-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2024; 14(10): 2548-2551
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20241410.22
Received: Sep. 28, 2024; Accepted: Oct. 21, 2024; Published: Oct. 23, 2024

Immunohistochemical Analysis of Morphological Changes in the Wall of the Duodenum of Rats under the Influence of Energy Drinks
T. Zh. Babazhanov1, A. S. Ilyosov2, A. U. Avezov3, G. Yu. Aytimova3
1Tashkent Medical Academy, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
2Navoi Innovation University, Navoi, Uzbekistan
3Urgench Branch Tashkent Medical Academy, Urgench, Uzbekistan
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

According to histochemical studies, from infancy to old age, the number of goblet cells in the intestine did not change, but at all age periods their number was higher in the distal part than in the proximal. This is due to the large number of bacteria in the distal region compared to the proximal one. A decrease in the number of acidic highly resistant age-related choledochomas and cins to bacterial glycosides is associated with an increase in the number of cases of inflammatory bowel diseases in elderly people and during puberty.
Keywords: Energy drinks, Morphological structure of duodenum, Microscopic structure of duodenum wall, Influence of energy drinks on human body, Morphological and morphometric changes of duodenum wall
Cite this paper: T. Zh. Babazhanov, A. S. Ilyosov, A. U. Avezov, G. Yu. Aytimova, Immunohistochemical Analysis of Morphological Changes in the Wall of the Duodenum of Rats under the Influence of Energy Drinks, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 14 No. 10, 2024, pp. 2548-2551. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20241410.22.
1. Introduction
- In Europe, energy drinks are considered biologically active supplements and are allowed to be sold only in pharmacies. Since 2013, Germany has had national legal limits for energy drinks containing caffeine, taurine, inositol and glucuronolactone [1,4,7,9,11,15]. Chronic consumption of energy drinks causes damage to the gastrointestinal tract in humans. According to scientists, those who are chronically addicted to energy drinks will develop diseases in their internal organs [3,5,6,8,10,12]. In this regard, the production of treatment, preventive measures, and correction methods for diseases of internal organs remains one of the urgent problems of modern medicine, therefore, there is a need to conduct scientific research on the study of the effects of these drinks on the living organism all over the world [2,13,14,16].The purpose of the study: Study and comparative evaluation of the morphological state of energy drinks in the duodenum and under conditions of biological detoxification.
2. Material and Methods
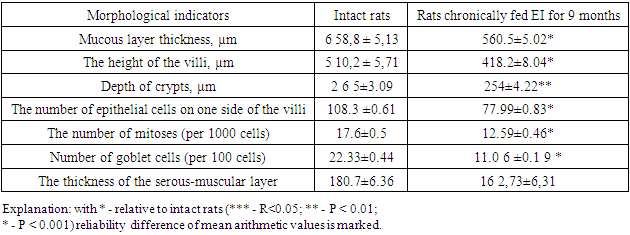
- Under experimental conditions, rats were decapitated 3 days after receiving 8.0 ml/kg of energy drinks per os for 3 months. Histopreparations were prepared by special standard methods by taking a sample from the duodenum and analyzing the obtained data [11,14,15,16].Based on the data obtained during our experiment, we can say that in immunohistochemical studies of the structures of the mucous membrane of the 12 digits of the rats that consumed energy drinks in a chronic state for 3 months, when we initially examined Ki 67, CDX-2, CD 163 and CK-20 markers, in some cases negative and low positive expression in 2 cases.All tissues are divided into 3 groups depending on the level of division, labile - rapidly dividing cells, the G 2 phase lasts for a very short period of time, stable cells reproduce for 1-6 months, the G 2 phase lasts for a long time, and permanent cells last a lifetime. it is divided into cells that are deprived of the possibility of a niche and are in the G 0 phase. This is mainly characterized by the presence of labile cells in the mucous membranes, continuous mitosis, and rapid G2 phase in immunohistochemical tests, resulting in a positive expression of the Ki 67 marker at a lower than normal level. As a result, staining is observed in cell nuclei, perinuclear areas, and perinuclear cytoplasm and is stained pale.In the course of our study, the morphological conditions of the 12-intestinal wall tissue and blood vessel structures of rats that chronically consumed energy drinks for 9 months were analyzed.According to the obtained results, the mucosa was atrophied, the number of villi and crypts decreased compared to the control group. In the mucous layer, there are many foci of desquamation in the epithelial layer, microerosions. Degenerative changes are detected in epithelial cells. Pyknosis and lysis processes were observed in the nuclei of epithelial cells. Processes of infiltration with mononuclear cells were observed in the muscular plate of the mucous membrane. These morphological changes were also confirmed by the lower values of all parameters compared to the control group animals in the morphometric examinations. In a small size, there are very few glands in the villi of the mucous membrane of the duodenum, most of them are stored in the submucosa. The serous-muscular layer is thickened. In the mucous membrane of the duodenum, there are very few almost goblet glands in the villi, most of them are stored in the submucosal layer, the thickness of the serous-muscular layer is thicker than that of the control group.Decreased secretory goblet cells and other types of enterocytes were found. In particular, there is a sharp decrease in goblet enterocytes that retain and produce sour mucopolysaccharides SHIFF, microerosion foci and necrobiosis cells in the epithelial cells covering the intestinal villi, lymphocyte infiltration processes were preserved in the villi stroma.In Brunner's glands, the secretory cells are sharply reduced, most of the secretory cells are swollen and necrobiosis occurs, interstitial swellings are preserved in the stroma, and an increase in the interstitial sparse fibrous connective tissue is detected.In Brunner's glands, the secretory cells are sharply reduced, most of the secretory cells are dying and necrobiosis, interstitial swellings are preserved in the stroma, and an increase in sparse fibrous connective tissue is detected.SHIFF-positive structures are reduced in the secretory cells of the submucosa layer, there are fibrinoid swellings and interstitial swellings, foci of lymphocytic infiltration at the border of the muscle layer. In the submucosa layer, the secretory cells show a significant decrease in size and shape of the cells containing the positive structures of SHIK, atrophy. At the border between the submucosa and muscle layers, there is an irregular and uneven thickening of sparse fibrous connective tissue.It was observed that in the secretory and covering epithelial cells of the submucosa layer, the positive structures of SHIK were sharply reduced and reduced in size, sparse and coarse fibrous connective tissue was preserved between the glands, and interstitial swellings were preserved in the stroma of the submucosa layer.Table 1 shows the morphometric parameters of duodenal tissue structures of experimental rats that consumed ED chronically for 9 months.
|
|
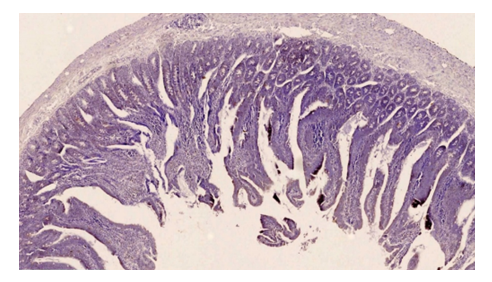
 | Figure 1. Duodenum of rats receiving chronic energy drinks for 9 months. Very moderate positive expression of the Ki 67 marker. Paint Dab chromogenic. Size 4x10 |
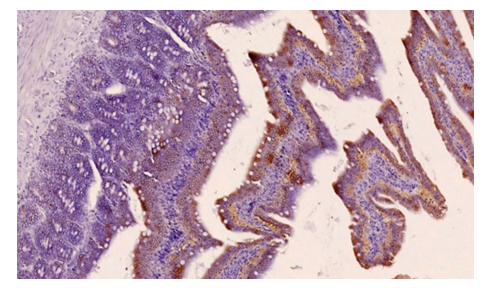
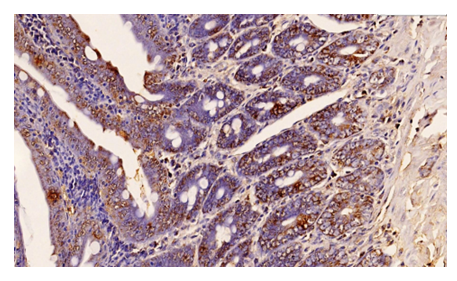 | Figure 3. Duodenum of rats receiving chronic energy drinks for 9 months. Medium positive expression of CDX-2 marker. Paint Dab chromogenic. The size is 10x10 |
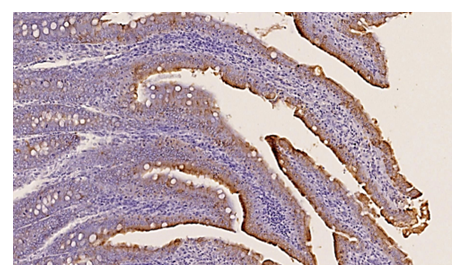 | Figure 4. Duodenum of rats receiving chronic energy drinks for 9 months. Medium positive expression of CK-20 marker. Paint Dab chromogenic. The size is 10x10 |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML