. Increased TNF-α confirms increased inflammation, since this cytokine is a key mediator of inflammation actively produced by macrophages. Increased VEGF indicates activation of angiogenesis, which is associated with hypoxia of prostate tissues and vascular dysfunction, especially pronounced in patients with metabolic syndrome.At the next stage of our research, we examined the levels of cytokines IL-2, IL-4, TNF-α and VEGF in the ejaculate of men in the control group and in patients with chronic prostatitis without metabolic syndrome (comparison group, n=25).The IL-2 level in the control group was 11.4±0.12 pg/ml, and in patients with CP without MS it increased to 13.8±0.11 pg/ml, which is 1.21 times higher than in the control (Fig. 3).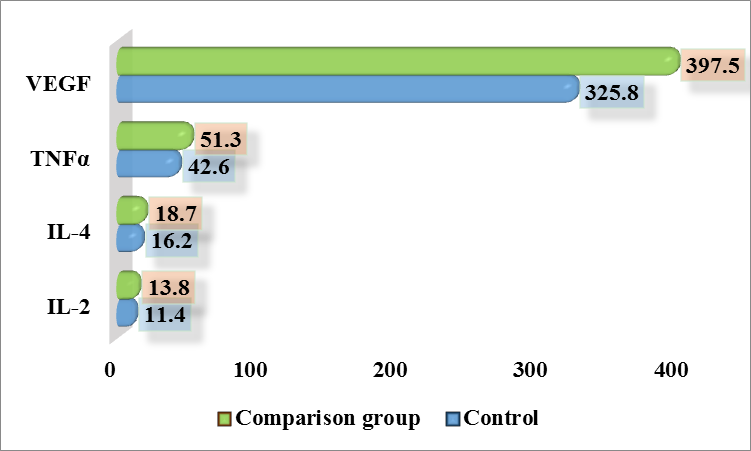 | Figure 3. IL-2 level in ejaculate in patients with chronic prostatitis without metabolic syndrome (comparison group), (pg/ml, P≤0.05) |
The IL-4 level in the control group was 16.2±0.10 pg/ml, and in the CP group without MS it increased to 18.7±0.28 pg/ml, which is 1.15 times higher than in the control.The level of TNF-α was 42.6±0.53 pg/ml in the control group and increased to 51.3±0.54 pg/ml in patients with CP without MS, which is 1.2 times higher than in the control.The VEGF level in the control group was 325.8±2.85 pg/ml, and in patients with CP without MS it increased to 397.5±2.40 pg/ml, which is 1.22 times higher than in the control.Thus, patients with chronic prostatitis without metabolic syndrome show a moderate but statistically significant increase in all studied cytokines compared to the control group. These changes reflect the activation of inflammatory and immune mechanisms, as well as the involvement of angiogenesis in the pathogenesis of chronic prostatitis.Next, the levels of cytokines IL-2, IL-4, TNF-α and VEGF in the ejaculate of men in the control group and in patients with chronic prostatitis with metabolic syndrome (main group, n = 20) were studied.The IL-2 level in the control group was 11.4±0.12 pg/ml, while in patients with CP with MS it increased to 17.5±0.11 pg/ml, which is 1.54 times higher than in the control (p≤0.05) (Fig. 4).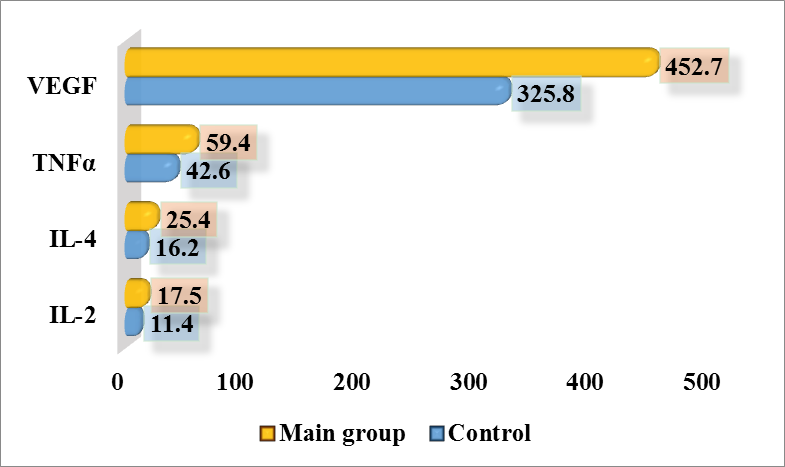 | Figure 4. IL-2 level in ejaculate in patients with chronic prostatitis with metabolic syndrome (main group), (pg/ml, P≤0.05) |
The IL-4 level in the control group was 16.2±0.10 pg/ml, and in patients with CP with MS it reached 25.4±0.30 pg/ml, which is 1.57 times higher than in the control (p≤0.05).The level of TNF-α in the control group was 42.6±0.53 pg/ml, and in patients with CP with MS it increased to 59.4±0.49 pg/ml, which is 1.39 times higher than in the control.The VEGF level in the control group was 325.8±2.85 pg/ml, while in patients with CP with MS it increased to 452.7±3.03 pg/ml, which corresponds to an increase of 1.39 times compared to the control.
4. Conclusions
Patients with chronic prostatitis and metabolic syndrome show a significant increase in all studied cytokines in the blood serum and ejaculate compared to the control group. These changes reflect a pronounced cytokine imbalance, as well as the involvement of angiogenesis in the pathogenesis of the disease. The data obtained confirm the significant impact of metabolic syndrome on the enhancement of inflammatory and immune disorders in chronic prostatitis.
References
| [1] | Albosale AH. Association Between Promoter Polymorphisms of IL-1B, IL-4 and IL-6 Genes and a Viral Load Infected Women with Human Papillomavirus // J. Reprod Infertil. - 2021. - No. 22 (2). - PP. 92-102. |
| [2] | Abdullaev KU, Yarmukhamedov A, S,. Gaibullaev AA Aripova TU,. Fayzullaeva N.Ya.: Diagnosis and prevalence of immune infertility in men with impaired fertility // Journal of theoretical and clinical medicine. 2024 No. 5. P. 56-60. |
| [3] | Baud D. Sperm Microbiota and Its Impact on Semen Parameters // FrontMicrobiol. - 2019. - No. 10. - P. 234-240. |
| [4] | Choi JB Analysis of bacterial community using pyrosequencing in semen from patients with chronic pelvic pain syndrome: a pilot study // Transl Androl Urol. - 2020. - No. 9 (2). - PP. 398-404. |
| [5] | Khamdamov I.B. Improving tactical approaches in the treatment of hernias of the anterior abdominal wall in women of fertile age // New day in medicine. Bukhara, 2022. -№ 10(48) - Р. 338-342. |
| [6] | Khamdamov I.B. Morphofunctional features of the abdominal press in women of reproductive age // New day in medicine. Bukhara, 2022. -№ 3(41)- Р. 223-227. |
| [7] | Khamdamova M.T., Akramova D. E. Genetic aspects of genital prolapse in women of reproductive age // New day in medicine. Bukhara, 2023. - No. 5 (55). - Р. 638-643. |
| [8] | Khamdamova M.T., Akramova D. E. Genetic aspects of genital prolapse in women of reproductive age // New day in medicine. Bukhara, 2023. - No. 5 (55). - Р. 638-643. |
| [9] | Khamdamova M.T., Teshaev Sh.Zh., Hikmatova M.F. Morphological changes of the thymus and spleen in renal failure in rats and correction with pomegranate seed oil // New day in medicine. Bukhara, 2024. - N. 3(65). - Р. 167-187. |
| [10] | Khamdamova M.T., Khasanova M.T. Various mechanisms of pathogenesis of endometrial hyperplasia in postmenopausal women (literature review) // New day in medicine. Bukhara. 2023. - No. 8 (58). - Р. 103-107. |
| [11] | Khamdamova M.T., Zhaloldinova M.M., Khamdamov I.B. The state of nitric oxide in blood serum in patients with cutaneous leishmaniasis // New day in medicine. Bukhara, 2023. - No. 5 (55). - Р. 638-643. |
| [12] | Khamdamova M.T., Zhaloldinova M.M., Khamdamov I.B. The value of ceruloplasmin and copper in blood serum in women wearing copper-containing intrauterine device // New day in medicine. Bukhara, 2023. - No. 6 (56). - Р. 2-7. |
| [13] | Khamdamov I.B. Improving tactical approaches in the treatment of hernias of the anterior abdominal wall in women of fertile age // New day in medicine. Bukhara, 2022. -№ 10(48) - Р. 338-342. |
| [14] | Khamdamov I.B. Morphofunctional features of the abdominal press in women of reproductive age // New day in medicine. Bukhara, 2022. -№ 3(41)- Р. 223-227. |
| [15] | Khamdamova M. T., Khasanova M.T. Genetic mechanisms of development of endometrial hyperplastic processes in women in menopacteric age // American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences 2025. - № 15(2): Р. 372-375. DOI: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20251502.2. |
| [16] | Oliveira GM Detection of cytomegalovirus, herpes virus simplex, and parvovirus b19 in spontaneous abortion placentas // J. Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. - 2019. - No. 32 (5). - PP. 768-775. |
| [17] | Wang, D. Cholesterol Induces Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition of Prostate Cancer Cells by Suppressing Degradation of EGFR through APMAP / S. Jiang, X. Song, et al. // Cancer Res. - 2019. - Vol. 79, No. 12. - P. 3063-3075. |






 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML