-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2025; 15(1): 145-148
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20251501.27
Received: Dec. 23, 2024; Accepted: Jan. 20, 2025; Published: Jan. 26, 2025

Study of the Efficacy of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation and Memantine in the Management of Motor Aphasia Following Ischemic Stroke
Adham Yusupov1, Ibodulla Qilichev2
1PhD Student, Department of Neurology, Medical Psychology and Psychotherapy, Urgench Branch of Tashkent Medical Academy, Urgench, Uzbekistan
2DSc., Professor, Department of Neurology, Medical Psychology and Psychotherapy, Urgench Branch of Tashkent Medical Academy, Urgench, Uzbekistan
Correspondence to: Adham Yusupov, PhD Student, Department of Neurology, Medical Psychology and Psychotherapy, Urgench Branch of Tashkent Medical Academy, Urgench, Uzbekistan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

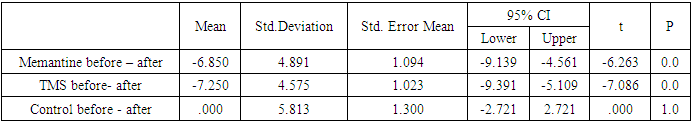
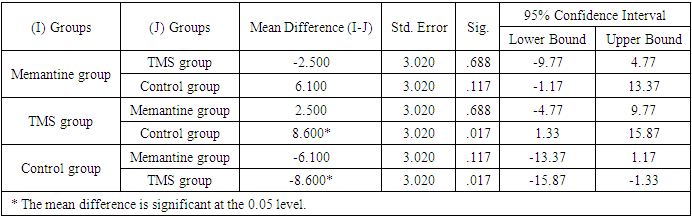
Background: To determine the effectiveness of Memantine and TMS in the treatment of aphasia developed after ischemic stroke. Methods: The study included 60 patients (36 males, 60%, and 24 females, 40%) with motor aphasia caused by ischemic stroke in the left middle cerebral artery territory. The patients were randomly divided into three groups. Patients in the first group received Memantine treatment according to a specific regimen, the second group underwent TMS therapy for 10 days, and the third group received TMS-placebo. Motor aphasia in patients was assessed before and after treatment using the Western Aphasia Battery (WAB) scale. Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS24 software. Results: Post-treatment mean scores of the Memantine group (CI=6.29; p<0) and the TMS group (CI=7.08; p<0) showed significant differences compared to the control group (CI=0; p>1). Post-treatment mean scores of patients in the TMS group were significantly different compared to the Memantine group (p=0.6) and the control group (p=0.01). Conclusions: Memantine and TMS are effective in the treatment of motor aphasia developed after ischemic stroke. TMS demonstrated better efficacy compared to Memantine. However, the effects of Memantine appeared earlier than those of TMS.
Keywords: Stroke, Aphasia, Treatment, Transcranial magnetic stimulation, Memantine
Cite this paper: Adham Yusupov, Ibodulla Qilichev, Study of the Efficacy of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation and Memantine in the Management of Motor Aphasia Following Ischemic Stroke, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 5 No. 1, 2025, pp. 145-148. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20251501.27.
1. Introduction
- Stroke is currently one of the leading causes of disability and mortality [1]. According to statistics, approximately 2 million people in the United States live with aphasia, and an additional 180,000 new cases are identified annually [18]. About 15% of individuals under the age of 65 who experience a stroke develop aphasia, and nearly 45% of individuals over the age of 85 experience post-stroke aphasia [19]. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) has been utilized in numerous studies as an innovative approach to treating stroke complications, including paralysis, dysphagia, dysarthria, pain, seizures, and aphasia [2-10]. Speech issues, such as stuttering, word-finding difficulties, and agrammatic speech, are observed in approximately 15-40% of patients with stroke [11]. According to the National Aphasia Association, aphasia is more prevalent than muscular dystrophy and Parkinson’s disease.Speech centers include Broca’s and Wernicke’s areas in the left hemisphere of the brain, their homologous areas in the right hemisphere, the prefrontal and premotor regions of the frontal lobe, and the inferior portion of the parietal lobe [12,13]. Bilateral cortical activation has been identified in various stages of stroke recovery using positron emission tomography and functional magnetic resonance imaging [14]. Numerous studies have demonstrated that low-frequency rTMS applied to the unaffected hemisphere of the brain can be effective in speech recovery [10]. Positive results have also been observed when high-frequency rTMS is applied to the affected hemisphere [10,15].Patients with aphasia face challenges in expressing their needs and desires. Some patients with aphasia understand their condition well, which can lead to severe depression. Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is a device that generates a magnetic field throughout the brain, producing short, intense waves [16]. Based on the principle of electromagnetic induction, TMS creates a rapidly changing magnetic pulse that penetrates the scalp and skull, reaching the cortex. The magnetic pulse, in turn, induces action potentials in cortical neurons [17]. Rhythmic TMS induces cortical depolarization and promotes neuroplastic changes in the brain. While TMS is a safe treatment method, rTMS may occasionally trigger seizures. It should be used cautiously in patients with focal brain damage, neurodegenerative diseases, electronic implants, cardiac pacemakers, or those taking seizure threshold-lowering medications such as antidepressants [16].
2. Materials and Methods
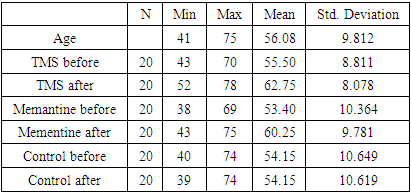
- The study included 60 patients with motor aphasia that developed after ischemic stroke. The patients’ demographic characteristics and medical histories were reviewed. The study involved 24 female and 36 male patients aged 40-75 who had experienced ischemic stroke in the middle cerebral artery territory. All patients were in the early or late recovery phases of stroke. Patients with contraindications to TMS, left-handed individuals, and those in the acute or residual stages of stroke were excluded from the study.The Western Aphasia Battery (WAB) scale, widely used to assess aphasia severity, was employed. This scale includes eight subtests with a total score of 100, evaluating speech, fluency, auditory comprehension, reading, writing, and apraxia.Patients were assigned random numbers through a computer program and divided into three groups: TMS-treated (20 patients), pharmacological treatment (20 patients), and control (20 patients).In the first group (n=20), rTMS was applied for 10 days along the precentral gyrus of the right hemisphere. The Broca area was identified using a neuronavigation protocol. TMS parameters were set as follows: duration – 30 minutes, frequency – 1 Hz, pulse count – 600, stimulation-to-pause ratio – 30:5 seconds, and motor threshold determined using the "5" rule. The resting motor threshold potential was identified in each patient’s right primary motor area (gr. precentralis). In the second group (n=20), the widely used drug Memantine (10 mg) was prescribed according to the following regimen: 5 mg in the morning for 7 days, followed by 10 mg in the morning for 7 days, and then 15 mg in the morning for 45 days. The control group (n=20) received TMS at 10% of the resting motor threshold potential between the cerebral hemispheres (vertex).
|
3. Results
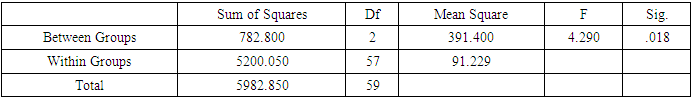
- ANOVA tests revealed significant differences among groups. Paired t-tests showed the following results: Memantine (6.29; 95% CI, 4.56 to 9.14; p<0.001), TMS (7.08; 95% CI, 5.1 to 9.4; p<0.001), with the post-treatment mean scores for these groups significantly differing from the control group (95%, -2.72 to 2.72; p>1) (Table 2).
|
|
|
4. Discussion
- The findings of this study demonstrate the efficacy of both Memantine and TMS in improving motor aphasia outcomes in post-stroke patients. The significant improvement observed in the TMS group suggests that this neuromodulation intervention may have a slightly greater therapeutic effect than Memantine. These results align with previous research highlighting TMS's role in promoting neuroplasticity and cortical reorganization post-stroke [6,9].The Memantine group showed substantial improvements in motor aphasia, supporting the role of pharmacological treatment in recovery. Memantine’s effect on preventing excessive calcium influx and promoting neuronal survival likely contributed to these outcomes, consistent with findings from earlier studies [10,15].Interestingly, the TMS group demonstrated a statistically significant difference compared to the control group, whereas the Memantine group’s difference, though clinically meaningful, did not reach statistical significance. This may be attributed to the shorter duration of TMS therapy or differences in individual responses to interventions. Further research is warranted to explore the long-term effects of these treatments and the potential benefits of combining pharmacological interventions with rTMS.The study underscores the importance of tailored rehabilitation strategies for post-stroke aphasia patients. Future studies could investigate combining Memantine and TMS to assess synergistic effects on speech recovery and functional outcomes.
5. Conclusions
- This study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of Memantine and TMS in treating post-stroke motor aphasia. Results demonstrated that both Memantine and TMS had significantly better therapeutic effects than placebo. Furthermore, TMS showed a statistically significant advantage over Memantine. These findings align with previous studies. Low-frequency TMS applied to the Broca area may stimulate the corresponding center in the contralateral hemisphere, facilitating alternative neuronal synapse formation.Memantine, a non-competitive NMDA receptor antagonist, prevents calcium ion influx into cells, thereby protecting them from damage. However, TMS, with its ability to enhance interhemispheric connectivity and cortical reorganization, proved more effective in this study.Future studies should include patients in the residual stage of stroke to further validate the effectiveness of Memantine. The Memantine-treated group showed more significant recovery compared to the control group. Ten sessions of low-frequency TMS significantly improved aphasia within two months. Our findings suggest that Memantine enhances neuroplasticity in the central nervous system.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML