-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2025; 15(1): 47-55
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20251501.09
Received: Dec. 20, 2024; Accepted: Jan. 12, 2025; Published: Jan. 16, 2025

Improvement of Methods of Prevention of Infection Generalization in Long-Term Non-Healing Wounds
Umarov Bakhtiyor Yatgarovich, Khamdamov Bakhtiyor Zarifovich
Bukhara State Medical Institute named after Abu Ali Ibn Sina, Uzbekistan
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

The use of our developed methods for predicting and preventing infection generalization in patients with NON-HEALING WOUNDS allowed us to reduce the incidence of this formidable complication by 2.6 times. This, in turn, resulted in a 1.6-fold reduction in the length of stay of patients in the clinic, and a 2.3-fold reduction in the duration of outpatient treatment.
Keywords: Wound, Infection, Prevention
Cite this paper: Umarov Bakhtiyor Yatgarovich, Khamdamov Bakhtiyor Zarifovich, Improvement of Methods of Prevention of Infection Generalization in Long-Term Non-Healing Wounds, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 15 No. 1, 2025, pp. 47-55. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20251501.09.
1. Introduction
- Long-term wound healing contributes to the cumulation of the number of such patients, which reached more than 40 million people worldwide 10 years ago. This type of spread of DNI was noted by P. Driscoll [1,3,18,19] as a "silent epidemic". However, after 5 years, there were reports of the number of patients with DNI reaching 500 million [2,4,20]. Such an impressive figure leads to an increase in financial costs in the healthcare system [5,7,21,26,27]. In particular, M. Olsson et al. conducted a calculation and showed that in developed countries such costs make up to 3% of total healthcare costs. The physiological process of wound healing includes four stages: hemostasis, inflammation, proliferation and scarring, the coordinated work of which ensures proper healing [6,8,28,29]. However, when wounds do not undergo this organized process, soft tissue healing slows down, and this ultimately leads to the development of DNI with such common signs as exudation, re-infection, tissue necrosis, defective re-epithelialization, and decreased angiogenesis. All this served as a prerequisite for more in-depth studies of the mechanisms of the body's immune response as a guarantee of the possibility of improving the results of treatment of patients with DNI.To date, the immunological aspects of DNI have been studied in certain nosological forms, in particular, in diabetic foot syndrome. Along with this, there is information regarding DNI in patients with concomitant diseases in the form of vascular diseases (both with arterial and venous lesions), obesity, and HIV infection [9,11,13,15,22,30].Conclusions were made about the direct influence of the above-mentioned concomitant diseases on all stages of wound regeneration. Thus, according to M. Bagheri et al., NWRD in patients with diabetes mellitus are associated with a highly proinflammatory profile caused by excessive expression of inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α, and decreased production of mediators that promote healing, including IL-10 and TGF-β. As stated by P.M. Seraphim et al., this leads to polarization of macrophages towards the M1 phenotype, activation and degranulation of CD8+ T cells, which leads to tissue necrosis.In non-healing wounds, certain factors are disrupted, which is partially responsible for the pathogenesis of injury. Mice deficient in IL-36 receptor antagonists exhibited impaired wound healing due to overproduction of IL-36γ, TGF-β, and CXCL1, excessive neutrophil and macrophage infiltration, and excessive granulation tissue formation [2,4,6,8,23,25]. Furthermore, the chemokine receptor CCR4 negatively affects chronic wounds induced by diabetes. Diabetic mice depleted of CCR4 exhibited decreased expression of wound healing-promoting cytokines such as IL-6, IL-12, IL-1β, TNF-α, and IL-10 [10,12,14,16,17,24]. During normal wound healing, cells in the injured area such as fibroblasts, keratinocytes and immune cells are induced by local mediators to secrete matrix metalloproteinase. Such mediators include various cytokines and growth factors involved in wound healing such as TGF-β, VEGF, EGF, interleukins and interferons. Matrix metalloproteinase is normally required in small amounts and is responsible for proper epithelialization and proliferation. However, their dysregulation leads to impaired epithelialization and is closely associated with DWRD. The process of complete DWRD regeneration does not occur when the immune system fails to continue the normal repair process, resulting in the prolonged presence of neutrophils and pro-inflammatory macrophages in the injured skin, which contributes to inflammation, tissue fibrosis and poor vascularization. Research in this area is ongoing, however, today it is necessary to clarify the causes of the development of generalization of the inflammatory process when using well-known methods of treating NCDs and to determine the role of changes in the immune status. This would allow us to develop effective methods of immunodiagnostics, as well as prediction and prevention of generalization of infection, which ultimately, in our opinion, can improve the treatment results for patients with NCDs.Purpose of the study. Development and comparative evaluation of the effectiveness of methods for preventing generalization of infection in long-term non-healing wounds.
2. Material and Methods
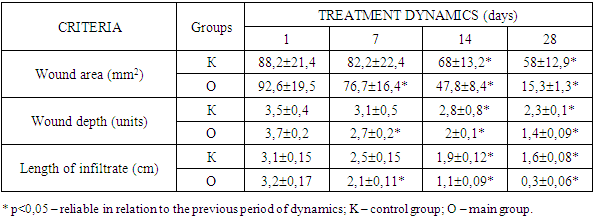
- The development and evaluation of the effectiveness of methods for preventing generalization of infection was carried out in patients with NCDs of the main group. At the same time, the use of the method we developed for predicting the probability of generalization of infection showed that out of 85 patients in the main group, 32 (37.6%) patients had a pronounced probability of developing generalization of infection. Among them, in 15.3% of cases (13 patients), such patients were represented by neutrophic ulcers of diabetic foot syndrome, in 11.8% of cases (10 patients) - bedsores and in 10.6% of cases (9 patients) - trophic ulcers against the background of varicose veins of the lower extremities.In 29 (34.1%) patients with DFU, the probability of developing generalization of the infection was insignificant. Among them, mainly (17.6% of cases - 15 patients) they were represented by bedsores. In the remaining 10.6% and 5.9% of cases, these were patients with trophic ulcers against the background of diabetic foot syndrome (9 patients) and varicose veins of the lower extremities (5 patients).Only in 24 (28.2%) patients of the main group, the probability of developing generalization of the infection was absent. Among them, 11 patients (12.9%) had bedsores, 5 patients (5.9%) had trophic ulcers of diabetic foot syndrome, and 8 patients (9.4%) had varicose veins of the legs.The complex of treatment and preventive measures in patients of the main group was based on the pathogenetic approach to influencing the course of the inflammatory process in the wound and preventing infection generalization.The entire complex of developed measures was used against the background of regular wound care, the use of medications (platelet antiplatelet agents, phlebotonic drugs, peripheral vasodilators, metabolic drugs, immunotropic and antibacterial agents).Surgical treatment of the wound (or debridement) was performed in the presence of a large amount of necrotic tissue and fibrin. Further tactics of local treatment of DNP depended on the degree of prognostic probability of infection generalization. In the absence of a prognostic probability of infection generalization, the method of choice for local wound treatment was the use of controlled negative pressure dressings (vacuum therapy).To conduct sessions of controlled negative pressure exposure to the wound, we used polyurethane foam dressings with 400-600 micron micropores. This ensured uniform distribution of controlled negative pressure over the entire surface of the DNP. This treatment option is known to be optimal in terms of generating both physical and biological reactions in the wound.Each session of controlled negative pressure was conducted in a vacuum mode of 0.1-0.15 atm. (76-115 mm Hg) for 9-10 minutes. Among the side effects of using this mode of controlled negative pressure exposure to the wound, a feeling of moderate pain in the wound area was noted by patients, which did not require the use of any analgesic medications.We conducted this technique in patients with no prognostic probability of infection generalization in DNP for an average of 5.5 ± 0.5 days, which allowed us to subsequently use surgical methods of wound closure. This regime and duration of sessions of exposure to controlled negative pressure on the wound allowed to control the humidity and amount of exudate in the wound.In case of patients with an insignificant prognostic probability of infection generalization, the regime of sessions using controlled negative pressure on the wound was extended on average to 8.4±0.8 days with the duration of each session up to 13-15 minutes. This allowed to minimize the moist environment of the wound and, accordingly, the amount of exudation, and thereby reduce the likelihood of its entry into the systemic bloodstream.However, in case of detection of a pronounced prognostic probability of infection generalization in patients with DNP, sessions using controlled negative pressure on the wound were insufficient. Despite the extension of sessions of vacuum therapy on average to 13.6±2.1 days, such patients, after each session of vacuum therapy, also received laser photodynamic therapy (LPDT) according to the method of B.Z. Khamdamov.For this purpose, after completion of the next vacuum therapy session, a photosensitizer was applied - 0.05% solution of mytilene blue belonging to the phenothiazine group with maximum absorption λ max (nm) - 668 nm with an exposure of 5 minutes. Then, after washing off the photosensitizer from the wound surface, the wound surface was illuminated with laser radiation using the ALT-Vostok device, model 03, corresponding to the technical conditions TSh 64-15302652-002:2010. The distance from the end of the light guide to the wound surface was 0.5-5.0 cm in the absence of thermal discomfort in the patient. The average wound irradiation time was 5.3 ± 0.5 minutes. For large wound areas, polypositional irradiation of wound surfaces was used by smoothly moving the terminal over the entire wound surface. The use of LFDT after each vacuum therapy session allowed to enhance the therapeutic effect on the wound not only by stimulating the growth of granulation tissue, but also by accelerating epithelialization due to maximum demarcation of the pathological focus.The general preventive effect on the possible probability of infection generalization in patients with DNR was carried out by using Neupogen® and Infliximab according to the scheme we developed.Neupogen® was used depending on the degree of prognostic probability of infection generalization in patients with DNR. Thus, patients with an insignificant probability of infection generalization were given Neupogen® by subcutaneous administration at a dose of 0.1-0.4 million U (1-4 μg) / kg per day once. In the presence of positive dynamics of changes in the prognostic probability of infection generalization on the 7th day of treatment, a repeated injection was used at the same dose. In patients with a high prognostic probability of infection generalization, Neupogen® was administered at a dose of 1.0 million IU (10 μg)/kg/day (maximum daily dose), with subsequent repeated administration on days 3 and 7 of the treatment. When the prognostic probability of infection generalization decreased to insignificant, the dose of Neupogen® was reduced to 0.1-0.4 million IU (1-4 μg)/kg to two injections every 72 hours. In the absence of a prognostic probability of infection generalization, Neupogen® injections were discontinued.Neupogen® is known to be a hematopoietic growth factor and a highly purified non-glycosylated protein consisting of 175 amino acids. It regulates the formation of functionally active neutrophils and their release into the blood from the bone marrow. The effectiveness of its use is due to a significant increase in the number of active neutrophils in the peripheral blood already in the first 24 hours after administration with a slight increase in the number of monocytes. Patients receiving Neupogen® require lower doses of antibiotics.Given the increased expression of TNF-α in patients with generalized infection, which in the long term can lead to endothelial dysfunction and progression of multiple organ failure, we also used Infliximab, known as a specific antibody against TNF-α, in patients with a high probability of sepsis. The drug was prescribed at a dose of 5 mg / kg on the 1st, 7th and 14th day of treatment. With an insignificant probability of developing generalized infection in patients with DNR, Infliximab was used at the same dose on the 1st and 7th days of treatment.Thus, prevention of generalized infection in patients with DNR includes a differentiated approach to local (vacuum therapy and LFDT) as well as general effects on the course of both the wound and inflammatory process, provides for the use of pathogenetically substantiated methods for correcting local and general immunity disorders. Results and discussion. The development and evaluation of the effectiveness of methods for preventing infection generalization were carried out in patients with DUPID of the main group. At the same time, the application of the method developed by us for predicting the probability of infection generalization showed that out of 85 patients in the main group, 32 (37.6%) patients had a pronounced probability of developing infection generalization. Among them, in 15.3% of cases (13 patients), such patients were represented by neutrophic ulcers of diabetic foot syndrome, in 11.8% of cases (10 patients) - bedsores and in 10.6% of cases (9 patients) - trophic ulcers against the background of varicose veins of the lower extremities. In 29 (34.1%) patients with DUPID, the probability of developing infection generalization was insignificant. Among them, they were mainly (17.6% of cases - 15 patients) represented by bedsores. In the remaining 10.6% and 5.9% of cases, these were patients with trophic ulcers against the background of diabetic foot syndrome (9 patients) and varicose veins of the lower extremities (5 patients).Only 24 (28.2%) patients of the main group had no probability of developing generalized infection. Among them, 11 (12.9%) patients had bedsores, 5 (5.9%) patients with trophic ulcers of diabetic foot syndrome and 8 (9.4%) varicose veins of the legs.The complex of therapeutic and preventive measures in patients of the main group was based on the pathogenetic approach in influencing the course of the inflammatory process in the wound and preventing generalization of infection.The entire complex of developed measures was used against the background of regular wound care, the use of medications (platelet disaggregants, phlebotonic drugs, peripheral vasodilators, metabolic drugs, immunotropic and antibacterial agents). Surgical treatment of the wound (or debridement) was performed in the presence of a large amount of necrotic tissue and fibrin. Further tactics of local treatment of DNP depended on the degree of prognostic probability of infection generalization.In the absence of prognostic probability of infection generalization, the method of choice in local treatment of wounds was the use of dressings with the effect of controlled negative pressure (vacuum therapy). To conduct sessions of exposure to controlled negative pressure on the wound, we used polyurethane foam dressings with micropores of 400-600 microns. This ensured uniform distribution of controlled negative pressure over the entire surface of the DNP. This treatment option is known to be optimal in terms of generating both physical and biological reactions in the wound.Each session of controlled negative pressure was carried out in a vacuum mode of 0.1-0.15 atm. (76-115 mm Hg) for 9-10 minutes. Among the side effects of using this mode of exposure to the wound of controlled negative pressure, a feeling of moderate pain in the wound area was noted by patients, which did not require the use of any analgesic medications. This technique in patients with no prognostic probability of infection generalization in DNP was carried out by us for an average of 5.5 ± 0.5 days, which allowed us to subsequently use surgical methods of wound closure. This mode and duration of sessions of exposure to DNP of controlled negative pressure allowed us to ensure control over the humidity and amount of exudate in the wound. In the case of an insignificant prognostic probability of infection generalization in patients, the mode of application of sessions using controlled negative pressure on the wound was extended to an average of 8.4 ± 0.8 days with the duration of each session up to 13-15 minutes. This allowed us to minimize the moist environment of the wound and, accordingly, the amount of exudation, and thereby reduce the likelihood of it entering the systemic bloodstream. However, in the case of detection of a pronounced prognostic probability of infection generalization in patients with DNP, sessions using controlled negative pressure on the wound were not sufficient. Despite the extension of vacuum therapy sessions to an average of 13.6±2.1 days, such patients were also given laser photodynamic therapy (LPDT) after each vacuum therapy session using the B.Z. Khamdamov method.For this purpose, after the completion of the next vacuum therapy session, a photosensitizer was applied - a 0.05% solution of mytilene blue belonging to the phenothiazine group with an absorption maximum λ max (nm) - 668 nm with an exposure of 5 minutes. Then, after washing off the photosensitizer from the wound surface, the wound surface was illuminated with laser radiation using the ALT-Vostok model 03 device, which complies with the technical specifications TSh 64-15302652-002:2010 (Figure 1). The distance from the end of the light guide to the wound surface was 0.5-5.0 cm in the absence of thermal discomfort in the patient.
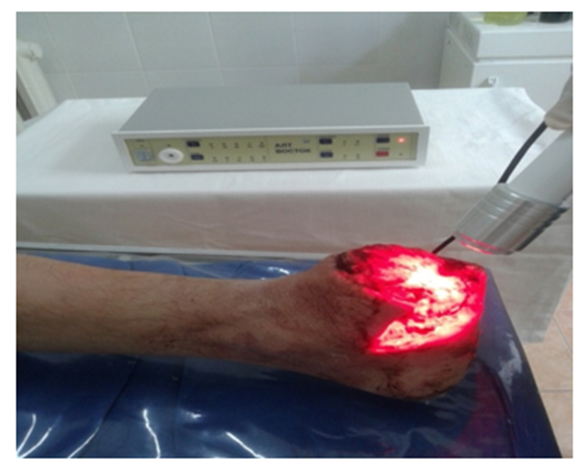 | Figure 1. General view of the application of laser photodynamic therapy in the treatment of long-term non-healing wounds |
|
|
3. Conclusions
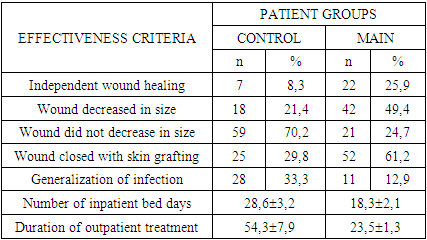
- 1. The use of differentiated approaches to wound treatment depending on the prognostic probability of infection generalization allowed us to achieve 2.3 times more cases of wound size reduction. In general, we noted such a treatment result in 35.5% (60 patients) of cases.2. The use of the methods we developed for predicting and preventing infection generalization in patients with DNR allowed us to reduce the incidence of this formidable complication by 2.6 times. This, in turn, was reflected in a reduction in the length of stay of patients in the clinic by 1.6 times, and the duration of outpatient treatment - by 2.3 times.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML