-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2024; 14(10): 2591-2596
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20241410.31
Received: Sep. 26, 2024; Accepted: Oct. 13, 2024; Published: Oct. 23, 2024

Comprehensive Approach to Diagnosing ASD in Children Using the Example of a Clinical Case Associated with a Variation of the SOX5 Gene
Rakhimova K. E.
Republican Children's Psycho-Neurological Hospital named after U.K. Kurbanov, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
Correspondence to: Rakhimova K. E., Republican Children's Psycho-Neurological Hospital named after U.K. Kurbanov, Tashkent, Uzbekistan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

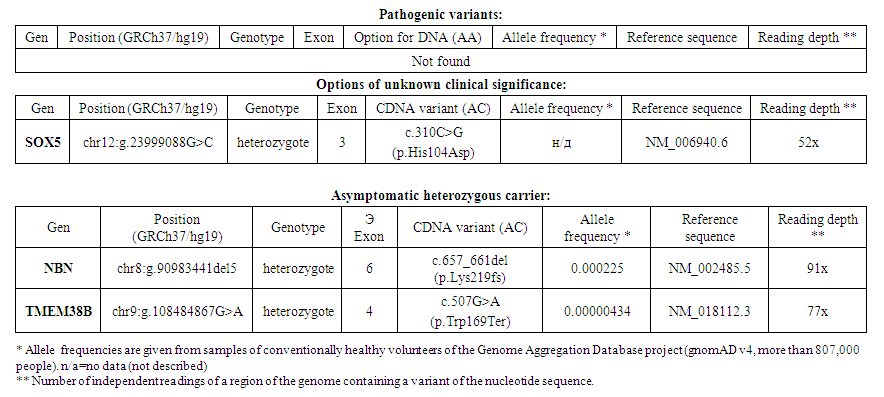
So far, more than 1,000 genes have been identified in which mutations are predictors of autism spectrum disorders. The influence of neurobiological factors has also been proven, making it possible to suspect these disorders in the early postnatal period. Despite the numerous evidence of a genetic factor in the development of autism spectrum disorders, the mechanisms of occurrence of these genetic disorders remain unclear, and therefore the description of family cases in which ASD is observed in combination with various features of the genome, which are not rarely found in conjunction with other disorders, is of particular interest psychomotor development. This study presents the results of a study conducted over five years. The results of this study were based on the complex psychological and neurophysiological status of three sibs, which have a similar developmental feature and genetic disorders inherited through the maternal line. A DNA sample from sibs and proband was searched for pathogenic and likely pathogenic variants in all coding regions of the genome. During next-generation sequencing, a variant of the nucleotide sequence c.310C>G in exon 3 of the SOX5 gene (chr12:g.23999088G>C) in a heterozygous state was identified, leading to the replacement of an amino acid in position 104 of the protein chain (p.His104Asp).
Keywords: Autism spectrum disorder, Cerebral palsy, Psychological research, Bioelectrical brain activity, Genetic disorder, Family case
Cite this paper: Rakhimova K. E., Comprehensive Approach to Diagnosing ASD in Children Using the Example of a Clinical Case Associated with a Variation of the SOX5 Gene, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 14 No. 10, 2024, pp. 2591-2596. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20241410.31.
1. Introduction
- ASD - neuroontogenetic development disorder manifesting in early childhood. This early onset significantly reduces the ability to detect and identify specific biomarkers in time that can predict the risks of developing ASD. ASD is characterized by a wide range of clinical manifestations, some patients require lifelong care, others, on the contrary, achieve professional success and are fully socialized. Currently, there are not enough complete comprehensive methods for correcting the main symptoms of autism. For example, therapy aimed at correcting behavior supposedly increases the IQ score and reduces the severity of speech disorders, while taking medications neutralizes the symptoms of agitation and hyperactivity. Over time, studies have shown a significant role for neuroimaging and genome-wide sequencing in the structure of ASD [1]. It is important to note that the number of children with ASD is growing every year [20]. Thus, according to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the number of registered cases increased from 1 to 36 people in 2023, or 1% of the population have ASD. The increase in statistical data is unclear, but this in turn confirms the influence of combined factors. In recent decades, the growth of scientific research focused on the study of etiological factors and methods for diagnosing ASD has reached record levels. After numerous studies, RAS has now been proven to be a polygenic disease and the search for genetic markers of autism is one of the central areas of research. Currently, over 1,000 genes have been identified whose mutations may be associated with autism (AutDB database data: autism.mindspec. org/autdb). Autistic disorders have been found to be associated with genetic mutations that may be hereditary or newly emerged (de novo) [2]. The genetic causes of ASD are indicated by research data from twins, siblings and other relatives [5,10]. Hundreds of genes have now been identified, variations in which are associated with ASD [14]. Copy number variation (CNV) is a type of structural adjustment that involves changes in the number of copies of certain sections of DNA that can either be deleted or duplicated. As with other types of genetic mutations, some CNVs are inherited, while others spontaneously occur in offspring and are absent in parents (de novo). There are databases SFARI Gene, AutDB, which collect information about genes in which variations are associated with autism, — now has more than a thousand records [3].In relation to the identification of the etiology and pathogenesis of autism, hereditary monogenic forms of autism are considered, which are known and sufficiently studied. It is believed that up to 10% of ASD cases are associated with known genetic syndromes, such as Fragile X syndrome, tuberous sclerosis, Rett syndrome, Angelman syndrome, etc. [4,8,12]. Combined with genetic predisposition, the action of environmental factors in the early stages of a child's development is recognized as equally important in the pathogenesis of autism [19]. The most influential factors currently considered are those whose exposure occurs in the early prenatal period of development [3,9]. Thus, autism - is a multifactorial disorder caused by genetic and environmental factors. Etiological heterogeneity, variable penetrance and broad phenotypic pleiotropy are now recognized as common characteristics of ASD genetics [5].In this regard, detailed descriptions of family cases in which certain genome disorders accompanied by autism spectrum disorders are found are of significant interest. This article provides data from a comprehensive longitudinal psychological and neurophysiological study of three cibs with symptoms of developmental disorders, which were found to have genetic disorders inherited from their mother [6,7].
2. Materials and Research Methods
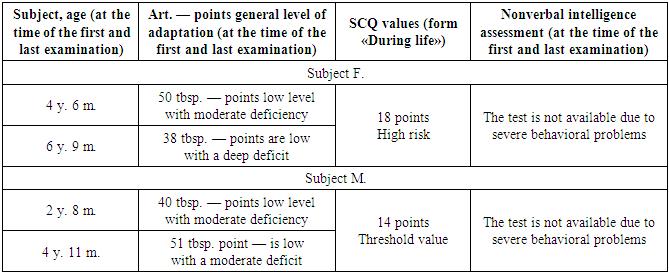
- Subjects: mother, father and three children (eldest daughter M, middle daughter M, youngest son M). Complaints: developmental disorder in all children. The study was conducted 7 times over 4 years. The eldest girl was 1 year old during the first visit, during the last - 5 years 4 months; the average girl was 1.5 years old and 3 years old during the last visit; the youngest boy was 2 months old during the first visit, during the last -8 months.The mother was 22 years old during the first examination, the father - was 29 years old. Thus, the mother gave birth to her first child at 21, her last - at 24 years old.Pregnancy and childbirth proceeded in all cases without complications. Delayed psycho-speech development was observed in all children, and in the older child - of the girl - it was most noticeable and previously caused concern among parents. Based on a consultation with a psychiatrist, the children were diagnosed as follows:F, eldest child, female, - Mixed specific psychological development disorders. With attention deficit hyperactivity disorder; ASD.M, middle child, girl, - delayed psycho-speech development with ASD elements;M., the youngest of the children, a boy, delayed psychomotor development.Psychological research: methods included in the diagnostic examination protocol for suspected autism spectrum disorders were used [2].1. Vineland Adaptive Behavior Scale VABS; allows you to identify the overall level of development of adaptive skills, assessing them in four areas of life: communication, everyday life skills, socialization, motor skills. The average (normative) level of development corresponds to 100+15 points.2. Intelligence test KABC-II (Kaufman Assessment Battery for Children); allows you to assess the level of development of nonverbal cognitive abilities in the form of a general index of nonverbal intelligence, the average standard value of which corresponds to 100 points (+15 points).3. The Social Communication Questionnaire (SCQ) is a parent-based screening technique that helps identify symptoms associated with autism spectrum disorders. Form «During life» is filled out taking into account the entire development history of the child and its use gives results (above 15 points for all cases, above 12 points, if there are accompanying factors such as hereditary burden), which may be grounds for referral for a more detailed examination [8,9].Result of analysis of full exome sequencing data.After consultation, parents were asked to do a genetic study on the eldest child, whose clinical picture was pronounced and the debut of manifestations was noted in the early stages of development. Genetic researchA genetic examination of full-exome – sequencing identified a heterozygous variant of unknown clinical significance c.310C>G (p.His104Asp) (potentially affecting splicing) in the SOX5 gene. (Table 1).
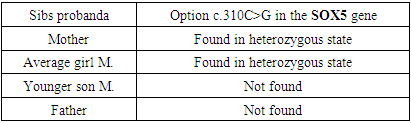
 | Table 1. Results of genetic examination of children and parents During full exome sequencing, the following nucleotide variants were identified in the proband |
|
3. Research Results
- DNA analysis of patients was carried out on a SeqStudio sequencer using direct automatic sequencing of PCR products.Variant annotations were performed on reference sequences NM_006940.6 (RefSeq database). The standard HGVS nomenclature (https://mutalyzer.nl/ version 2.0.25) was used to name the variants [11,12].The search for the c.310C>G variant (p.His104Asp) in the SOX5 gene using the Sanger sequencing method in family members – in the father and younger brother was not identified; in the mother of the proband and younger sister, the desired variant was identified in a heterozygous state.Psychological research:Children were examined 7 times over 4 years. Table 2 presents the summarized results of the psychological examination at the time of the first and last meeting with the family.Subject F. (the eldest child in the family, a girl) was examined three times using the Vineland Adaptive Behavior Scale, as well as the SCQ social but communication questionnaire. At the first meeting, parents were concerned about the expressed difficulties of communication, maladaptive behavior, and significant delay in psycho-speech development. At the age of 4.5, the girl did not attend preschool educational institutions and studied at home with her parents. At the age of 6, the girl was diagnosed with ASD and prescribed antipsychotic therapy. At all ages, the level of adaptation was assessed as low with a moderate deficit of 4 years 6 months (50 points) and a severe deficit of 6 years 9 months (38 points). The decrease in the last examination was associated with an episode of developmental regression that occurred at the age of 6 years (this fact was reported by the mother), with a subsequent improvement by the age of 7 years associated with the administration of drug maintenance therapy in the form of rispolept. Selected areas of adaptive behavior were investigated and the following patterns were identified. At all ages, the strongest side of subject B. is the field of motor skills; the least developed areas of socialization and communication [13,14]. Interestingly, at the age of 5 years 11 months there was a decrease in raw scores (1st examination — 25 points, 2nd examination — 15 points, 3rd — 27 points) and the overall standard score on the «Communication» scale, which indicated a deterioration in the development of communication skills in this age period, followed by improvement at the age of 6 years 9 months. The socio-communicative questionnaire (form«During life») was filled out by parents for age F. 5 years 4 months. The score is — 18, which exceeds the threshold and indicates a high risk of autism spectrum disorder. Subject M. (the middle child in the family, a girl) was examined three times using the Vineland Adaptive Behavior Scale, as well as the SCQ Social Communication Questionnaire. On the first visit, the parents were concerned about their son's delayed psycho-speech development, which, however, was less pronounced than that of his sister. The child did not attend the preschool educational institution; during the last visit, the boy was worried, it was difficult to establish contact with him, he refused to complete tasks.At all ages, the level of adaptation was assessed as low with a moderate deficit (at 2 years 8 months and 4 years 11 months) and with a mild deficit (at 4 years 1 month). This pattern is associated with a slowdown in the development of motor and everyday life skills in V. after 4 years. The evaluation of selected areas of adaptive behavior revealed the following patterns. At all ages, the strongest side of subject V. is the sphere of everyday and motor skills, the least developed sphere of communication and socialization. However, the line of development of socialization and communication skills, unlike skills in the motor and household spheres, had a continuous, positively progressive character [15,16].ScQ Score Sum (Form «Lifetime») — 14. Given the unfavorable family history of the presence of developmental characteristics in the other two sibs, this value can be considered sufficient to be identified as a risk group for the development of autistic disorders.
|
4. Discussion
- In the described family with hereditary maternal burden, three children were born with certain functioning disorders. The children were born to young parents who did not have bad habits. Based on the results of a full-exome sequencing study, a heterozygous variant of an unknown clinical value of c.310C>G (p.His104Asp) (potentially affects splicing) in the SOX5 gene was identified.The search for the c.310C>G variant (p.His104Asp) in the SOX5 gene using the Sanger sequencing method in family members – in the father and younger brother was not identified; in the mother of the proband and younger sister, the desired variant was identified in a heterozygous state [19,20].Based on the clinical picture, family history and data and molecular genetic study, we found that copy number variations (CNVs) in the SOX5 gene identified in these ASD patients may also contribute to the development of other neurodevelopmental disorders. Characterized by delayed speech and psychomotor development, decreased intelligence, autistic behavioral traits, etc. Genetic analysis found various genome disorders (CNVs) in children, two of which were inherited from their mother. In 2 cases out of three, a significant increase in the altered area of the chromosome inherited from the material can be associated with disruption of the functioning of certain genes of this chromosome, which manifested itself in autism spectrum disorder diagnosed by psychiatrists and confirmed methods of psychological examination. The older and younger daughters showed the same mutations, and since the clinical picture of the children is significantly similar, it can be assumed that these cases are associated with the identified mutation. Moreover, the identified gene is part of the database of genes whose mutations may be associated with autism (data from the AutDB database: autism.mindspec. org/autdb). In the average child, autistic disorders were significantly milder than in the eldest daughter. In conclusion, I would like to note that this is the first description of a family case in which three children had some kind of developmental disorder, and in two cases these disorders were pronounced and associated with ASD and gross delay in psycho-speech development. All family members underwent a genetic examination, the results of which showed that the mother had severe genomic instability. An extremely important observation has been made based on genetic analysis: all children inherited these mutations with a significantly increased number of repetitions. The older and middle child has a very high probability that the cause of autism spectrum disorders is a mutation in the SOX5 gene. The youngest child was not identified and is probably not related to his mental state. Thus, a fairly complete comprehensive genetic, psychological and neurophysiological study of a family case made it possible to understand the structure of the identified disorders and suggest their possible causes. The disease is associated with heterozygous mutations in the SOX5 gene. This gene encodes a protein that is involved in the processes of regulation of transcriptional activity. Variations appear with different phenotypic expressions, suggesting that these changes are only one of a variety of factors contributing to the development of autistic traits. In the future, further investigation of their association with neurodevelopment and autism is needed to better understand the pathogenicity of CNVs.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML