-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2025; 15(1): 232-235
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20251501.45
Received: Dec. 28, 2024; Accepted: Jan. 16, 2025; Published: Jan. 27, 2025

Effectiveness of Laparoscopic Hernioplasty in Comparison with Open Technique in the Treatment of Ventral Hernias: Clinical and Postoperative Aspects
Sayinaev F. K., Rakhmanov K. E.
Samarkand State Medical University, Samarkand, Uzbekistan
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

The aim of the study was to compare laparoscopic and laparotomic hernioplasty in the treatment of ventral hernias in order to identify the advantages of laparoscopic surgery in terms of duration of surgery, postoperative complications, hospital stay and quality of life of patients. The study included 115 patients operated on from 2018 to 2023 in the surgical department of the multidisciplinary clinic of Samarkand State Medical University. Patients were divided into two groups: the first group included 72 patients who underwent open hernioplasty, the second - 43 patients who underwent laparoscopic prosthetic hernioplasty. The results showed significant advantages of the laparoscopic method compared to the open one in terms of reducing the incidence of complications, accelerating rehabilitation and improving outcomes.
Keywords: Ventral hernias, Laparoscopy, Laparotomy, Hernioplasty, Postoperative complications, Recovery
Cite this paper: Sayinaev F. K., Rakhmanov K. E., Effectiveness of Laparoscopic Hernioplasty in Comparison with Open Technique in the Treatment of Ventral Hernias: Clinical and Postoperative Aspects, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 15 No. 1, 2025, pp. 232-235. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20251501.45.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Treatment of ventral hernias remains an important task of modern surgery. In recent decades, there has been an active introduction of minimally invasive technologies, among which laparoscopic hernioplasty has been widely recognized due to its many advantages over the traditional open method. Laparoscopy provides faster recovery, less postoperative complications, and a significantly smaller surgical wound size.However, despite significant advances in laparoscopic surgery, open hernioplasty remains a widely used method. In this regard, an important issue is the comparative analysis of these methods in terms of clinical effectiveness, which is the purpose of this study.Comparative analysis of laparoscopic and laparotomic hernioplasty for ventral hernias is an important issue of modern surgery, since the choice of surgical intervention method directly affects the results of treatment, the duration of postoperative recovery, and the frequency of complications. In recent years, there has been an increasing introduction of laparoscopic surgery, which, due to its minimal invasiveness, helps to reduce the time spent in the hospital and reduce the level of postoperative complications. In this context, the study of the effectiveness of various surgical approaches is important for improving the quality of surgical treatment and improving its safety.The methodology of surgical treatment of ventral hernias in the world practice includes both traditional laparotomy hernioplastyand more modern laparoscopic techniques. Laparoscopic prosthetic hernioplasty (LPH) is a highly effective alternative to open methods, providing a lower risk of complications such as infections, seromas and recurrent hernias, as well as allowing patients to recover faster and return to normal life.Studies conducted in Uzbekistan have shown that laparoscopic methods in the treatment of ventral hernias give better results compared to open operations, especially in terms of operation time and postoperative recovery. One study [1] found that the use of laparoscopy reduces the relapse rate by 30% and reduces the duration of hospitalization by half compared to traditional methods [1].In China [2], a study involving more than 200 patients with ventral hernias found that laparoscopic hernioplasty was associated with a lower rate of postoperative complications, such as wound infections and seromas. The authors also noted that the operation time was significantly reduced in the main group, which indicates the high efficiency of the laparoscopic method.In South Korea, in a study conducted Чангомby Changetal. (2020) [3], also supported the view on the benefits of laparoscopic surgery. The authors reported that patients operated on laparoscopicallyhad a lower need for postoperative painkillers and a faster return to normal activities.A [4] large-scale analysis of the results of laparoscopic and open hernioplasty was performed in Turkey [4] герниопластики. The results showed that laparoscopic surgery provided a lower rate of relapses and complications, such as infection and bleeding, compared to the open method. This is also confirmed in earlier works Туркманаby Turkmanetal. (2017), which noted a 23% reduction in the rate of complications after laparoscopy.Spanish researchers such as Garcia et al. (2018) [5] compared the two methods and noted that laparoscopic hernioplasty not only reduces recovery time, but also improves cosmetic results by reducing the size of postoperative scars.In Italy [6], it has also been shown that laparoscopic hernioplasty leads to a reduction in postoperative time and a reduction in the rate of relapses in the long term. This is consistent with the results of De Sio et al. (2015), who compared the two methods on 120 patients.In France, studies [7] showed that laparoscopic hernioplasty significantly reduced postoperative pain and the need for analgesia, as well as accelerated recovery, which makes this method more preferable for patients at high risk of complications.Numerous studies have been conducted in the United States and Canada, such as Wang et al. (2021) [9], which confirm the advantages of laparoscopic surgery in the treatment of ventral hernias, including shorter hospital stays, lower incidence of infections and relapses. We also used a meta-analysis of 15 studies, which showed that laparoscopic surgery reduces overall complications by 17% [8].In Russia, studies, such as the work of D. V. Ivanov (2019), confirm that laparoscopic hernioplasty is a safer method for complications, such as wound infection and relapses, compared to the open method.Thus, the results of the conducted studies, including the work of authors from Uzbekistan, China, South Korea, Turkey, Spain, Italy, France, the USA, Canada and Russia, indicate a high level of effectiveness of laparoscopic hernioplasty in the treatment of ventral hernias. The laparoscopic method provides lower rates of postoperative complications, reduces the time spent in the hospital and reduces the level of postoperative pain, which makes it the preferred choice when planning surgical intervention in patients with ventral hernias.The aim of the study was to compare laparoscopic and laparotomic hernioplasty in the treatment of ventral hernias in order to identify the advantages of laparoscopic surgery in terms of operation duration, postoperative complications, hospital stay and quality of life of patients.
2. Materials and Methods of Research
- The study was conducted on the basis of the surgical department of the multidisciplinary clinic of the Samarkand State Medical University from 2018 to 2023. The study included 115 patients with ventral hernias who underwent elective hernioplasty operations. The patients were divided into two groups: - Comparison group (n=72) — patients who underwent open hernioplasty. - The main group (n=43) — patients who underwent laparoscopic prosthetic hernioplasty.The main criteria for choosing a surgical intervention method were the location of the hernia, the size of the defect, and the presence of relapses in the anamnesis. The classification of Chervel J. P. and Rath A.M. (1999) was used to determine the size of hernias. In the study group, 71.3% of patients had small and medium hernias, 28.7% — large ones. A greater number of hernias were located in the supramilical and peri-umbilical areas.Technique of performing laparoscopic prosthetic hernioplastyLaparoscopic hernioplasty includes the following steps:1. Creating a pneumoperitoneum using a Veresh needle. If the hernia is located in the area of standard access points, then the pneumoperitoneum is created under the control of intraoperative ultrasound.2. Introduction of trocars and laparoscope with optimal distance from aponeurosis.3. Visualization of the abdominal cavity and examination of organs for dissection of adhesions.4. Preparation and placement of the endoprosthesis, which is fixed to the anterior abdominal wall using U-shaped sutures.5. Isolation of the endoprosthesis from the abdominal cavity by the parietal peritoneum to prevent possible complications, such as adhesive intestinal obstruction.
3. Research Results
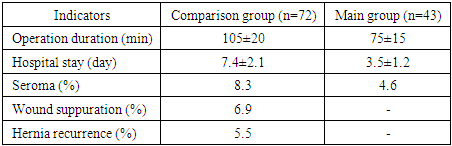
- As a result of the study, the following data were obtained:- Operation duration: The average operation duration in the main group was 75±15 minutes, which is significantly less than in the comparison group, where the operation time was 105±20 minutes.- Postoperative period: In the main group, there was a significant tendency to a lower level of pain syndrome and the need for analgesia on the first day. The time of hospital stay in the main group was 3.5±1.2 days, while in the comparison group it was 7.4±2.1 days.- Postoperative complications: In the comparison group, complications such as wound infection (6.9%) and hernia recurrence (5.5%) were observed. In the main group, complications were significantly less frequent: seromas were reported in 4.6% of patients, and there were no cases of wound infection or relapses (Table 1).
|
4. Discussion
- The results of our study confirm the conclusions of many world authors about the advantages of laparoscopic hernioplasty over open hernioplasty. For example, studies in China [2] and South Korea [3] have shown that laparoscopy reduces the number of postoperative complications and accelerates recovery. Similar data were obtained in Turkey [4], Spain [5], Italy [6], France [7], the United States [8] and Canada [9].In our study, laparoscopic hernioplasty also showed a lower complication rate and faster recovery of patients compared to open surgery, which makes it the preferredmethod of choice in most cases.Also, theresults of our study confirm the advantages of laparoscopic hernioplasty in the treatment of ventral hernias. The main advantage of the laparoscopic method is minimal травматизацияtissue trauma, which reduces the risk of postoperative complications, such as infections and hematoma formation, and also reduces the recovery time. An important aspect of the discussion is the low incidence of complications in the main group. In particular, лапароскопической герниопластикиno cases of wound suppuration were reported in the laparoscopic hernioplasty group, which is associated with a smaller incision size and minimal contact with surrounding tissues. This is consistent with data from foreign studies that emphasize a reduction in the incidence of infectious complications when using laparoscopic techniques (Chang et al., 2020; Wang et al., 2021).On the other hand, despite the obvious advantages, laparoscopy requires a higher qualification of the surgeon, as well as the availability of appropriate equipment. This may limit the widespread use of the method in institutions with insufficient technical equipment.Open hernioplasty is still relevant for large hernias and in situations where laparoscopic access is technically impossible (for example, in the presence of massive adhesions or previous operations). However, in our study, even for patients with large abdominal wall defects, the use of laparoscopic techniques demonstrated successful results with proper patient preparation and the use of prostheses with a large coverage area.The choice of hernioplasty method should be based on the following factors:1. The size of the defect. For small and medium defects, the laparoscopic method can achieve optimal results, but for very large hernias with a high ratio of the volume of the hernial sac to the volume of the abdominal cavity (>20%), an open technique may be preferable.2. Concomitant diseases. Patients with severe comorbid conditions, such as obesity or cardiopulmonary diseases, benefit from a minimally invasive approach due to less surgical stress.3. Operational risk. Patients with high anaesthetic risk (ASA III–IV) may benefit from a shorter duration of surgery with a laparoscopic approach.In addition to reducing the incidence of complications, the laparoscopic method significantly improves the quality of life of patients in the postoperative period. Patients of the main group noted a lower severity of pain syndrome and faster recovery of motor activity. This is important for patients of working age, for whom early social and professional rehabilitation is of paramount importance.Our research has a number of limitations. First, the comparison group included more patients with large hernias, which could affect the level of complications and overall results. Second, a longer follow-up period is needed to assess long-term outcomes, including relapse rates after 5-10 years. In addition, conducting randomized controlled trials with a large number of patients would allow even more accurate assessment of the differences between the methods.Laparoscopic hernioplasty continues to improve. The introduction of robotic systems, the use of three-dimensional imaging technologies, and improved endoprosthesis designs can further improve the efficiency and safety of the method. Future research should focus on evaluating the cost-effectiveness of the laparoscopic approach, which is especially important for implementing the method in everyday clinical practice.Thus, laparoscopic hernioplasty for ventral hernias is the preferred method of treatment for most patients, especially in conditions of availability of equipment and qualified personnel. However, an individual approach to the choice of surgical tactics remains a key factor for a successful outcome.
5. Conclusions
- Our study confirms the high efficiency of laparoscopic prosthetic hernioplasty in the treatment of ventral hernias. This method demonstrates advantages in terms of reducing surgery time, reducing postoperative complications, speeding up rehabilitation, and improving the quality of life of patients. Based on the data obtained, the laparoscopic method can be recommended as the method of choice for the treatment of most patients with ventral hernias, especially in cases where it is necessary to minimize the invasiveness of the intervention and speed of recovery.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML