-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2025; 15(3): 606-610
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20251503.25
Received: Feb. 16, 2025; Accepted: Mar. 3, 2025; Published: Mar. 8, 2025

Morphofunctional Parameters of the Spleen in Experimental Rheumatoid Arthritis and Changes After Treatment
Mahmudova Guljamol Fazliddinovna, Turdiyev Mashrab Rustamovich, Nurboboev Adham Uyg’unovich
Bukhara State Medical Institute named after Abu Ali ibn Sino, Bukhara, Uzbekistan
Correspondence to: Mahmudova Guljamol Fazliddinovna, Bukhara State Medical Institute named after Abu Ali ibn Sino, Bukhara, Uzbekistan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

In rats called rheumatoid arthritis, significant changes in the morphology of the spleen were observed: its size and mass increased. The mass of the spleen in 18-month rats was 1257±8.15 mg, while in 24-month rats the rate was 1203.79±5.63 mg. This condition is explained by the fact that young rats have a high level of immune system activity and its decline with age. In white non-breeding rats treated with NAID, the recovery process of spleen tissue was noted, but the indicators did not approach full normality. The mass of the spleen was 1205±7.12 mg in 18-month-old rats and 1138±6.21 mg in 24-month-old rats.
Keywords: Spleen, Rheumatoid artgritis, Complex Freund's adjuvant, Immune system, Meloxicam
Cite this paper: Mahmudova Guljamol Fazliddinovna, Turdiyev Mashrab Rustamovich, Nurboboev Adham Uyg’unovich, Morphofunctional Parameters of the Spleen in Experimental Rheumatoid Arthritis and Changes After Treatment, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 15 No. 3, 2025, pp. 606-610. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20251503.25.
1. Introduction
- The participation of macrophages in the immune response is multifaceted. They eliminate up to 90% of the antigen and expose the remaining part in a more immunogenic form – as a superantigen. The interaction of macrophages with activated T and B lymphocytes is essential for the development of most immune responses. Macrophages create a microenvironment for lymphocytes. The size and shape of macrophages are variable and depend on the functional status of the cell, organ, and the entire organism [1,7]. Their nuclei are large, contain a nucleolus, and a small amount of chromatin is condensed near the nuclear membrane. Macrophages with a developed lysosomal apparatus are of the phagocytic type, while those with a developed endoplasmic reticulum are secretory macrophages found in periarterial areas. The third group of macrophages consists of dendritic cells located in the germinal centers of the spleen’s lymph follicles [2,9]. Due to their numerous functions, the spleen can be considered an indicator of various pathological conditions, including liver and blood system diseases, infections, autoimmune diseases, and connective tissue disorders.Rheumatoid arthritis (RA), an autoimmune disease, significantly affects all body systems. This indicates a positive correlation between the presence of RA and several other diseases and disorders [3,8]. Therefore, with RA, the risk of cardiovascular issues changes. Over 10 years, the risk of developing cardiovascular pathology in RA patients is 1%, but chronic inflammation adversely affects the endothelium, leading to its dysfunction, which significantly increases the risk of cardiovascular disease. Additionally, RA contributes to cardiovascular complications due to changes in the local architecture of large vessels. Specifically, subclinical damage to the common carotid artery is observed with prolonged RA. Furthermore, patients with RA show increased brain hyperperfusion and a rise in arterial hypertension. The risk of atherosclerosis also increases [4,9].According to foreign scientists, based on observations in inflammatory arthritis of rodents, it has been proven that sympathetic dysfunction contributes significantly to the pathophysiology of RA through the effect on the immune function of the spleen [5,10]. The SNS circuit for the spleen and lymph nodes includes preganglionic cholinergic fibers whose nerve terminals innervate postganglionic neurons ending in the spleen and lymph nodes. Noradrenaline is the main neurotransmitter and binds to adrenergic receptors expressed on immune cells, blood vessels and connective tissue cells. β2-adrenergic receptors are the predominant subtype of adrenergic receptors expressed in spleen cells. Normally, ligand binding to this receptor leads to signaling through G coupled proteins and activation of protein kinase A. This increases Th2-type immune responses and Treg cell function, resulting in improved immune response resolution. Conversely, in the context of chronic high SNS activation, splenic β2-adrenergic receptor expression may be reduced and signaling may shift from protein kinase A to mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. In the lymph nodes, signaling switches from protein kinase A to G-coupled protein receptor kinase pathways. These changes are characterized by reduced Treg cell function and stimulation of Th1 and/or Th17 immune responses [6,9].According to the scientific data of many scientists, an increase in the size of the liver and spleen, that is, hepatomegaly and splenomegaly, was observed in patients with rheumatoid arthritis [7,11].According to the analysis of the literature, there is almost no information about the morphological characteristics of the spleen of patients with rheumatoid arthritis, and the fact that the morphometric dimensions of the spleen in patients with this disease have not been studied, justifies the relevance of this study. The purpose of the study. Study of the morphological, morphometric and immunohistochemical indicators of the spleen of purebred rats in experimental rheumatoid arthritis and pathogenetic treatment.
2. Material and Methods
- Morphological studies of this experimental rheumatoid arthritis related to spleen tissue were carried out in the research laboratory of immunohistochemistry and pathogistology located in the vivarium and simulation center of the Bukhara State Medical Institute.In order to carry out experimental studies, 100 mixed-sex, 18-24-month-old white rats weighing 350-500 g were selected. All laboratory animals were obtained from the same vivarium and were performed on non-white rats aged 18-24 months. These adult (18-24 months old) white outbred rats were kept under standard vivarium conditions with relative humidity (50-60%), temperature (19-22°C) and light regime (12 h dark and 12 h light). Vivarium buildings were cleaned every morning, cages and rooms were cleaned in special clothes. The corpses of the animals that died during the experiment were buried in the soil, and the corpses of white-bred rats were chlorinated before the burial, after completing the relevant documents (certificate on the destruction of dead or killed laboratory animals). treated with a 20% solution of lime. N.A. Nuraliev in the formulation of a standard vivarium food ration for laboratory animals. and all. (2016) based on the recommendations in the methodological manual.Animals in the experiment were divided into 3 groups:first group control group-laboratory animals (n=20) fed with standard vivarium ration, healthy rats;the second group - laboratory animals (n=40) were fed with a standard vivarium diet, in which rheumatoid arthritis with a blanket Freund was called;the third group - laboratory animals (n=40) were fed standard vivarium ration, infected rats were treated with NAID for 2 weeks. (meloxicam 1 mg / kg once a day for 14 days).Our first group was a control group, 20 white non-breeding bats selected to compare results with the rest of the groups and housed in separate cells.In the remaining 80 rats, rheumatoid arthritis was called by the method of the adyuvant Freund in laboratory conditions.Required materials:Complex Freund's Adjuvant (CFA): an oily mixture containing mycobacteria (Mycobacterium tuberculosis). It was administered in special doses.Animals: mostly 18-24 months old, healthy white broodless rats. Injection equipment: fine needles of 27-30 sizes.Injection site: usually injected into the muscles of the hind limbs of the animal (intra-muscular) or under the tail.
3. Results and Discussions
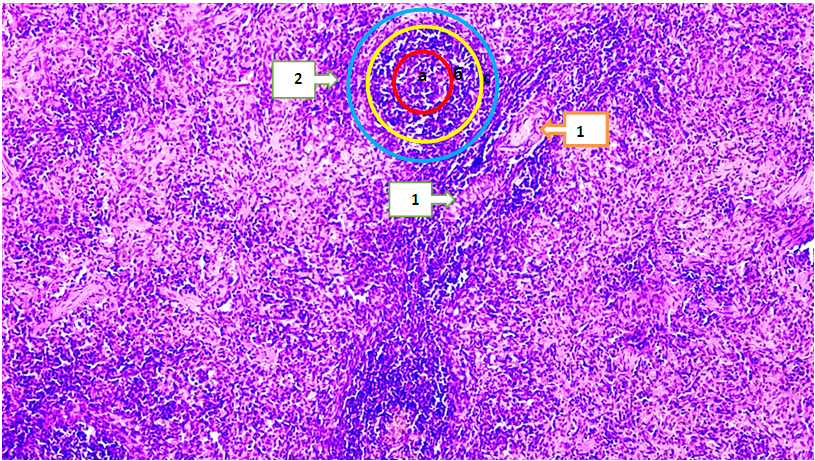
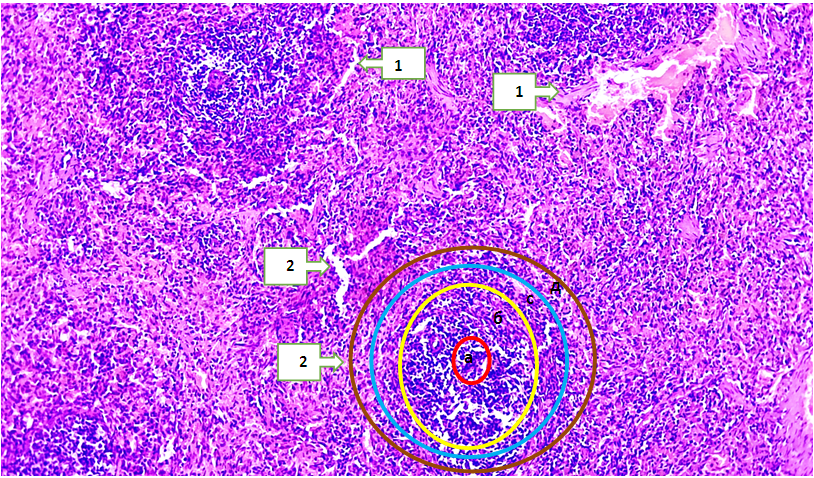
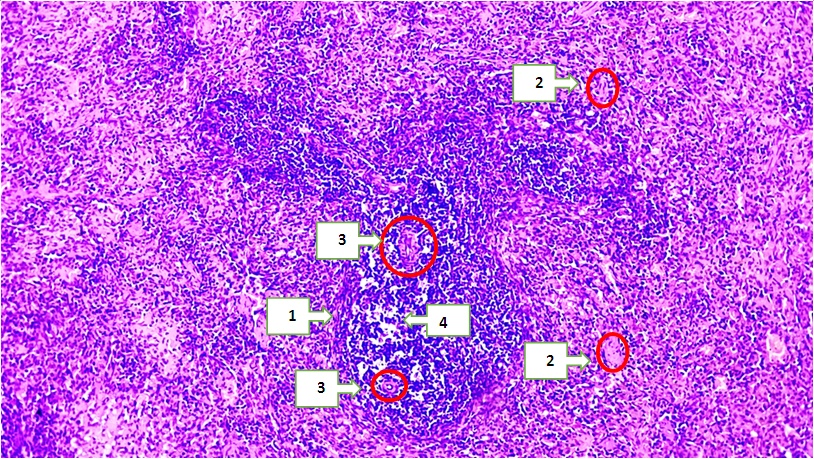
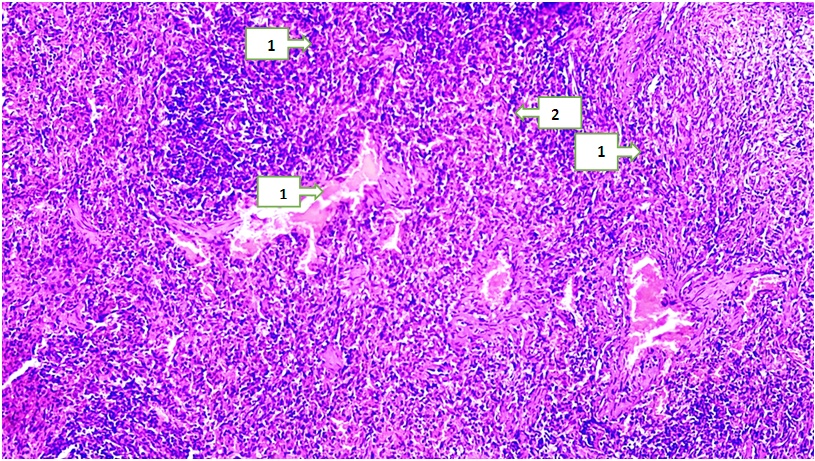
- The Adyuvant Freund is a transparent, light yellow liquid that contains 1.5 ml of mannide monooleat, 8.5 ml of paraffin oil and 10 mg of inactivated dried Mycobacterium tuberculosis in 10 ml ampoules each. This product is designed for research purposes. A full auxiliary Freund of 0.07-0.08 ml was sent to white laboratory male rats with an average weight of 400 g (the full AF content is an inactivated vaccine of BSJ (2 mg/ml (1 teaspoon lanolin and 30 tea Vaseline) in the fat environment)) was intradermally injected into the pads of the hind legs. In the next 14 days, the main indicators of the condition of animals were recorded once a week: the diameter of the circumference of the ankle joints, rectal and local temperature, ECHT, the number of leukocytes in the peripheral blood. On the 14th and 28th days after the introduction of full AF, rats were immobilized daily. On the 28th, the animals were capitalized. Blood was taken to analyze a number of biochemical indicators.We treated rats with rheumatoid arthritis, taken as Group 3 in our experiment, by giving NAID for 2 weeks. To do this, we gave rats meloxicam 1 mg / kg once a day for 14 days. All experimental white-breed rats were decepitated on an empty stomach in the morning at the end of the experiment, and the organs were measured.The analysis of the macroscopic, microscopic, orgonometric and histomorphometric indicators of the spleen, isolated from white non-breeding rats called experimental rheumatoid arthritis, was studied in the experiment. Macroscopically, when the spleen organ was seen the glare of the capsule covering the top of the organ was reduced, the spleen color was found to be darker red than the control group. The Shape of the spleen is usually found to be slightly rounded at the edges in a conical shape with a rim. Macroscopically, it can be seen that the spleen sizes have become relatively large, no other manifested changes have been detected. When the resulting micropreparations are analyzed, it is determined that the capsule surrounding the spleen tissue from the outside has become unevenly thickened, these changes were observed in almost all micropreparations of the spleen. Specific changes in the white pulp of the spleen, such as a decrease in the amount of lymphocytes, an increase in the amount of blood in the blood vessels of the spleen, that is, signs of dimming, were observed. Inside the vessels, signs of adhesion of small blood-shaped elements with each other and to the vascular wall were identified. Red pulp, plasma components that passed from the vascular interval to the tissue in the stroma were identified, and the accumulation of many eroded blood-shaped elements in the red pulp was found especially in the accumulation of yellow tongues formed from the accumulation of erythrocytes, that is, the accumulation of hemosiderin pigments. It was also found that in the red pulp, lymphocytes and macrophages accumulate scattered and concentrated. When white pulp is seen, Primary and secondary lymphatic nodes with developed areas are visible. In the Perarterial lymph mucosa, lymphocytes are visible, developing in the marginal and mantle areas, with slightly increased lymphocyte content and surface area. The area of reproduction is seen to develop lymphocytes.In the 18-month-old white non-breeding bats in the experimental group, it weighed 1,257±8.15 mg and in the 24-month-old bats 1,203.79±5.63 mg. In 18-month-old rats, the high severity of the spleen means the activity of their immune system and the development of spleen tissue. In rats at 24 months of age, however, a decrease in the severity of the spleen indicates a decrease in immunity and changes in the structure of the spleen as age progresses. The morphology of the red pulp varies from its area in 18-month-old white zotless rats to its area of 115398.23±2.36 mkm2 and in 24-month-old rats to 995237.31±2.45 mkm2, spleen bands and venous sinus area have been observed to expand, the diameter of venous sinuses is 0.48 ± 0.01 in 18-month-old rats and 0.31±0.03 Mkm2 in 24-month-old rats it has been found to be 81,747 ± 1.21 Mkm2 in bats and 73,118±1.11 mkm2 in 24-month-old bats.
4. Conclusions
- 1. In rats called rheumatoid arthritis, significant changes in the morphology of the spleen were observed: its size and mass increased. The mass of the spleen in 18-month rats was 1257±8.15 mg, while in 24-month rats the rate was 1203.79±5.63 mg. This condition is explained by the fact that young rats have a high level of immune system activity and its decline with age. 2. In white non-breeding rats treated with NAID, the recovery process of spleen tissue was noted, but the indicators did not approach full normality. The mass of the spleen was 1205±7.12 mg in 18-month-old rats and 1138±6.21 mg in 24-month-old rats. Changes in red pulp: the diameter of the venous sinuses was 0.38±0.01 µm in rats at 18 months, 0.25±0.05 µm in rats at 24 months. The area of venous sinuses decreased to 74,381±1.19 mkm2 at 18 months and 69,251±0.99 mkm2 at 24 months. The total area of red pulp was 984-35.24±1.97 mkm2 in 18-month rats, 875-61. 19±2.01 mkm2 in 24-month rats.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML