-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2025; 15(3): 776-779
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20251503.60
Received: Feb. 26, 2025; Accepted: Mar. 16, 2025; Published: Mar. 21, 2025

Dynamic Changes in the Isolated Pathogens in Patients with Purulent Inflammation of the Face and Jaw Area Treated with the Lymphotropic Method
Narziyeva Dilfuza Bakhtiyorovna, Bekmuratov Lukmon Rustamovich
Samarkand State Medical University, Teacher Samarkand, Uzbekistan
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

This article presents information on the effective therapeutic effects of using the local lymphotropic treatment method in the management of 161 patients with furuncles, carbuncles, and abscesses in the face and jaw area. It is shown that the use of antibiotics via intravenous or intramedullary injection is less effective compared to the lymphotropic method. The lymphotropic administration of antibiotics reduces the resistance of microorganisms that cause purulent processes to antibiotics and enables the widespread use of this treatment method in outpatient care.
Keywords: Bacteria, Furuncle, Carbuncle, Pus, Microorganisms, Antibiotics, Wounds
Cite this paper: Narziyeva Dilfuza Bakhtiyorovna, Bekmuratov Lukmon Rustamovich, Dynamic Changes in the Isolated Pathogens in Patients with Purulent Inflammation of the Face and Jaw Area Treated with the Lymphotropic Method, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 15 No. 3, 2025, pp. 776-779. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20251503.60.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The use of antibiotics in the treatment of purulent diseases of the soft tissues of the face and jaw is one of the main factors for the successful healing of wounds without complications [1,3]. The positive aspect of using antibiotics is that the introduction of the drug into the wound area is dependent on the high activity of the drug, the microorganism's sensitivity to the antibiotic, and the duration of maintaining the therapeutic concentration of the antibiotic at the inflammation site [2,5]. Numerous studies have shown that when antibiotics are administered locally to the organism, their effectiveness increases, as they create high therapeutic concentrations in the pathological focus [3,7]. The discovery of important mechanisms of the lymphatic system's involvement in the inflammatory process has led to the widespread clinical implementation of the lymphotropic method for drug delivery [4,6].
2. Research Purpose
- The aim of the research is to study the dynamic changes in the state of microorganisms isolated during the treatment of patients with purulent inflammation of the face and jaw.
3. Research Materials and Methods
- In the course of the research, patients were divided into two groups: a control group and a main group consisting of patients with purulent inflammation of the face and jaw. The form of the disease in the control group was selected to match that of the main group.Samples for research and bacteriological examination were taken from the patients in the main group four times: on the 1st, 3rd, 7th, and 10th days of the disease. In clinical practice, patients in the main group received intratympanic antibacterial drugs from the cephalosporin group using the lymphotropic method. For patients with furuncles and carbuncles identified in the face and jaw area, an intralymphatic antibiotic was selected, and on the first day after surgical intervention, the antibiotic was administered according to the method proposed by Y.M. Levin via the endolymphatic method.Bacteriological studies included isolating pure cultures of pathogens and determining their titers. The effectiveness of treating purulent processes in the face and jaw area was assessed using bacteriological examination on the 1st, 3rd, 7th, and 10th days of treatment.
4. Results and Discussion
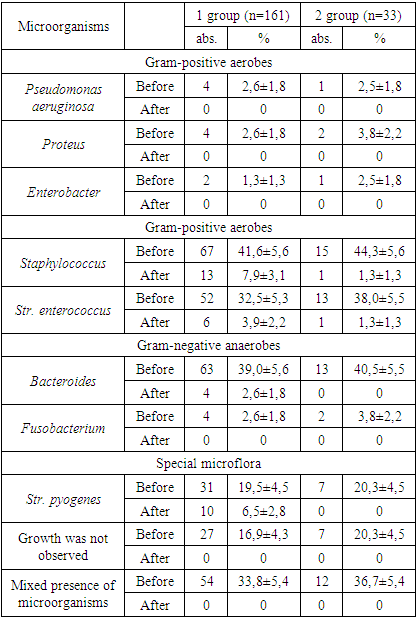
- Based on the localization of the purulent wound, the patients were distributed as follows: in the nose area – 25%, upper lip – 18%, lower lip – 13%, chin area – 12.4%, jaw, cheek, infraorbital, forehead, and temporal areas – 28%, preauricular and submandibular areas – 3.1%.When the effectiveness of lymphotropic treatment for various types of inflammation was studied dynamically, it was observed that on days 3, 7, and 10, microorganisms were isolated mainly in mono-, di-, and polymicrobial forms. The association of microorganisms was diverse: aerobes – 3.5%, anaerobes – 9.5%, and mixed anaerobic-aerobic bacteria – 14.8%.Treatment of purulent inflammatory processes in the face and jaw area with an intralymphatic antibiotic, using both lymphotropic and traditional treatment methods, showed that the most common microorganisms responsible for the development of purulent processes were staphylococci, peptostreptococci, and bacteroides. In some cases, bacilli and fusobacteria were also identified. Among the microorganisms, anaerobic actinomycetes were found in 10 to 15% of cases. These findings align with the data presented in the literature and confirm the etiological role of the skin and mucosal resident microflora in the development of the inflammatory process.In 96% of cases, an association of aerobic-anaerobic bacteria was found, with strict anaerobic bacteria that do not form spores (Pepto coccus spp. – 19%, Bacteroides fragilis – 21%) being identified. Staphylococcus aureus was detected in 60% of the samples, while Staphylococcus epidermidis was isolated in 19% of cases. A decrease in the number of microorganisms in the wound was observed on day 3 of treatment in both the 1st and 2nd group of patients, with this tendency being significantly noticeable only on day 10 in the 2nd group.
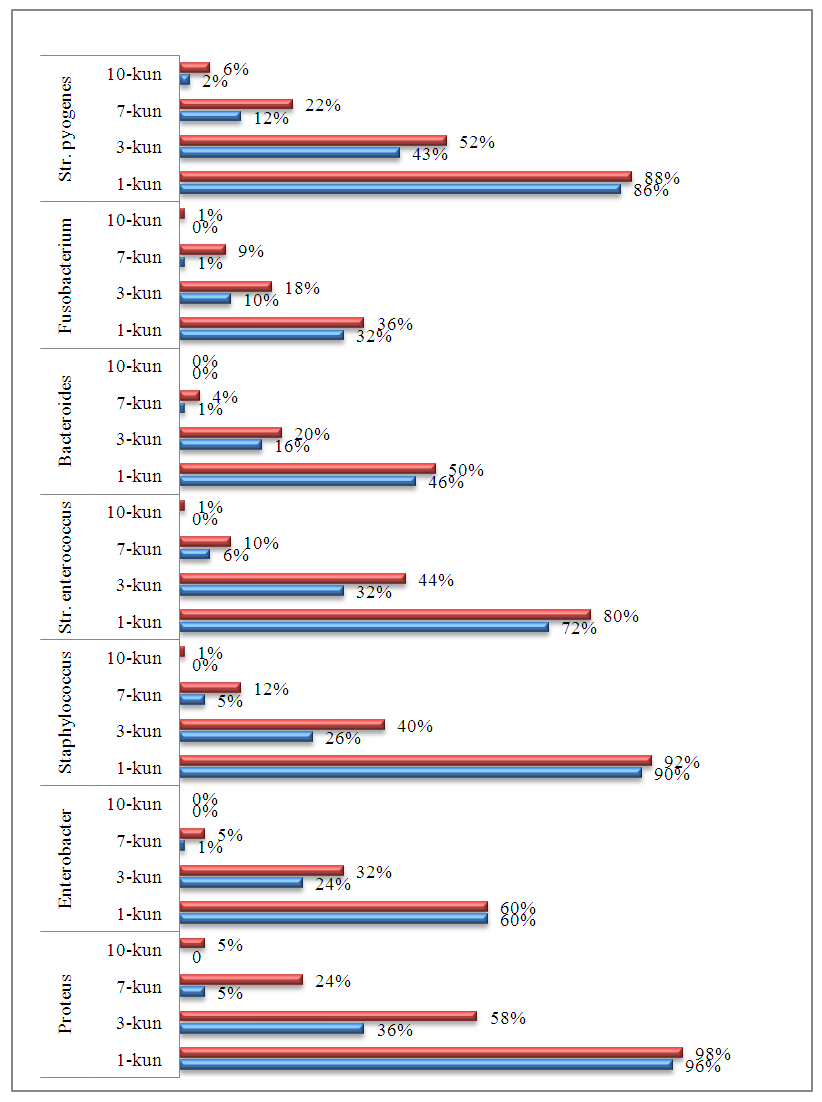 | Figure 1. Dynamic changes in the microbial landscape isolated from purulent inflammations in the face and jaw area. Day = kun |
|
5. Conclusions
- The application of lymphotropic antibacterial therapy in the treatment of patients with purulent diseases of the skin has been found to contribute to a faster cessation of the inflammatory process, slow the development of the severe form of the disease, reduce the number of potential complications, and shorten the treatment time. As a result, it has a positive effect on the patient’s economic condition. This method allows for the reduction of the antibiotic dosage used in the treatment and the number of injections required per day, and, due to the eradication of microbes in the lymphatic vessels and lymph nodes, it enhances the barrier function of the lymph nodes.All of the above makes the lymphotropic method highly applicable in the treatment of purulent diseases of the skin, such as furunculosis, carbunculosis, and abscesses, especially in the outpatient treatment of patients.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML