Rakhmanov Kosim Erdanovich1, Khamdamov Olim Dilmurodovich1, Davlatov Salim Sulaymonovich2
1Samarkand State Medical University, Samarkand, Republic of Uzbekistan
2Bukhara State Medical Institute, Bukhara, Republic of Uzbekistan
Correspondence to: Rakhmanov Kosim Erdanovich, Samarkand State Medical University, Samarkand, Republic of Uzbekistan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Abstract
Relevance. Lung echinococcosis is a parasitic disease caused by the larval stages of the parasite Echinococcus granulosus. This disease remains a significant medical and social problem, especially in regions endemic for echinococcosis. Pulmonary cysts are often combined with cysts of other organs, such as the liver, which complicates diagnosis and treatment. The aim of this study is to evaluate the effectiveness of modern surgical approaches, including the use of ultrasound dissector SONOCA 300 and the author's technique of residual cavity elimination, to improve the results of treatment of patients with pulmonary and pleural echinococcosis. Material and methods of research. The results of treatment of 207 patients with pulmonary echinococcosis admitted to the surgical department of the multidisciplinary clinic of Samarkand State Medical University in the period from 2010 to 2023 were included in the basis of the study. The patients were distributed into two groups. The comparison group included 98 patients operated on from 2010 to 2016, who underwent surgical interventions using traditional methods after standard diagnostics. Since 2017, surgical interventions for pulmonary echinococcosis were improved using modern technologies. From 2017 to 2023, 109 patients who were included in the main group were operated on. The results of the study and their discussion. Due to introduction in practice of the above mentioned innovations in lung echinococcosis surgery in the main group of patients it was possible to reduce patients' stay in hospital, in the postoperative period body temperature in patients with complicated forms of echinococcosis normalised earlier. Due to reduction of indications for semi-closed methods of capitonage of residual cavity the number of patients discharged for outpatient treatment with drains decreased from 28,8% to 4,7%. Conclusions. Introduction of modern technologies into the surgical practice of pulmonary echinococcosis and liquidation of the residual cavity by the modified method allowed to improve the quality of rendered care by reducing the rate of immediate postoperative complications from 13.5% to 2.4% (p=0.027 according to the χ2 criterion) and recurrence of the disease from 9.3% to 1.4% (p=0.031 according to the χ2 criterion).
Keywords:
Pulmonary echinococcosis, Surgical treatment
Cite this paper: Rakhmanov Kosim Erdanovich, Khamdamov Olim Dilmurodovich, Davlatov Salim Sulaymonovich, Improvement of Surgical Treatment of Pulmonary Echinococcosis, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 14 No. 12, 2024, pp. 3334-3338. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20241412.54.
1. Relevance
Lung echinococcosis is a parasitic disease caused by the larval stages of the parasite Echinococcus granulosus [2,5,10]. This disease remains a significant medical and social problem, especially in regions endemic for echinococcosis. Pulmonary cysts are often combined with cysts of other organs, such as the liver, which complicates diagnosis and treatment [3,8]. The main objectives of surgical treatment of pulmonary echinococcosis are radical removal of the cyst, prevention of recurrence and elimination of the residual cavity [4,11]. However, classical methods, such as the Bobrov-Spasokukotsky, Vishnevsky and Vakhidov capitonage methods, do not always provide proper results due to the high incidence of complications such as infection of the residual cavity, formation of fistulas and recurrence of the disease [1,5,9].Modern surgical technologies, including the use of cavitation ultrasonic dissectors, can significantly improve the quality of treatment [6,7]. Ultrasound tissue disintegration ensures high precision of surgery, minimising traumatisation of surrounding structures, and modified methods of residual cavity elimination reduce the risk of postoperative complications.
2. The Aim of This Study
To evaluate the effectiveness of modern surgical approaches, including the use of ultrasound dissector SONOCA 300 and the author's technique of residual cavity elimination, to improve the results of treatment of patients with pulmonary and pleural echinococcosis.
3. Material and Methods of Research
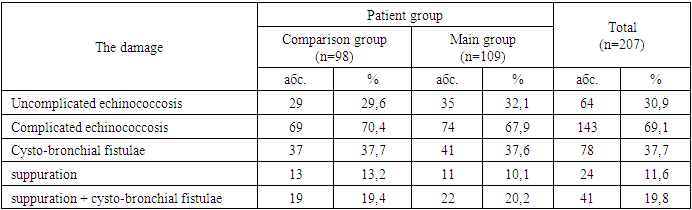
The results of treatment of 207 patients with pulmonary echinococcosis admitted to the surgical department of the multidisciplinary clinic of Samarkand State Medical University in the period from 2010 to 2023 were included in the basis of the study. The patients were distributed into two groups. The comparison group included 98 patients operated on from 2010 to 2016, who underwent surgical interventions using traditional methods after standard diagnostics. Since 2017, surgical interventions for pulmonary echinococcosis were improved using modern technologies. From 2017 to 2023, 109 patients who were included in the main group were operated on.Of 207 patients with pulmonary echinococcosis, 199 (96.1%) patients had echinococcosis detected for the first time and 8 (3.9%) patients had recurrent echinococcosis. In all patients with recurrent pulmonary echinococcosis, the recurrence was primary. All patients in the anamnesis underwent one operation in other hospitals.Analysing the data on localisation of echinococcal cysts in pulmonary echinococcosis, a total of 237 cysts were found in different segments. We noted a more frequent lesion of the right lung in 113 (54,6%) patients, of which 86 (76,1%) patients had cysts in the lower lobe. Isolated lesion of the left lung was in 66 (31,9%) patients. In 28 (13.5%) patients the echinococcosis lesion was in both lungs.The localisation of lung cysts was based on the division of lungs into segments. It should be emphasised that echinococcal cysts were most often localised in the lower lobes of the VII - X lung segments, which made 136 (65.7%) cases.The majority of patients were admitted to the hospital in a planned procedure. Therefore, the structure of lesions was dominated by patients with I and II clinical stage of parasite viability according to Melnikov's classification, which amounted to 191 (92,3%) people. In the preoperative period it was possible to determine complicated cysts in 59 (28,5%) cases. The structure of complications was dominated by suppuration of echinococcal fluid, which was stated in 27 (45.8%) patients. During the operation in 143 (69.1%) cases cystobronchial fistulas were detected (Table 1).Table 1. Distribution of patients with pulmonary echinococcosis by type of complications
 |
| |
|
All patients admitted with the diagnosis of pulmonary echinococcosis underwent a set of clinical, laboratory and instrumental investigations.Among 98 patients of the comparison group 111 surgical interventions were performed (13 patients with both lungs affected).After achieving adequate exposure, open echinococcectomy with puncture and opening of the cyst was applied to the patients of the comparison group. Closed, ideal echinococcectomy was performed through wide thoracotomy access and was applied only to 5 (4.5% of 111 patients of the comparison group) patients with peripheral location of the echinococcal cyst. Of these, 2 patients underwent atypical lung resection and 3 patients underwent enucleation of the cyst with dense fibrous capsule. A total of 5 cysts were removed by closed method. Out of 111 patients 136 cysts were removed.The next stage was the choice of residual cavity elimination. 131 cysts (96.3% out of 136) were removed by the open method. The essential point of the technique of organ-preserving surgical intervention is the elimination of the residual cavity. In patients of the comparison group, the Bobrov-Spasokukotsky, Vishnevsky and Vakhidov capitonage methods were most often used.In 33 (24.3%) cases of the comparison group, semi-closed echinocolectomy was performed. The indications for residual cavity elimination by semi-closed method were as follows: 1) regid residual cavity in the lung with the presence of bronchial fistula and signs of suppuration or bronchial breakthrough; 2) residual cavity with a diameter greater than 15 cm with perifocal inflammation and infiltration; 3) prevention of the development of postoperative bronchopleural fistula if it is impossible to suture it at the bottom of the residual cavity. In the postoperative period, the drainage tube was removed from the residual cavity not immediately, but in stages, partially after 14 days. We attribute this to gradual healing and closure of the residual cavity in the lung.Among 109 patients of the main group 127 surgical interventions were performed (18 patients with both lungs affected). Among 127 patients of the main group, a total of 166 cysts were removed. Atypical lung resection, perfect echinococcectomy and total pericystectomy were performed using cavitation ultrasonic dissector aspirator (SONOCA 300) (Fig. 1) in 3, 7 and 22 patients respectively, total 34 cysts.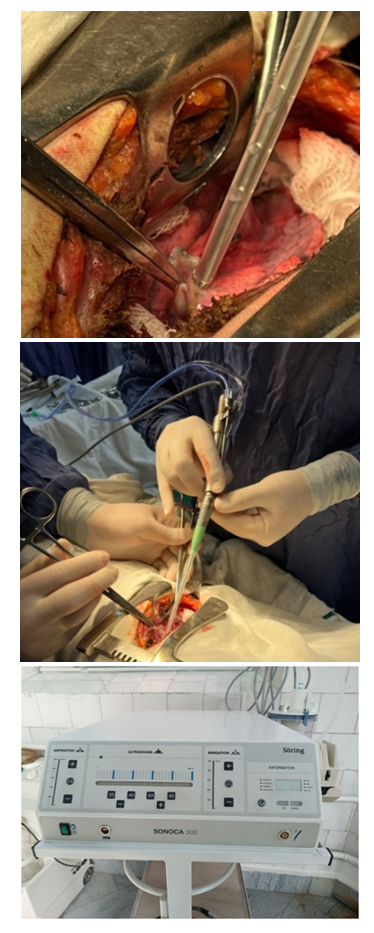 | Figure 1. Total pericystectomy with ultrasound-guided dissector aspirator (CUSA) - SONOCA 300 for echinococcosis of the lung |
Atypical lung resection and perfect echinocolectomy with excision of the cyst with fibrous capsule was performed in patients with marginal location of the cyst. Total pericystectomy was performed in calcified, thickened complicated cysts.After open echinococcectomy in the main group of patients in 28.9% of cases the residual cavity was eliminated by V. Vakhidov's method, in 9.0% of cases echinococcectomy according to Vishnevsky was performed. In the main group of patients, when cystobronchial fistulas were detected, the principle of not eliminating cystobronchial fistulas was followed. Like the authors I.Y. Deineka, 1968 and A. Aytos et al., 1977 we consider that bronchial fistulas serve as a natural drainage for the residual cavity, and therefore it is inexpedient to suture them [12]. Therefore, in the main group of patients the semi-closed method of capitonage was reduced from 24.3% to 3.6%. Thus, ascending infection of the residual cavity was prevented.In addition, in comparison group patients after conventional suturing of the residual cavity we often observed inadequate sealing of the residual cavity, therefore, we have developed a modified method of capitonage of the residual cavity.The method was carried out as follows: after treatment of the residual cavity, it was liquidated with insertion sutures. Further, a flap on a pedicle from the parietal pleura was cut out and staggered and fixed to the suture line of the eliminated residual cavity, thus achieving adequate germitisation and preventing bronchopleural communication (Fig. 2).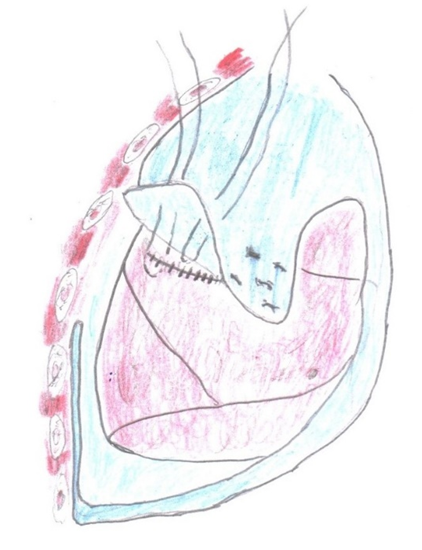 | Figure 2. Our proposed method of eliminating residual cavity after pulmonary echinococcectomy |
Surgical tactics in multiple bilateral pulmonary echinococcosis was determined as follows. In the presence of complications, first of all, surgical intervention was performed on the side of the complicated process. In the absence of complications we always operated on the side where there were cysts of large size.In the most severe category of patients with multiple bilateral lung lesions, the lung with a greater number of cysts was operated initially. Tense (large and giant) cysts with signs of atelectasis or lung collapse were operated as a priority. Surgical intervention on the opposite side was performed in 2-3 months depending on the general condition, age, and postoperative course.In 1 (0.8% of 127 patients of the main group) patient with a suppurative cyst of the middle lobe of the right lung (V segment) of intraparenchymatous location and perifocal inflammation after intraoperative consultation lobectomy was performed in order to prevent arterial bleeding during the operation and threatening complications in the early postoperative period, such as long non-healing residual cavity, which may cause pleural empyema.The operation was completed by drainage of the pleural cavity, as a rule, with one lower drain.In uncomplicated course, the drainage tube from the pleural cavity was removed in 3-5 days (on average in 4.1±0.05 days) after control radiography under the condition of complete decompression of the operated lung. In 6 patients with semi-closed capitonage method drainage tubes from the residual cavity were removed in average two weeks after the operation. This period was necessary for reliable obliteration of the pleural cavity around the intrapulmonary tube and the residual cavity itself.
4. The Results of the Study and Their Discussion
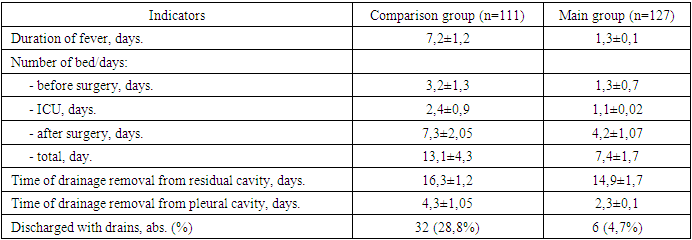
Due to introduction in practice of the above mentioned innovations in lung echinococcosis surgery in the main group of patients it was possible to reduce patients' stay in hospital, in the postoperative period body temperature in patients with complicated forms of echinococcosis normalised earlier. Due to reduction of indications for semi-closed methods of residual cavity capitonage the number of patients discharged for outpatient treatment with drains decreased from 28.8% to 4.7% (Table 2).Тable 2. Course of postoperative period in patients with pulmonary echinococcosis
 |
| |
|
Duration of operation plays an important role in improvement of immediate results of surgical treatment of patients with pulmonary echinococcosis. In patients of the main group in comparison with the control group it was possible to reduce the duration of intervention by 30 min. and accordingly its traumatism due to the use of minithoracotomy and simplification of the technique of elimination of ‘complex’ residual cavities by suturing with additional hermitisation with parietal pleura.The combination of tactical and technical aspects aimed at reducing the traumatic nature of surgical intervention and the introduction of the above-mentioned innovations contributed to the reduction of unsatisfactory immediate results. Due to the leakage of echinococcal fluid into the surrounding tissue, anaphylactic shock was observed in 2 patients of the comparison group during the operation. Intraoperative signs of anaphylactic shock in patients under general anaesthesia with the use of ventilation were: rash, decreased blood pressure, tachycardia. After intensive therapy of anaesthesiologists the patients were brought out of shock. In 5 (2.1%) patients there was infiltration of cyst contents into surrounding tissues, of which 4 (3.6%) patients of the comparison group. Postoperative pleurisy and wound infections did not occur.Intraoperative complications decreased from 7.2% to 1.6%, and complications in the early postoperative period from 13.5% to 2.4% (Table 3).Тable 3. Immediate results of surgical treatment of pulmonary echinococcosis
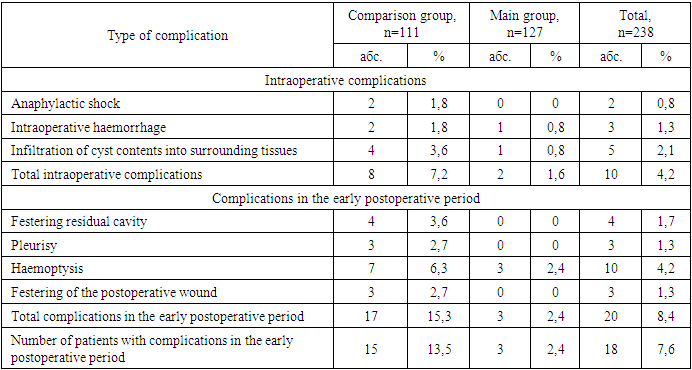 |
| |
|
The long-term results in 144 (69.6%) out of 207 operated patients for pulmonary echinococcosis were analysed. Of these, 75 (76.5% of the total number of 98 patients of the comparison group) patients from the comparison group and 69 (63.3% of the total number of 109 patients of the main group) patients from the main group. To evaluate the long-term results, the patients were subjected to a thorough questionnaire, outpatient and inpatient examination.One of the main indices characterising the effectiveness of surgical intervention in echinococcosis is the disease recurrence rate. When studying the nature of recurrence (true recurrence, residual cyst or reinvasion), we compared the localisation of the primary operated and re-detected cysts, the terms of recurrence, the peculiarities of previously used methods of surgical intervention, the number, size and complications of primary cysts.Out of 144 patients examined in distant terms, recurrence of echinococcosis was noted in 8 (5.5%) patients, including 7 (9.3%) cases in the comparison group and only 1 (1.4%) case in the main group.
5. Conclusions
The use of ultrasonic dissector aspirator SONOCA 300 makes it possible to use radical modern methods of surgical interventions in echinococcosis more widely, to perform them bloodlessly, with good final aero- and haemo- with minimal traumatisation of tissues in the area of impact with destruction and aspiration of peri-cystic parenchyma, which reduces to zero the probability of leaving germinal elements of echinococcal cyst in this area. Introduction of modern technologies into surgical practice of lung echinococcosis and liquidation of the residual cavity by the modified method allowed to improve the quality of rendered care due to reduction of the frequency of immediate postoperative complications from 13,5% to 2,4% (p=0,027 according to χ2 criterion) and recurrence of the disease from 9,3% to 1,4% (p=0,031 according to χ2 criterion).Information about the source of support in the form of grants, equipment, and drugs. The authors did not receive financial support from manufacturers of medicines and medical equipment.Conflicts of interest. The authors have no conflicts of interest.
References
| [1] | Abdurakhmanov D. S., Rakhmanov Q. E., Davlatov S. S. Surgical tactics in patients with liver echinococcosis // Electronic innovation bulletin. – 2021. – №. 4. – С. 15-19. |
| [2] | Alvi M. A. et al. Past and present of diagnosis of echinococcosis: A review (1999–2021) // Acta Tropica. – 2023. – Т. 243. – С. 106925. |
| [3] | Davlatov S. S. et al. The importance of morphological forms of echinococcal cysts on the frequency of recurrence of the disease // Journal of Humanities and Natural sciense. – 2024. – №. 11 [2]. – С. 26-30. |
| [4] | Gregoriadis G // In: Liposomes in Biological Systems // Eds. G. Gregoriadis, A. Allison - Chichester N.Y. Brisbane -Toronto. 19M). P. 25-86. |
| [5] | Mirkhodjaev I.A. The role of cytokines in the development and course of liver echinococcus // Journal: "Biology and Integrative Medicine", 2020, No. 2, p. 62-75. |
| [6] | Rakhmanov K. E., Davlatov S. S., Abduraxmanov D. Sh. Correction of albendazole disease after echinococcectomy of the liver // International Journal of Pharmaceutical Research (09752366). – 2020. – Т. 12. – №. 3. |
| [7] | Rakhmanov, K. E., Davlatov, S. S., & Abduraxmanov, D. Sh. (2020). Correction of albendazole disease after echinococcectomy of the liver. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Research, 13, 4044- 4049. doi:10.31838/ijpr/2020.13.01.596. |
| [8] | Shamsiyev A. et al. The role of chemotherapy in prophylaxis of the liver echinococcosis recurrence // European science review. – 2016. – №. 5-6. – С. 143-144. |
| [9] | Shamsiyev A. M. et al. Development of surgical treatment of echinococcosis of the liver (literature review) // Modern innovations: topical areas of scientific research. – 2017. – С. 45-49. |
| [10] | Shamsiyev A. M. et al. Development of surgical treatment of echinococcosis of the liver (literature review) // Modern innovations: current directions of scientific research. – 2017. – С. 45-49. |
| [11] | Zaki Z., Ali A. Immunity response of mice infected with laser irradiated protoscoleces of Echinococcus granulosus // Journal of Education and Science. – 2021. – Т. 30. – №. 3. – С. 34.0-44.0. |





 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML

