-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2024; 14(12): 3392-3393
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20241412.66
Received: Dec. 3, 2024; Accepted: Dec. 20, 2024; Published: Dec. 31, 2024

Laparoscopic Adenomectomy: Postoperative Complication
Akhmedov M. S.1, Maksumov M. F.1, Kholikov S. R.2
1North-Western State Medical University named after I.I. Mechnikov, Saint-Petersburg, Russian Federation
2Mari State University, Yoshkar-Ola, Republic of Mari El
Correspondence to: Maksumov M. F., North-Western State Medical University named after I.I. Mechnikov, Saint-Petersburg, Russian Federation.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Laparoscopic adenomectomy has gained prominence as a minimally invasive approach for removing benign adenomas. While the technique offers reduced recovery time and minimal scarring, certain postoperative complications remain a concern. This review evaluate the spectrum of complications, including hemorrhage, infection, injuries, to adjacent structure, recurrence, and wound healing, issues. Through a detailed analysis of available literature, the review aims to provide on overview of risk factors, clinical symptoms, and recommendation for minimizing comlplication in laparoscopic adenomectomy.
Keywords: Laparoscopic adenomectomy, Minimally invasive surgery, Postoperative complications, Surgical outcomes, Adenoma recurrence, Hemorrhage
Cite this paper: Akhmedov M. S., Maksumov M. F., Kholikov S. R., Laparoscopic Adenomectomy: Postoperative Complication, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 14 No. 12, 2024, pp. 3392-3393. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20241412.66.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Laparoscopic adenomectomy has become the standard surgical approach for the removal of benign adenomas, thanks to advancement in minimally invasive techniques. The procedure offers several benefits, including shorter hospital days, faster recovery, and reduced postoperative pain compared to open surgeries. However complications such as hemorrhage, infection, and recurrence continue to challenge surgeon. This review synthesizes findings from the literature to assess the incidence, cause, and management of complications in laparoscopic adenomectomy, aiming to inform clinical practice and future research directions.
2. Materials and Methods
- This review is based on an extensive literature search conducted using databases such as PubMed, Scopus, and google scholar. The search terms included “laparoscopic adenomectomy”, “postoperative complication”, and “minimally invasive surgery”. Studies published between 2015 and 2023 were included, focusing on clinical outcomes, complications, and management strategies. Data from case series, randomized controlled trials, and meta-analysis were evaluated. Inclusion criteria required studies to report complications following laparoscopic adenomectomy explicitly. Articles with limited sample sizes or without clear documentation of postoperative outcomes were excluded.
3. Result and Discussion
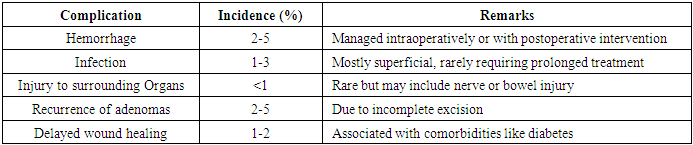
- 1. The prevalence of complications following surgeryAccording to studies, laparoscopic adenomectomy has an overall complication risk of 5% to 15% [1,2]. Complication are categorized into somatic (infection and systemic responses) and surgical (technical failures or site-specific injuries).
|
4. Factors Influencing Complications
- Several factors influence the occurrence of complications after laparoscopic adenomectomy. These include the patient’s age, comorbidities, adenoma size and location, and, surgeon experience. Advanced techniques, such as the use of robotic assistance and improved imaging modalities, have been shown to reduce complication rates.
5. Discussion
- The low incidence of complications in laparoscopic adenomectomy demonstrates its safety and efficacy as a minimally invasive procedure. However, the management of complications such as hemorrhage and infection requires robust intraoperative and postoperative strategies. Surgeon training and patient selection are critical for optimizing outcomes. Emerging techniques, including robotic surgery and enhanced imaging guidance, offer promise for further minimizing complications [4,6,9].
6. Future Directions
- To further improve outcomes, research should focus on developing standardized protocols for managing complications and refining surgical techniques. Studies exploring patient-specific risk factors and the role of enhanced recovery pathways in laparoscopic adenomectomy are needed.
7. Conclusions
- Laparoscopic adenomectomy remains a safe and effective technique for managing benign adenomas, with a low overall complication rate. While complications such as hemorrhage, infection, and recurrence are rare, careful patient selection, surgeon expertise, and adherence to advanced surgical techniques are essential for minimizing risks. Continued research and technological advancements hold promise for further improving patient outcomes in this field.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML