-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2024; 14(12): 3185-3190
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20241412.20
Received: Nov. 28, 2024; Accepted: Dec. 10, 2024; Published: Dec. 16, 2024

Improvement of the Method of Treatment of Patients with Acute Calculous Cholecystitis Complicated by Choledocholithiasis
Radjabov Anvar Islomovich, Safoev Bakodir Barnoevich, Boltaev Timur Shavkatovich
Bukhara State Medical Institute, Bukhara, Uzbekistan
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

This scientific article is devoted to improving the treatment results of patients with acute calculous cholecystitis complicated by choledocholithiasis by improving minimally invasive methods. The results of the study led to the development of a more effective method for treating patients with choledocholithiasis, which contributed to a decrease in intraoperative and postoperative complications, as well as a decrease in the duration of surgery and the length of stay of patients in the hospital. The article is based on a retrospective and prospective study of patients with acute calculous cholecystitis complicated by choledocholithiasis, who were treated in the general surgery department of the Central Hospital of the Medical Department of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of the Republic of Uzbekistan, for the period 2018-2023.
Keywords: Cholelithiasis, Choledocholithiasis, Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography, Endoscopic papillosphincterotomy
Cite this paper: Radjabov Anvar Islomovich, Safoev Bakodir Barnoevich, Boltaev Timur Shavkatovich, Improvement of the Method of Treatment of Patients with Acute Calculous Cholecystitis Complicated by Choledocholithiasis, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 14 No. 12, 2024, pp. 3185-3190. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20241412.20.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- All over the world, cholelithiasis is rightfully considered one of the most common diseases and is second only to atherosclerosis, leaving behind peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum. In this regard, the treatment of well-being disease, as cholelithiasis was figuratively called, is one of the most important problems of modern surgeons [3,7]. According to various authors, gallstone disease affects from 10 to 40% of the population of various ages. Mortality in different age groups in acute calculous cholecystitis in emergency surgery varies from 1 to 50% or more. In planned and delayed operations performed against the background of relieved acute inflammatory phenomena, after a comprehensive examination and preparation of patients, it does not exceed 0.5-1% [4,10]. In all countries of the world, the number of patients increases approximately twice over the past decade. The increase in the incidence of cholelithiasis is accompanied by an increase in the frequency of its complicated forms. In women, cholelithiasis occurs 2-6 times more often than in men. Large-scale epidemiological studies have established that the main risk factors for developing cholelithiasis are heredity, overweight, hyperlipidemia, and belonging to the female sexу. The incidence increases with age. About 2.5 million biliary tract surgeries (mainly cholecystectomy) are performed annually in the world [1,5]. This dissertation research serves to a certain extent to fulfill the tasks stipulated in the Decree of the President of the Republic of Uzbekistan No. UP-6110 of November 12, 2020 "On measures to introduce fundamentally new mechanisms in the activities of primary health care institutions and further improve the effectiveness of reforms in the health system", as well as in other regulatory documents, taken in this direction [2,6].In our country, among the large-scale measures implemented to improve the health care system, special attention is paid to early diagnosis of diseases, prevention and reduction of their complications. In this regard, 4 out of 7 priority areas indicated in the development strategy of the new Uzbekistan for 2022-2026 were noted: comprehensive measures aimed at implementing the program on public health, increasing the capacity of medical workers and developing the health system for 2022-2026 [8,9].Objective: to improve the results of treatment of patients with acute calculous cholecystitis complicated by choledocholithiasis by using minimally invasive methods of treatment with nitroglycerin and electroactivated aqueous solution-A (EAS-A).
2. Material and Research Methods
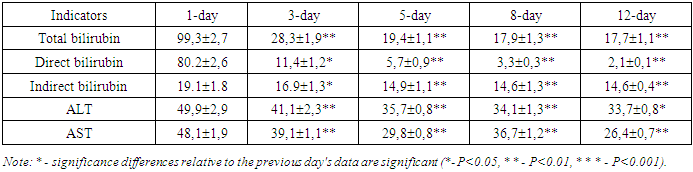
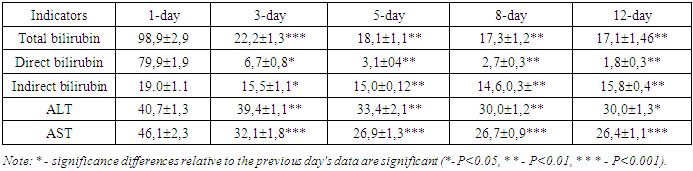
- The clinical characteristics of patients are given and are described the means used, clinical and laboratory, instrumental research methods and methods of treatment of patients are described.The work is based on the results of examination and treatment of patients with acute calculous cholecystitis complicated by choledocholithiasis who were treated in the General Surgery Department of the Central Hospital of the Medical Department of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of the Republic of Uzbekistan for the period 2018-2023.All 46 patients examined had acute calculous cholecystitis complicated by choledocholithiasis, in the treatment complex of which, in addition to the methods used, retrograde lavage of the lumen of the common bile duct with an electroactivated solution of EAS-A was used in order to accelerate the time of stopping the cholangitis process.All examined patients had their body temperature and respiratory rate urgently measured on the day of admission, objective liver examination (palpation, percussion), ultrasound, and, if necessary, multislice computed tomography or computed tomography of the abdominal organs were performed. Laboratory blood tests, conservative general strengthening and symptomatic therapy, and preparation for minimally invasive surgical intervention - endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography and endoscopic papillosphincterotomy with lithoextraction were performed. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography was performed if choledocholithiasis was suspected, to determine the nature of mechanical jaundice, and to study the anatomy of the ducts before surgery. If a blockage or narrowing of the ducts was detected, additional procedures were performed:1) insertion of a catheter to remove excess bile;2) removal ofgallstones from the bile ducts;3) sphincterotomy: a small incision in the area of the external opening of the common bile duct, which ensures the normal outflow of bile and the exit of small gallstones.Endoscopic papillosphincterotomy was performed in an operating room equipped with modern X-ray equipment used for additional monitoring.The procedure was performed using endoscopic equipment and a special instrument, which is a thin tube with a cutting tip.After completing the main manipulations, stones were removed according to the indications, and a biopsy was performed if necessary.To prepare an electroactivated aqueous solution, we used the Espero-1 NPF device, developed in 1998 by S. A. Alekhin, an employee of the Tashkent medical Institute. Bioelectroactivator type "Espero-1" is approved by the Pharmaceutical Committee of the Republic of Uzbekistan for obtaining drugs used in medical and clinical practice, and was widely used by employees of the V.Vakhidov Research Institute.All examined patients were admitted in satisfactory condition up to 30% and in moderate condition up to 70%. In most cases, patients were admitted with complaints of increased body temperature, general weakness and malaise, sweating, lack of appetite, pain in the right hypochondrium.During retrograde cholangiographic intervention, materials were taken from the bile duct contents for bacteriological examination. Antibiotic therapy was carried out taking into account the sensitivity of the identified microflora. The sensitivity of microorganisms was determined by the "disk-diffusion" method.The leukocyte intoxication index (LII) was also assessed separately - the ratio of neutrophilic leukocytes to lymphocytes, monocytes and eosinophils and the lymphocyte index (LI). The level of endogenous intoxication was assessed by the volume (degree) of medium molecular weight peptides (MMP), spectrometry at a wavelength of 210 nm. All patients had their total bilirubin, ALT and AST levels determined in the blood from the moment of admission. The bilirubin level in the blood serum was determined using the Van den Berg method.Mathematical processing of the obtained data results was carried out by methods of variation statistics. Using the method of variation statistics, the arithmetic mean (M), its error (±m), 95% confidence interval CI, Student's criterion (t) at different levels of significance (P) were determined. Results were considered reliable at P<0.05.
3. Results and Their Discussions
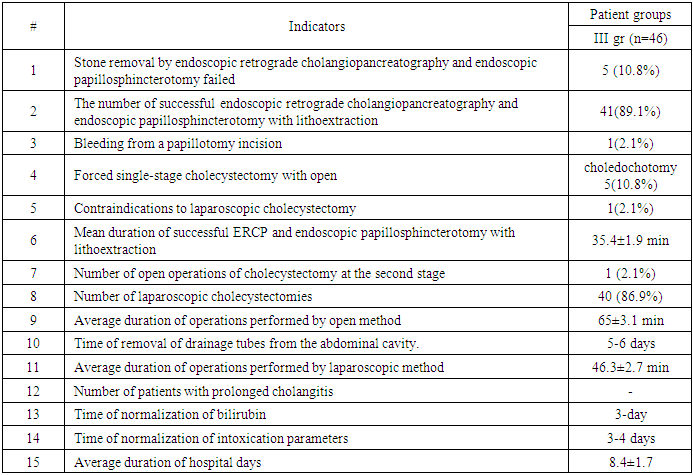
- In order to speed up the time of stopping the cholangitis process, the treatment complex was supplemented with retrograde lavage of the lumen of the common bile duct with an electroactivated aqueous solution of EAS-A, which has the following properties, expressed by antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial actions.Of the 46 patients examined, the first stage of the operation was successful in 41 (89.1%) patients and resulted in complete removal of stones from the common bile duct. The duration of the first stage of operations with successful completion of ERCP and endoscopic papillosphincterotomy with lithoextraction averaged 35.4±1.9 minutes.All such patients underwent the second stage of surgical intervention – cholecystectomy – after the acute inflammatory process in the lesion had been stopped and the intoxication indices and blood bilirubin had been normalized by the 5th-6th day. In 5 (10.8%) patients, due to dense wedging and high location of the calculus against the background of severe spasm of the muscular structures of the common bile duct, the first stage of the operation was unsuccessful – it was not possible to remove the calculi by endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography and endoscopic papillosphincterotomy with lithoextraction. In 1 (2.1%) case, intraoperative bleeding from the vessels of the common bile duct was observed during the first operation due to technical difficulties. In 5 patients (10.8%), removal of common bile duct stones by antegrade route with drainage of the common bile duct lumen and one-stage cholecystectomy was forcedly performed against the background of acute cholecystitis with high intoxication of the body. Of the 41 patients (89.1%) in whom stones were successfully removed at the first stage using endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography and endoscopic papillosphincterotomy with lithoextraction, in 40 patients (97.5%) after general detoxification and anti-inflammatory conservative therapy, delayed operations were performed by the 5-6th day: laparoscopic cholecystectomy. In 1 (2.1%) patient, due to the presence of a contraindication to laparoscopic surgery at the second stage, on the 6th day after successful endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography and endoscopic papillosphincterotomy with lithoextraction, cholecystectomy was performed using an open laparotomy method.Thus, in patients of the third group, in only 7 cases (15.2%), open surgeries were performed using a midline laparotomic approach (Figure 1).
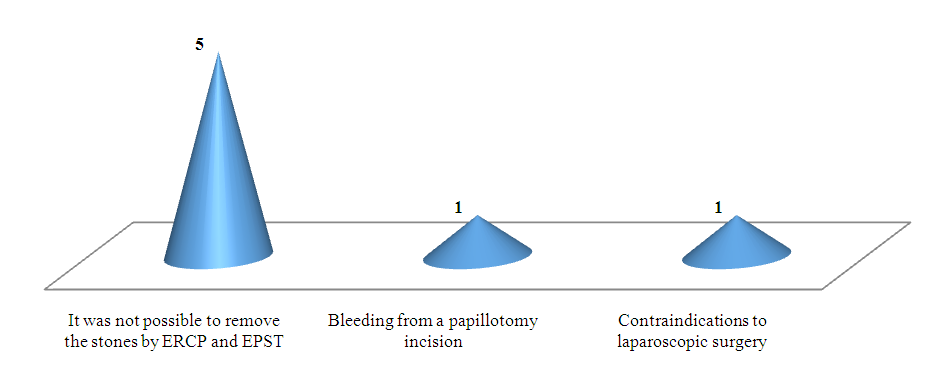 | Figure 1. Distribution of patients operated by open method at the first stage according to reasons of conversion |
|
|
4. Conclusions
- The use of minimally invasive methods in combination with nitroglycerin and EAS-A in the treatment of patients with acute calculous cholecystitis complicated by choledocholithiasis during endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography, endoscopic papillosphincterotomy and lithoextraction more effectively affects the treatment results, while the number of unsuccessful endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography decreases from 25.8% to 10.8%, forced one-stage cholecystectomies with choledochotomy from 35.5% to 10.8%. The average duration of successful endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography is reduced from 52.2±2.8 min to 35.4±1.9 min. The number of two-stage operations increases from 64.5% to 89.1%. Intraoperative bleeding complications are reduced from 9.7% to 2.1%. The periods of normalization of bilirubin and normalization of intoxication indices are 3-4 days. The average length of hospital stays for such patients is 8.4±1.2 days. Taking into account the comparative analysis of the obtained research results, an optimal method for treating patients with acute calculous cholecystitis complicated by choledocholithiasis has been developed using minimally invasive surgical treatment methods with nitroglycerin and EAS-A.
References
| [1] | Adams MA, Hosmer AE, Wamsteker EJ, Anderson MA, Elta GH, Kubiliun NM et al (2015) Predicting the likelihood of a persistent bile duct stone in patients with suspected choledocholithiasis: accuracy of existing guidelines and the impact of laboratory trends. // Gastrointest Endosc 82(1) р. 88–93. |
| [2] | Cirocchi R, Cozza V, Sapienza P, Mingoli A. Percutaneous cholecystostomy as bridge to surgery vs surgery in unfit patients with acute calculous cholecystitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. // Surgeon. 2023 Aug; 21(4): e201-e223. |
| [3] | Garcés-Albir M, Martín-Gorgojo V, Perdomo R, Molina-Rodríguez JL, Muñoz-Forner E, Dorcaratto D, et al. Acute cholecystitis in elderly and high-risk surgical patients: is percutaneous cholecystostomy preferable to emergency cholecystectomy? // J Gastrointest Surg. 2020; 24(11) р. 2579–2586. |
| [4] | Jagtap N, Hs Y, Tandan M, Basha J, Reddy DN. Clinical utility of ESGE and ASGE guidelines for prediction of suspected choledocholithiasis in patients undergoing cholecystectomy. // Endoscopy. 2020 Jul; 52(7) р. 569-573. |
| [5] | Vargheese S, Nelson T, Akhtarkhavari A, Patra SR, Algud SM. Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy in Acute Calculous Cholecystitis: A Secondary Center Experience. //Cureus. 2023 Jun 28; 15(6) р. 41-49. |
| [6] | Ramírez-Giraldo C, Isaza-Restrepo A, Rico-Rivera EX, Vallejo-Soto JC, Van-Londoño I. Laparoscopic cholecystectomy versus percutaneous catheter drainage for acute calculous cholecystitis in patients over 90 years of age. // Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2023 May 13; 408(1): 194. p. 330-342. |
| [7] | Maruta A, Iwashita T, Iwata K, Yoshida K, Uemura S, Mukai T, Yasuda I, Shimizu M. Permanent endoscopic gallbladder stenting versus removal of gallbladder drainage, long-term outcomes after management of acute cholecystitis in high-risk surgical patients for cholecystectomy: Multi-center retrospective cohort study. // J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2021 Dec; 28(12) р. 1138-1146. |
| [8] | Rakhmatov Shuhrat Sharofovich, Safoev Baqodir Barnoyevich. The Influence of an Electro Activated Aqueous Solution on the Dynamics of Biochemical Parameters and the Rate of Wound Healing in the Treatment of Purulent Diseases of Soft Tissues on an Outpatient Basis // Central Asian Journal of Medical and Natural Science (CAJMNS). – Mongolia, 2021, Осtober. No 5 – р. 361–367. |
| [9] | Rakhmatov Sh.Sh. Evaluation of the results of local application of 25% dimethyl sulfoxide solution in combination with an electroactivated aqueous solution in the treatment of purulent diseases of soft tissues in outpatient settings. Tibbiyotda yangi kun. - Bukhara, 2022, No. 7 (45). - P. 280-285. |
| [10] | Safoev B.B., Rakhmatov Sh.Sh., Arashev R.R. Elektroaktivlangan suvli eritmaning yumshok tўkimalarning yiringli kasalliklarini outpatient sharoitda davolashdagi samaradorligi // Tibbiyotda yangi kun. - Bukhara, 2021, No. 1 (33). – 233–237. |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML