-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2025; 15(3): 509-513
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20251503.05
Received: Feb. 15, 2025; Accepted: Mar. 3, 2025; Published: Mar. 5, 2025

Diagnosis of Tuberculous Spondylitis in Current Medical Practice
Babоev Abduvakhob Sakhibnazarovich
Deparment of Osteoarticular Tuberculosis of Rebuplican Specialized Scientific Practical Medical Center of Phtiziology and Pulmonology, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
Correspondence to: Babоev Abduvakhob Sakhibnazarovich, Deparment of Osteoarticular Tuberculosis of Rebuplican Specialized Scientific Practical Medical Center of Phtiziology and Pulmonology, Tashkent, Uzbekistan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

The study was based on the results of the examination and treatment of 75 (100%) patients diagnosed with tuberculous spondylitis (TS). The patients' ages ranged from 20 to 80 years, with an average age of 52 years. There were 35 men (46.7 ± 0.58%) and 40 women (53.3 ± 0.58%). Additionally, a comparison group of 50 (100%) patients (21 men (42 ± 0.7%) and 29 women (58 ± 0.7%)) diagnosed with pyogenic spondylitis (PS), aged 25-77 years, with an average age of 58 years, was studied. Highly suggestive MRI and CT signs of TS and their prevalence were as follows: thoracic spine involvement in 50.7%, involvement of more than two vertebrae in 22.7%, vertebral body collapse in 36%, involvement of the vertebral pedicles in 9.3%, unclear boundaries of the destruction cavity in 58.7%, sequestrum in 10.6%, and subligamentous abscess spread to two or more vertebrae in 25.3%. The sensitivity, specificity, and positive predictive value of P1NP serum elevation for the differential diagnosis of TS and PS were 84.2%, 62%, and 95.2%, respectively. In 12 (16 ± 0.4%) patients with negative QFT results, tuberculous spondylitis was confirmed histologically in 3 (4 ± 0.23%) patients, bacteriological confirmation was obtained in 7 (9.3 ± 0.33%) patients, and both histological and bacteriological confirmation was obtained in 2 (2.7 ± 0.19%) cases.
Keywords: Tuberculous spondylitis, Pyogenic spondylitis, Quantiferon TB Gold
Cite this paper: Babоev Abduvakhob Sakhibnazarovich, Diagnosis of Tuberculous Spondylitis in Current Medical Practice, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 15 No. 3, 2025, pp. 509-513. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20251503.05.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- In the Republic of Uzbekistan, bone and joint tuberculosis has the highest incidence rate among cases of extrapulmonary tuberculosis. Tuberculous spondylitis (TS) represents 80% of all musculoskeletal tuberculosis cases [12]. The most severe complications of TS include paresis, paralysis, and dysfunction of the pelvic organs, with up to 60% of cases leading to a lasting loss of functionality despite treatment with anti-tuberculosis medication, pathogenetic therapy, and surgery [1]. Pathogenetically, the destruction of the vertebra in TS occurs as a result of the formation of infectious granulomas after hematogenous dissemination of Mycobacterium tuberculosis into the blood-rich spongy bone of the vertebral bodies, and the progression of the disease is manifested by the occurrence of caseous necrosis of the growing granuloma, exudation, increased cytokine activity, which activates osteoclasts [5,17].Diagnosing TS is challenging because the early stages of the disease present with a vague clinical picture. As a result, even primary medical doctors rarely order an MRI of the affected spine segment, except in rare cases, since pain is reflected muscle pain. Only after several months or more, after the destruction of the spinal motor segment, instability and neurological symptoms appear, the general condition of the patient worsens, at this stage, depending on the visual signs, a diagnosis of spondylitis, pathological fracture, spondylopathy or even metastasis is established [17]. For differential diagnosis in these cases, a percutaneous trephine biopsy of the affected vertebra is recommended. The sensitivity of this procedure in detecting tuberculous inflammation is generally no more than 60%, depending on the patient population.The diagnostic process for patients suspected of having tuberculosis includes tuberculin testing, which is used to assess the body's specific sensitivity to Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Currently, tuberculin skin tests (Mantoux test, Diaskintest etc.) and IGRA test (Quantiferon TB Gold, Wantai TB- IGRA) are used. However, current diagnostic methods for TB infection (TST, IGRA, and TBST) have a variety of limitations. The IGRA cannot distinguish between active tuberculosis and latent tuberculosis infection, and the TBST is limited by the same problem [13].
2. Purpose
- To determine the capabilities of laboratory, radiological and immunological tests in the diagnosis of TS.
3. Materials and Methods
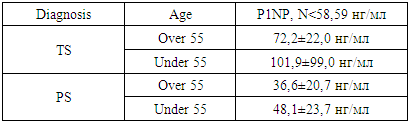
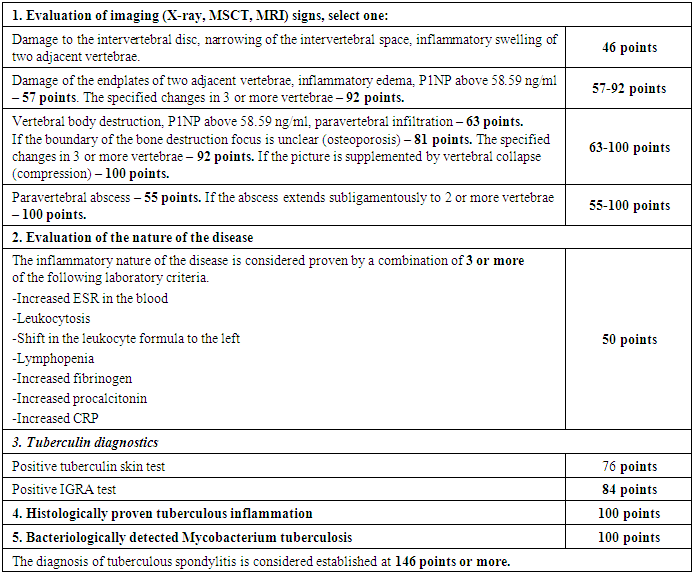
- The study was based on the results of examination and treatment of 75 (100%) patients diagnosed with TS. The age of the patients ranged from 20 to 80 years. The average age was 52 years. There were 35 men (46.7 ± 0.58%), 40 women (53.3 ± 0.58%). In addition, a comparison group of 50 (100%) patients (21 (42 ± 0.7%) - men, 29 (58 ± 0.7%) - women) diagnosed with pyogenic spondylitis (PS), aged 25-77 years, the average age was 58 years, was studied. Patient examination was conducted through general clinical assessments and specialized laboratory tests, based on their symptoms and medical history on the Biossays 240 Plus biochemical analyzer (Snibe Diagnostic, Shenzhen, China) and Finecare™ FIA Meter Plus, Wondfo Biotech (Guangzhou, China), chest X-ray (CT was performed as indicated), ultrasound examination of internal organs on the Siemens Acuson device (Berlin, Germany), ECG on the BTL-08 SD device (in the older age group, an echocardiogram was performed on the Siemens Acuson device (Berlin, Germany).During a general examination, the presence and number of BCG revaccination scars were determined.After the orthopedic examination, MRI (MRI SIGNA HD / e, 1.5 Tesla, General Electric, USA) and CT (Siemens Definition AS 64, Germany) were performed to study the affected segment of the spine.Bone metabolism was studied by determining the bone formation marker - P1NP (N-terminal telopeptide) in the blood serum on an automatic electrochemiluminescent immunoassay analyzer Cobas e 411 (Roche Diagnostics, Switzerland).All patients were tested using the Quantiferon TB Gold (QFT) laboratory test to detect tuberculosis infection. This test identifies INF-γ (gamma interferon) released by sensitized T cells, which are stimulated in vitro by specific proteins (ESAT-6, CFP-10, TB7.7 (p4)) from Mycobacterium tuberculosis, a part of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex.Tissue samples collected during surgical procedures were fixed in formalin, stained with hematoxylin-eosin and cut with a microtome, then examined under a microscope. The presence of central necrosis surrounded by epithelioid and Pirogov-Langhans cells confirmed tuberculous inflammation of the spine.Pathological tissues and fluids obtained during surgeries, punctures, fistula drainage, and sputum were examined bacteriologically. Molecular genetic methods used included GeneXpert® MTB/Rif (Sunnyvale, California, USA) and GenoType MTBDRplus (Hain Lifescience GmbH, Nehren, Germany). Mycobacterial culture growth was assessed using the BACTEC MGIT 960 medium (Becton Dickinson India Pvt. Ltd., Gurgaon, India) and cultured on solid Lowenstein-Jensen medium. The tuberculosis diagnosis was made based on a developed evaluation algorithm based on clinical, laboratory, and tomographic data, scored in points.A combination of isoniazid (H) 75 mg, rifampicin (R) 150 mg, ethambutol (E) 275 mg, and pyrazinamide (Z) 400 mg fixed-dose anti-tuberculosis drugs was prescribed for 3 months, followed by H and R for 10 months. According to body weight, 3 tablets (less than 55 kg), 4 tablets (over 55 kg), or 5 tablets (over 70 kg) were administered daily. In cases of drug resistance to H and R, levofloxacin 1000 mg, linezolid 600 mg, clofazimine 100 mg, and cycloserine 750 mg were given daily, along with bedaquiline 200 mg three times a week (after 14 days, 400 mg daily) for 22 months.Statistical analysis of the study was carried out using modern computer systems such as IBM/PQ of the latest generation using a package of standard Excel programs.
4. Results
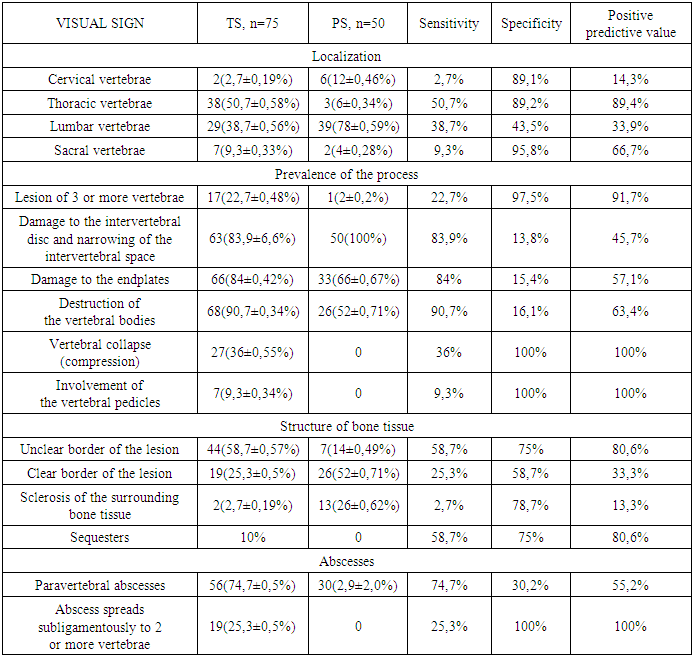
- The clinical presentation of both TS and PS included pain in the affected spine segment, radiating along the nerve roots, along with symptoms of body intoxication. Severe pain and immobility were observed in 18(36±0.68%) patients with TS and 13(7±0.69%) patients with PS. Both TS and PS patients had BCG vaccination scar, BCG vaccination and revaccination scars were determined in 30(40±0.57%) patients with TS and 20(40±0.69%) patients with PS.Intoxication syndrome was expressed by fatigue, increased body temperature, decreased appetite. Laboratory tests revealed moderate anemia (TS-Hb 118±9.04 g/l, erythrocytes - 3.6±0.31*1012/l; PS-Hb 118.3±15.4 g/l and erythrocytes - 3.6±0.5*1012/l), C-reactive protein (CRP), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) procalcitonin (PCT) and fibrinogen (Fg) elevation: TS -CRP 65.3±50.7 mg/ml, ESR 30.5±18.4 mm/h, PCT 0.15±0.07 ng/ml and Fg 7.75±3.8 g/l; PS- CRP 117.3±107.9 mg/ml, ESR 39.4±21.7 mm/h, PCT 0.3±0.2 ng/ml, Fg 6.8±3.3 g/l. The leukocyte formula remained within the normal range in TS: leukocytes - 6.7±1.1*109, band cells - 1.3±0.9%, segmented cells - 64.2±5.1%, eosinophils - 1.6±0.8%, lymphocytes - 27.2±4.1%, monocytes - 5.5±1.9%. In PS patients the leukocyte formula was also within the normal range: leukocytes - 8.3±2.9*109, band cells - 1.9±1.4%, segmented cells - 62.5±3.1%, eosinophils - 2.2±1.3%, lymphocytes - 26.8±2.4%, monocytes - 6.5±1%. Toxic hepatitis with increased transaminase levels and liver enlargement on ultrasound was noted in 7 (9.3±0.34%) TS patients and 11 (22±0.59%) PS patients. Weight loss was observed in 10 (13.3±0.39%) patients with TS, while no weight loss was found in patients with PS.MRI and CT features of TS were the thoracic spine involvement in 50.7±0.58% of cases, with 3 or more adjacent vertebrae affected and formation of kyphosis in 22.7±0.48%. Bone tissue destruction occurred in 90.7±0.34%, and total vertebral destruction was seen in 36±0.55% of cases. Osteoporosis of the paravertebral bone tissue was founded in 58.7±0.57%. Subligamentous spread to one, two, or three vertebrae was observed in 25.3±0.5%, and the intervertebral disc remains intact in 16% of cases. In patients with PS MRI and CT predominantly showed involvement of the lumbar spine in 39 (78±0.59%), with the intervertebral disc affected in all cases, no vertebral collapse, no involvement of the vertebral pedicles, no sequester formation and subligamentous abscess spreading to two or more vertebrae (Table 1).
|
|
5. Discussion
- Approximately 25% of the global population is infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The risk of active tuberculosis development increases with greater immunodeficiency, which is caused by the growing population living with HIV (39.9 million people worldwide in 2023), diabetes (537 million adults in 2021 [15]), liver diseases (1.69 billion people in 2019 [9]), autoimmune diseases, and the use of corticosteroids.The primary diagnostic methods for TS include MRI, CT, tuberculin skin tests, and IGRA tests. TS is most commonly differentiated from PS, which accounts for 1.5-2% of all osteomyelitis cases [17].Ahmad N et al, 2020 determined overall sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value and diagnostic accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosing spinal tuberculosis, taking histopathology findings as gold standard was 92.13%, 84.48%, 90.11%, 87.50% and 89. 12% respectively [2].In our patient population, highly suggestive visual signs of TS and their prevalence were as follows: thoracic spine involvement in 50.7%, involvement of more than two vertebrae in 22.7%, vertebral body collapse in 36%, involvement of the vertebral pedicles in 9.3%, unclear boundaries of the destruction cavity in 58.7%, sequesters in 10.6%, and subligamentous abscess spread to two or more vertebrae in 25.3%.Bone tissue destruction is both a pathogenetic stage of TS and a frequent (over 90%) visual indicator of the condition. This destruction is associated with an increase in PINP levels in the blood during TS, following bone surgeries, and in cases of bone metastases. Ying M et al. (2023) showed the significance of bone-specific alkaline phosphatase, pro-collagen type I N-terminal pro-peptide (PINP), and pro-collagen type I C-terminal pro-peptide (PICP) markers as prognostic and predictive indicators of bone metastases in prostate cancer patients [16].We have determined the diagnostic value of elevated P1NP for the differential diagnosis of TS and PS, sensitivity 84.2%, specificity 62%, positive predictive value 95.2%. Hamada Y et al, 2022 in their systematic review and meta-analysis found, that when combining all studies on Diaskintest, C-Tb, and C-TST, the pooled sensitivity in TB infection was 76% (95%CI: 70–81%, 17 studies) in individuals with HIV-negative or unknown status and 63% (95%CI: 53–73%, 5 studies) in HIV-positive individuals. Two studies assessed test sensitivity of QFT 90% (95%CI: 79–95%) in TB infection. In four head-to-head studies including both adults and children with and without HIV, IGRA sensitivity was 72% (95%CI:63-79%) in TB infection. The pooled sensitivity across 6 studies on IGRA was 77% (95%CI: 66-85%) in TB infection [8]. However, due to possible latent tuberculosis infection and BCG vaccination, it is difficult to draw unambiguous conclusions regarding the specificity of tuberculin skin tests and IGRA tests.In our study, among the 12 (16±0.4%) patients with a negative QFT result, tuberculous spondylitis was confirmed histologically in 3 (4±0.23%) patients, bacteriological confirmation was obtained in 7 (9.3±0.33%) patients, and both histological and bacteriological confirmation was obtained in 2 (2.7±0.19%) cases.Based on the presented material, we proposed a point system of diagnostic criteria for TS (Table 3).
|
6. Conclusions
- Both CT and MRI should be performed for diagnosing TS cases, because MRI is more sensitive for detection of bone and soft tissue edema, and CT shows bone structure. Early diagnosis of TS continues to pose a significant public health challenge and requires a comprehensive approach, relying on radiological assessments, immunological tests, as well as histological and bacteriological results.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML