-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2024; 14(10): 2494-2496
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20241410.09
Received: Sep. 28, 2024; Accepted: Oct. 10, 2024; Published: Oct. 15, 2024

The Results of Anamnestic Data of Children Born Prematurely with Extremely Low, Very Low and Low Body Weight
N. N. Ergasheva, G. I. Yuldsheva
Tashkent Pediatric Medical Institute, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

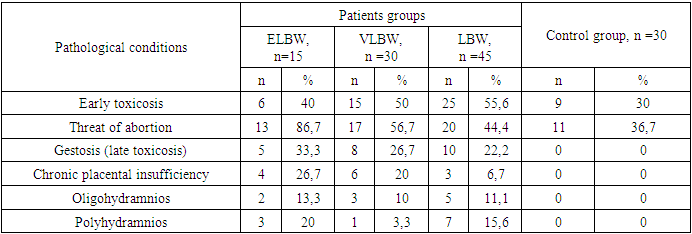
A detailed study of obstetric anamnesis was carried out, risk factors for prematurity of newborns, the neurological status of these patients were described, and clinical and instrumental characteristics of newborns with low body weight were given. According to the study, an important factor influencing the condition of the child at birth and further postnatal events should be considered the course of labor, the method of delivery. The most common complications of pregnancy in the mothers of the main group were the threat of termination of pregnancy, chronic fetoplacental insufficiency, early toxicosis, gestosis, lack of water and polyhydramnios.
Keywords: Prematurity, Extremely low body weight, Very low body weight, Gestational age, Preterm birth
Cite this paper: N. N. Ergasheva, G. I. Yuldsheva, The Results of Anamnestic Data of Children Born Prematurely with Extremely Low, Very Low and Low Body Weight, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 14 No. 10, 2024, pp. 2494-2496. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20241410.09.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Low birth weight in children at an early age is combined with increased morbidity and functional disorders, 10-20% of children with very low and extremely low birth weight subsequently become disabled, intrauterine development delay is also a prognostically unfavorable factor. The incidence of adverse outcomes among surviving children born weighing up to 1000 g reaches 40-50%, rising to 70-90% at birth of children weighing 500-750 g. Prematurely born children form a risk group for the occurrence of behavioral disorders (disorders of activity and attention, neuropathies, emotional abnormalities, disorders of psychological development) [2].Purpose of the study. The aim of the work was to study the anamnestic data on the birth of premature babies and risk factors manifested during the neonatal period of premature babies born with ELBW, VLBW and LBW.
2. Materials and Methods of Research
- To achieve this goal, mothers of 90 children (main group) born prematurely were examined which all mothers were treated in the neonatal pathology department of the 1st City Clinical Children's Hospital, in the City Perinatal Center, in clinic “Family medical house” in 2019-2023. The control group included mothers of 30 examined children of the same age.
3. Results and Discussion
- In our study, a burdened obstetric and gynecological history was observed in n=15 (16.6%) mothers whose children were born with ELBW, in n=30 (33.3%) - with VLBW, and in n=45 (50%) - with LBW. The age of the mothers of the examined children at the time of delivery ranged from 17 to 47 years, on average, 29.9 ± 7.5 years (no significant differences between the main group and the control group, p>0.05). At the same time, in the 1st group (children with ELBW), the average age of mothers at the time of birth was 30.1 ± 8.4 years, in the 2nd (children with VLBW) - 28.9 ± 7.7 years and in 3- th (children with LBW) - 26±6.0 years. In the control group, the average age of mothers at the time of delivery was 28.4 ± 6.1 years, while there was only one (3.3%) woman in the age group of 35-44 years and there were no women 45 years and older. The proportion of women in labor aged 35-44 years was 20.0% in the 1st group, 13.3% in the 2nd, 8.9% in the 3rd, and 6.7% - of those at 45 years and older respectively, there were none in the LBW and control groups. Indicators for the serial number of this pregnancy and childbirth in mothers of children born prematurely and in the control group are given in Table 1. The percentage of children born from the 1st pregnancy in the control group was 13.3%. In the group with ELBW it was 40.0%, with VLBW - 33.3%, with LBW - 44.4%. The proportion of 2nd and 3rd pregnancies in a row were quite close in mothers of all groups. Compared with the control group (67.7%), there was a trend towards a higher incidence of the 4th and higher serial number of pregnancy: in the 1st group - 20.0%, in the 2nd - 20.0%, in 3rd - 15.6%, control - 10%.
|
|
|
|
4. Conclusions
- Thus, when studying the obtained anamnestic data, it can be said with certainty that pregnancy and/or childbirth in all mothers of the study group of children born with ELBW, VLBW and LBW proceeded with complications. An analysis of the state data at birth showed that in children of the main group born with ELBW, VLBW, LBW, it was defined as moderate and severe, while in the control group it was satisfactory.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML