-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2025; 15(2): 432-438
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20251502.34
Received: Jan. 27, 2025; Accepted: Feb. 16, 2025; Published: Feb. 28, 2025

Evolution of Perspectives on Clinical Features, Disease Progression, and Treatment Strategies for Multiple Sclerosis
Khalimova Khanifa Mukhsinovna1, Parpieva Yulduz Ravshanovna2
1Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, Department of Neurology and Medical Psychology, Tashkent Medical Academy, Uzbekistan
2Assistant, Department of Neurology and Medical Psychology, Tashkent Medical Academy, Uzbekistan
Correspondence to: Khalimova Khanifa Mukhsinovna, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, Department of Neurology and Medical Psychology, Tashkent Medical Academy, Uzbekistan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

This article analyzes the clinical and radiological dissociative and associative forms of multiple sclerosis (MS) and the pharmacological measures used in their treatment. The study assessed the neurological, immunological and radiological conditions of patients and studied the effectiveness of modern therapeutic approaches. The results showed the effectiveness of treatment regimens using complex immunomodulatory therapy and glucocorticosteroids in the treatment of multiple sclerosis. The study is aimed at identifying effective treatment methods for each type of the disease, reducing relapses and improving the quality of life of patients. This study can be recommended as a scientific and practical guide to the treatment of multiple sclerosis.
Keywords: Multiple sclerosis, Clinical-radiological dissociative form, Clinical-radiological associative form, Immunomodulatory therapy, Glucocorticosteroids, Kurtzke scale, MRI analysis
Cite this paper: Khalimova Khanifa Mukhsinovna, Parpieva Yulduz Ravshanovna, Evolution of Perspectives on Clinical Features, Disease Progression, and Treatment Strategies for Multiple Sclerosis, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 15 No. 2, 2025, pp. 432-438. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20251502.34.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
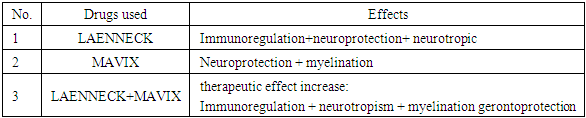
- Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a disease of the nervous system that occurs as a result of damage to the myelin sheath around nerve fibers in the brain and spinal cord of the central nervous system (CNS) [1]. This disease gradually leads to a decrease in functional capacity. The clinical course of the disease is characterized by a set of classic signs, which are Charcot's triad (nystagmus, intention tremor, and slurred speech) and Marburg's pentad (nystagmus, intention tremor, and slurred speech). tremor, slurred speech, optic nerve disc (OND) temporal atrophy, loss of abdominal reflexes) and Markov sexta (visual impairment (concentric narrowing of the visual field, scotomas), vestibular disorders, signs of damage to the eye motor nerve (ptosis, strabismus, diplopia, (sigh), pyramid disruptions, sensitive breakdowns (mostly vibration sensitivity), pelvic organs and mental disorders. However, given the somewhat peculiarities of the course of the disease today, the set of clinical symptoms in the initial and recurrent periods is somewhat different from the above-mentioned set of symptoms. In the initial period of TS, the following symptoms (polyneuropathy, myelopolyneuropathy, facial nerve neuropathy, afferent paresis, retrobulbar neuritis) may also appear in the form of a complex monosytoma [5,6]. This disease mainly affects people aged 20-40 years and is more common in women. The clinical manifestations of multiple sclerosis are very diverse, since their expression depends on the individual patient and the stage of development of the disease. Clinical and radiological features of the disease dissociative and clinical -radiological associative shapes TC's complexity and diagnosis further makes it difficult [2].In the last decade, a number of algorithms based on relapse frequency, disease progression, and MRI data have been adopted to evaluate the effectiveness of TS treatment. These algorithms require regular treatment, which helps to continuously monitor the effectiveness of the treatment [3-5]. The use of various approaches in the treatment of TS helps to effectively control the disease, reduce the number of relapses and positively affect the patient's quality of life.Clinical and radiological dissociative forms, clinical and radiologist signs to each other suitable absence with is characterized. This case, some in patients radiologist inspections through observed changes in clinical symptomatology suitable absence possible means. Thus together, clinical- radiological associative forms, clinical and radiologist expressions to each other filling and their mutual connection exists to be with described [6].In the last decade, a number of algorithms based on relapse frequency, disease progression, and MRI data have been adopted to evaluate the effectiveness of TS treatment. These algorithms require regular treatment, which helps to continuously monitor the effectiveness of the treatment [5]. The use of various approaches in the treatment of TS helps to effectively control the disease, reduce the number of relapses and positively affect the patient's quality of life. Man placental on the basis of hydrolyzate (BG). combined preparation - Laennec, the amount of BG in its composition is 112 mg to organize will. From now on outside of macroelements: N, P, C, S, Ci, Na, Mg, Ca, K; microelements: Zn, Br, Si, Fe, Mn, c, Se, Cr, V, Cu, Li, B, Co, low molecular regulatory peptides human growth factor as (GF): insulin similar (IGF), hepatocytic (HGF), fibroblasts (FGF), epidermal (EGF), nerve growth growth factor (NGF), granulocyte colonial growth factor (G-CSF) and macrophages (M-GSF), V 1 growth of cells transformable factor (TGF B1), growth factors PDGF-BB, vessels growth factor (VEGF), TNF-α, from this outside interleukins (IL-1, IL-2, IL-3, IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, IL-12), erythropoietin, interferon (IFN-γ), leptin, dehydroepiandrosterone, amino acids, and in exchange the ones that don't both (threonine, serine, proline, glycine, etc anine, methionine, lecine, isoleucine, valine, phenylalanine, histidine, lysine, arginine, taurine, aspartic acid, glutamine acid, cystine), nucleic acid, organic acids, nucleosides, glycosaminoglycans (glucuron and hyaluron acids, chondroitin sulfate), vitamins (PP, C, D and V group vitamins). of the drug the base organization doer important from the aspects one this placental of cells neurotrophic function. Placenta drugs this clearly neurotrophic function row scientific in research showing passed. Example for Ibanez CF Jekyll-Hyde of the spent experiences that showed that the laboratory in rats chair nerve from injury to recover was in progress of axons regenerative growth and the myelin sheath with wrapping in those who received stage BG one bath that it accelerated showed (r =0.001) [7]. Nerve growth growth factor (NGF) of the brain duties for important factor is, exactly in the placenta his/her humidity manager factor [6]. NGF neurotrophic from the function outside neuroprotector task both is, this process NGF cell internal signal receptor which is tyrosine kinase through the enzyme (TrkA). activates. Immunoplacental of preparations immunoregulator effect of the following impact mechanisms contained in the drug oh my god and his/her compounds and antioxidant properties to the surface arrival as a result to do increases [7]. The most important cell inside processes activation of JNK/SAPK signals through leukocytes transcription (NF- kappa B and AP-1) results in an increase in the amount of IL-8 increase with expression [8] Who is YS and others by in mice planted experience to the results according to the application of BG as a result peripheral of T- cells in the blood, to him similar harvest was cytokines and CD4(+) cells number decreased [9]. The neuroophthalmological effect of placental cell preparations was investigated in a study by Girotto G. and Malinverni W., in which the drug was prescribed to 54 patients with varying degrees of anatomical and functional changes in the eyes, various dystrophic processes of the retina (myopia, age-related changes) [10]. In the scientific work, the level of visual acuity, photosensitivity, electrophysiological activity of the retina checked. The drug was administered intramuscularly (3 ml/day) for 20 days, and the above parameters were checked before and after the treatment. According to the unique composition of Laennec, its anti-inflammatory properties slow down the "cytokine storm" process that occurs in TS and prevent the erosion of the myelin sheath. receives, as well as in the cells of the central and peripheral nervous system remyelination, neurotrophic and increases neuroprotective properties.Taking into account the above-mentioned properties of Mavics and Laennec drugs and their neurometabolic synergism when used together, we developed a complex treatment regimen and obtained an invention patent (IAP07257). We used it in combination not only for TS, but also for RIS and KIS to prevent disease progression and ensure long-term remission.
|
2. Materials and Methods of the Study
- All our patients with multiple sclerosis were treated in the departments of the 1st RKSH and in outpatient settings, a total of 64 subjects were enrolled. Patients with a diagnosis of multiple sclerosis were monitored for treatment measures. All patients in the divided clinical-radiological associative (CRA) and clinical-radiological dissociative (CRD) groups underwent outpatient and inpatient treatment at the 1st Republican Clinical Hospital. Clinical and neurological changes were assessed using Kurzke's FS and EDSS, MRI criteria for determining the degree of disability for, according to the McDonald 2017 MRI criteria. [4]; clinical-radiological associative types of TS developed based on the diagnosis: relapsing-remitting and secondary progressive types, in addition, RIS and KIS were obtained from the clinical-radiological dissociative types. All patients examined were between 18 and 40 years old, and all were monitored during the period of the disease, the duration of which did not exceed 14 to 60 days. Our patients underwent MRI (with contrast) and immunological examination (between 3 and 6 months) before and after treatment, the degree of disability using the EDSS scale (days 1 and 35 of treatment, the functional state of the nervous system using the Kurzke scale, and the psychoemotional status using the HADS.
3. Results of the Study
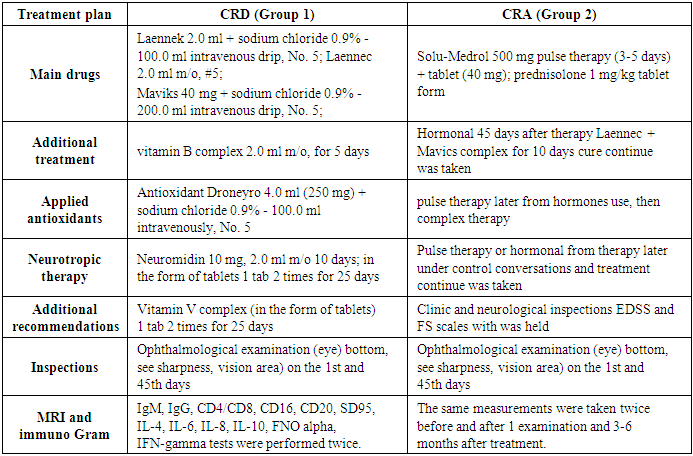
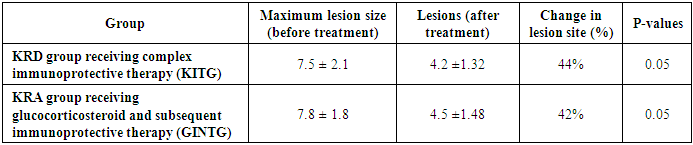
- Our patients received combined placental hydrolysate 2.0 + Monosialoganglioside GM1 40 mg (LAENNEK 2.0 ml intravenously and intramuscularly for 10 days) + (maviks-40 mg intravenously for 5 days) as a basic treatment, as well as symptomatic treatment (vitamin B complex, anticholinesterase, kentron). Before the observation phase of treatment, all of our patients were required to retrospectively refrain from taking the above drugs and GCS. All 64 patients in our study were between 18 and 40 years old, and we divided them into 2 large groups: Group 1 (n=34) is the CRD group, with radiological foci located mainly in the paraventricular, subcortical, and tentorial areas, with mild to moderate clinical symptom complexes, immunological humoral and autoreactive cells increased 1.5-2 times above normal, and patients with an EDSS score of up to 3.5 points received combined placental hydrolysate 2.0+Monosialoganglioside GM1 40 mg and symptomatic antioxidant (Droneuro), central and peripheral remyelinating drug (Kentron), vitamin B complex, and anticholinesterase (Neiromidin) therapy.The second group (n=30) was CRD, with radiological MRI foci located in the occipital juxtocortical, cerebellar, dorsal brain, and brainstem, and with severe clinical and neurological symptom complexes (acute progressive vision loss, scotoma, pronounced atrophy of the optic nerve, impairment of all types of sensation, pronounced pyramidal and cerebellar dysfunction, immunological humoral and autoreactive cells increased 3-4 times above normal and EDSS score above 5.5 points). The treatment phase was initially hormonal therapy (500 mg Solu-Medrol for 3-5 days or GCS (prednisolone) 1-2 mg/kg) and after 1.5 months, GCS + base + neuroprotective (Maviks) therapy for immunomodulatory purposes (combined placental hydrolyzate 2.0+Monosialoganglioside GM1 40 mg) and symptomatic therapy was performed.The purpose of our study was not to compare the treatments between these two groups, but to analyze the results of the combination developed on the basis of a patent for the invention, which was used to achieve remission without immunosuppression in the early stages of the disease, and in the group receiving hormonal therapy, to form a balance of the post-hormonal immune system, create a criterion for remission, prevent subsequent relapse, and provide a booster effect.All groups of patients underwent regular clinical neurological and radiological and immunological, neuropsychological re-examination (from the first examination day and up to 60 days) in dynamics before and after treatment.For group 1 (the scheme of drugs used by KRD: Laennek 2.0+sodium chloride 0.9%-100.0 v/i drip No. 5 and 2.0 m/o No. 5, recommended to patients. Basic therapy Maviks 40 mg+ of sodium chloride 0.9%-200.0v/i drip #5 every 10 days, vitamin V complex 2.0 m/o for 5 days, then 1 tab 2 times for 25 days, antioxidant-droneiro 4.0 (250mg) + sodium chloride 0.9%-100.0v/i drip for #5 day, kentron 40 mg m/o 10 days, neuromiddin 10 mg 2.0 m/o 10 days, then in the form of tablets 1 tab 2 times 25 recommended during the day.2 For the (CRA) group, those who received pulse therapy (500 mg Solu-Medrol for 3-5 days). After pulse therapy (40 mg-) or those who did not receive it, GCS (prednisolone 5 mg) was given at a dose of 1 mg/kg (45 days). Patients who received GCS in tablet form were monitored throughout the course. After 45 days of hormonal therapy, treatment was continued for 10 days in the Laennec + Mavics complex.
|
|
|
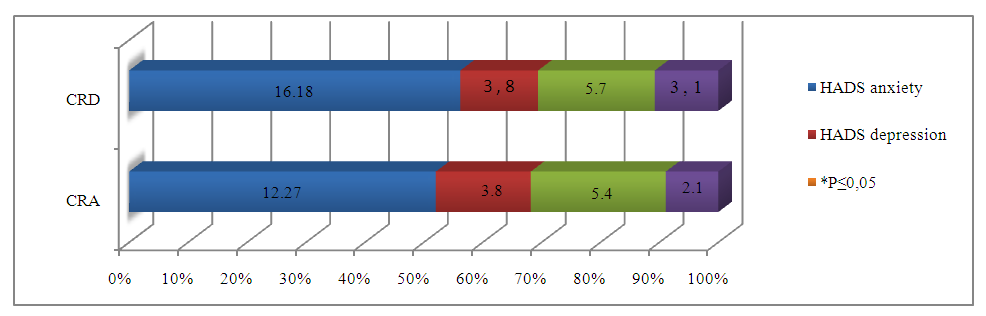 | Figure 1. In monitoring groups Differences in psycho-emotional states after treatment according to the HADS (Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale) scale |
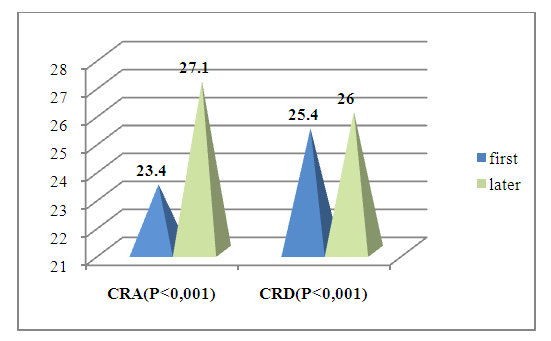 | Figure 2. Dynamics of cognitive function assessment using the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) scale before and after treatment in CRA and CRD |
|
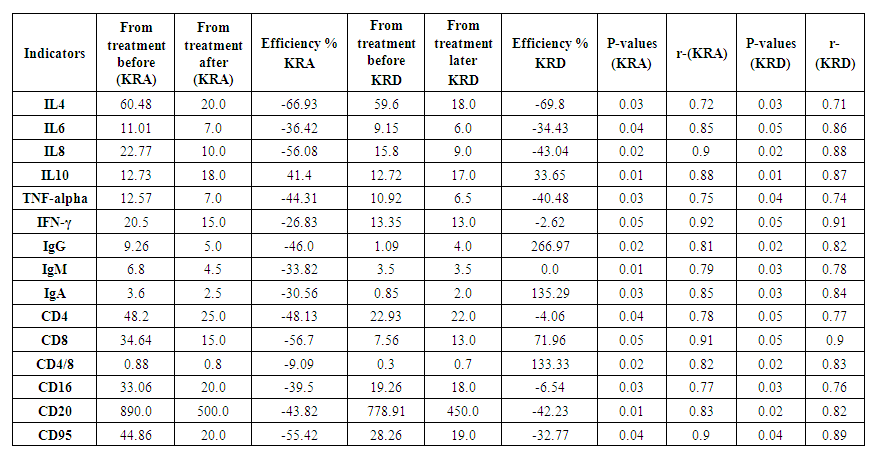 | Table 5. Post-treatment comparison analysis of autoreactive cells between groups |
4. Discussion
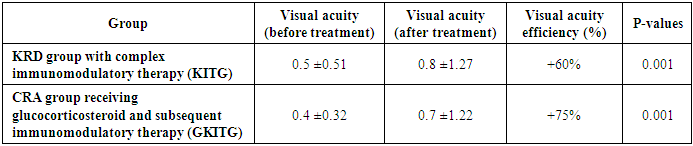
- To summarize the results, significant changes were noted in the CRA and CRD groups before and after treatment (see Figure 2). In particular, the treatment did not significantly affect the FS index in the CRA and CRD groups, while the EDSS index decreased by 1.5 and 2.33 times in these groups. MRI criteria In the KRA and KRD groups it decreased by 1.86 and 1.79, while the neuroophthalmological results decreased by 1.5 and 2.0 times. Anxiety level decreased 1.23 and 1.35 times after treatment, depression index decreased 1.52 and 1.36 times, cognitive functions tended to increase in both groups, that is, KRD was lower compared to KRA group. These results demonstrate the effectiveness of the treatment process in the KRA and KRD groups, confirming the scientific validity of the investigations. According to the results of the post-hoc assessment, the average duration of relapses in the CRA group was 4.0±1.2 months (33%), the average duration of remissions was 8.0±1.5 months (67%), and the number of relapses was 2–3 times per year, while in the CRD group the average duration of relapses was 2.0±0.8 months (17%), the average duration of remissions was 10.0±1.3 months (83%), and the number of relapses was 1–2 times per year. The higher proportion of the total remission time in the CRD group indicates the superiority of the mild course of the disease over CRA, the absence of a hormonal stage of treatment, and this scientifically substantiates the need for immunomodulatory, neurometabolic and supportive therapy (placental hydrolysate-Laennec) treatment in accordance with the type and course of the disease.
5. Conclusions
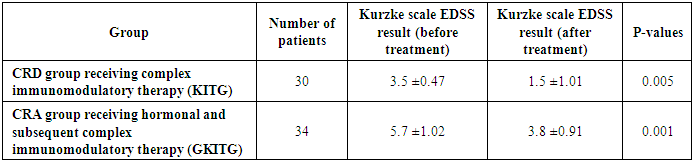
- The results of the study clearly showed the effectiveness of drug treatment measures used in various forms of multiple sclerosis (MS). It was found that treatment measures carried out on the basis of a special plan were highly effective in improving the general condition of patients in KRD (clinical-radiological dissociative) and KRA (clinical-radiological associative) groups.In the CRD group, patients treated with the Laennec and Mavics-based complex immunomodulatory therapy (CIT) regimen showed a decrease in the level of disability (on the EDSS scale) from 3.5±0.47 to 1.5±1.01 points. The therapy helped restore the myelin layer, reduce immunological damage to nerve fibers, and reduce the risk of disease relapse. There was also an improvement in the general psychoemotional state of the patients.In the CRS group, a treatment plan was used, including glucocorticosteroids (GCS) followed by complex immunomodulatory therapy. In this group, the level of disability (on the EDSS scale) decreased from 5.7±1.02 to 3.8±0.91 points. During treatment with GCS, it was noted that the severity of acute attacks of the disease decreased, the state of the immune system was balanced, and the general functional state of the patients improved.At the same time, it was found that the number of relapses decreased significantly in both groups over the last 6 months of treatment. This further confirms the effectiveness of the complex treatment measures used. These results demonstrate the importance of scientifically based approaches in the treatment of multiple sclerosis and the great potential of these treatment methods in improving the quality of life of patients.Overall, the study opened up the possibility of effective management of clinical and radiological forms of the disease in patients with multiple sclerosis by using modern therapeutic approaches. This and future treatment measures further to improve basis as service does.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML