-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2024; 14(11): 2815-2817
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20241411.29
Received: Oct. 18, 2024; Accepted: Nov. 9, 2024; Published: Nov. 12, 2024

Factor Analysis of Recurrence of Toxic Forms of Goiter
Zayniyev Alisher Faridunovich
Samarkand State Medical University, Uzbekistan
Correspondence to: Zayniyev Alisher Faridunovich, Samarkand State Medical University, Uzbekistan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

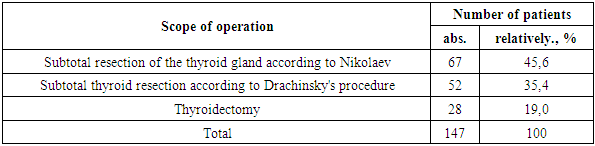
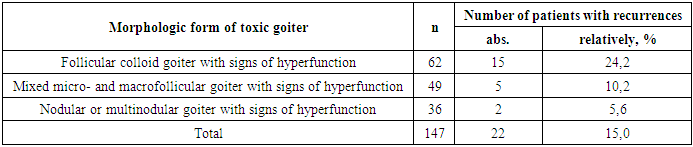
Relevance. At present, one of the most urgent problems of surgical treatment of patients with toxic goiter remains and it is connected, first of all, with the development of recurrences in the postoperative period. Purpose of the study: Determination of factors influencing the incidence of recurrence of toxic goiter. Materials and methods: The long-term results of surgical treatment were studied in 147 patients with toxic goiter operated in the surgical department of the multidisciplinary clinic of Samarkand State Medical University. All patients underwent cytologic and postoperative histologic examination before surgery. Results: In most cases follicular colloid goiter with signs of hyperfunction was verified in 62 patients (42,2%) and mixed micro- and macrofollicular goiter with signs of hyperfunction in 49 patients (33,3%), nodular or multinodular goiter with signs of hyperfunction was observed in 36 patients (24,5%). The volume of operation most often (45,6%) corresponded to subtotal resection according to Nikolayev with thyroid tissue in the volume of 6-8 g, in 35,4% of patients subtotal resection of thyroid gland according to Drachinsky with tissue up to 4 g on one side was performed and in 21,4% of patients thyroidectomy was performed. Duration of the disease of toxic goiter up to 2 years was determined in 11 (7,5%) patients, from 2 to 5 years in 34 (23,1%), from 5 to 7 years in 52 (35,4%), from 7 to 10 years in 13 (8,8%) and 37 (25,2%) patients with the disease duration more than 10 years. Conclusions: It was revealed that the recurrence rate depends on the duration of the disease, morphologic structure of the thyroid gland, the volume of surgical intervention and the level of antibody to thyroperoxidase.
Keywords: Toxic goiter, Thyroidectomy, Subtotal thyroid resection, Recurrence
Cite this paper: Zayniyev Alisher Faridunovich, Factor Analysis of Recurrence of Toxic Forms of Goiter, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 14 No. 11, 2024, pp. 2815-2817. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20241411.29.
1. Introduction
- Diffuse toxic goiter (DTZ) is a disease characterized by increased production of thyroid hormones and diffuse enlargement of the thyroid gland (thyroid) of varying degrees. The incidence of new cases of DTZ varies from 30 to 200 per 100,000 population per year [3]. In regions with normal iodine supply DTZ is the most frequent cause of persistent thyrotoxic state, and in iodine-deficient regions DTZ competes with functional autonomy of the thyroid in the etiologic structure of toxic goiter [2,4]. Currently, one of the most urgent remains the problem of surgical treatment of patients with toxic goiter, and this is primarily due to the development of recurrences in the postoperative period. There are supporters of radical and organ-preserving operations. When performing organ-preserving surgeries, researchers point out the need to preserve part of the gland tissue to prevent postoperative hypothyroidism, which will avoid taking thyroid medications [2]. Proponents of radical surgeries consider organ-preserving operations unreasonable, as it increases the risk of disease recurrence up to 25-40% [1,4,6]. Ismailov S.I. et al. argue that the etiology and morphologic structure of toxic goiter play the main role in the pathogenesis of relapse development rather than the volume of the performed surgery [3,8]. The lack of a unified point of view on the factors determining the risk of postoperative recurrences in toxic goiter served as a basis for the study.
2. Purpose of the Study
- Determination of factors affecting the incidence of recurrence of toxic goiter.The long-term results of surgical treatment were studied in 147 patients with toxic goiter operated in the surgical department of the multidisciplinary clinic of Samarkand State Medical University. The age of patients at the time of surgery was from 13 to 74 years, the average age was 36.4±7.2 years. Among them 132 (89.8%) were women, 15 (10.2%) were men. Thyrotoxicosis was noted in 123 patients (83,7%), functional autonomy of thyroid gland was revealed in 24 (16,3%). All patients underwent cytologic and postoperative histologic examination before surgery.In most cases, follicular colloid goiter with signs of hyperfunction was verified in 62 patients (42.2%) and mixed micro- and macrofollicular goiter with signs of hyperfunction in 49 patients (33.3%), nodular or multinodular goiter with signs of hyperfunction was observed in 36 patients (24.5%) (Table 1).
|
|
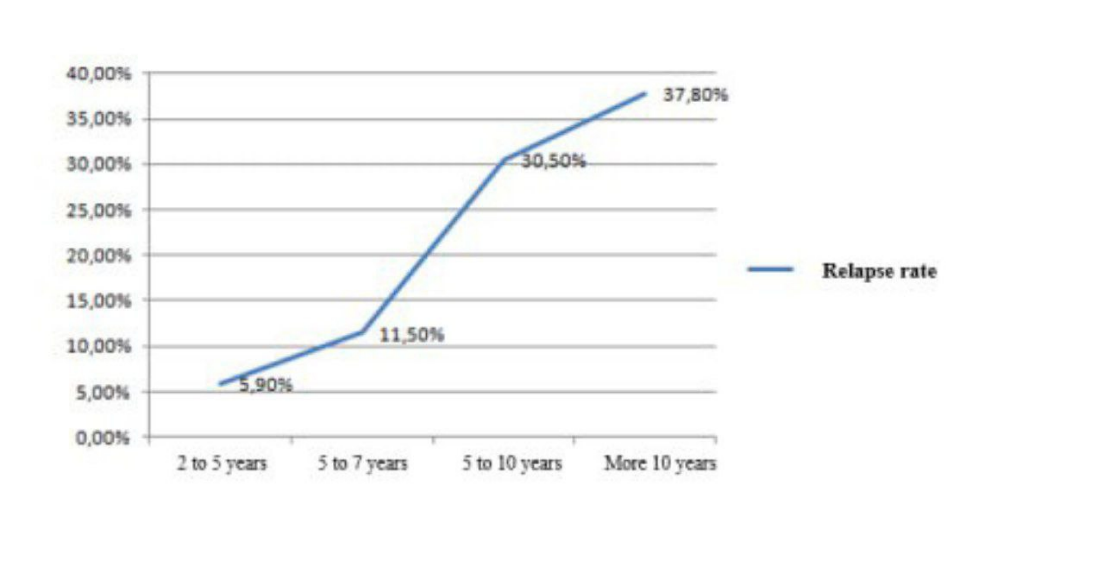 | Figure 1. Dependence of toxic goiter recurrence on the duration of the disease |
|
|
|
3. Conclusions
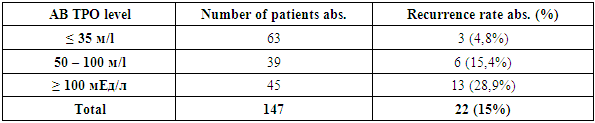
- Based on factor analysis of the long-term results of surgical treatment of toxic goiter defined:1. There is a direct correlation between the recurrence rate of toxic goiter and the duration of the disease before surgery, i.e. the longer the disease, the higher the recurrence rate. The highest recurrence rate was observed in patients with disease duration more than 10 years - 37,8%.2. The morphologic structure of the thyroid gland also affects the frequency of toxic goiter recurrence. The highest recurrence rate was determined in follicular colloid goiter with signs of hyperfunction - 24.2%.3. The recurrence of the disease depended on the volume of surgical intervention. Patients operated on in the volume of thyroidectomy had no recurrence of the disease.4. There is a clear pattern of recurrence rate with the initial level of AB TPO before surgery. The higher the level of antibodies to thyroperoxidase in patients, the higher the recurrence of toxic goiter in the postoperative period.Information about the source of support in the form of grants, equipment, and drugs. The authors did not receive financial support from manufacturers of medicines and medical equipment.Conflicts of interest. The authors have no conflicts of interest.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML