-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2024; 14(8): 2111-2115
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20241408.34
Received: Jul. 29, 2024; Accepted: Aug. 24, 2024; Published: Aug. 30, 2024

An Analysis of the Structural Characteristics of the Carotid Artery in Individuals with Metabolic Syndrome
B. L. Khoshimov
Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) in Medical Sciences, Alfraganus University, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
Correspondence to: B. L. Khoshimov, Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) in Medical Sciences, Alfraganus University, Tashkent, Uzbekistan.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Background: Metabolic syndrome is a condition characterized by a combination of metabolic disorders that increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Understanding the vascular changes that occur during metabolic syndrome is crucial for developing effective therapeutic strategies. Objectives of Study: This study aimed to examine the structural alterations in the carotid artery in individuals with metabolic syndrome and to evaluate the therapeutic potential of sunchoke in mitigating these vascular changes. Methods: The study was conducted using white laboratory rats, divided into three groups: a control group, an experimental group with induced metabolic syndrome, and a treatment group receiving sunchoke. Morphological and morphometric analyses were performed on the carotid artery using histological staining methods, and the results were statistically analyzed. Results: The study revealed significant thickening of the internal elastic membrane and a reduction in the muscle layer thickness in the carotid artery of rats with metabolic syndrome. The number of smooth muscle cells also decreased. However, in the group treated with sunchoke, these pathological changes were significantly corrected, with the carotid artery structure closely resembling that of the control group. Conclusions: Metabolic syndrome induces destructive changes in the vascular structure, particularly in the carotid artery. The administration of sunchoke demonstrated a positive therapeutic effect by restoring the normal morphological features of the artery. These findings suggest that sunchoke may be a valuable therapeutic agent in managing vascular complications associated with metabolic syndrome.
Keywords: Analysis, Structural characteristics, Carotid artery, Individuals, Metabolic syndrome, Morphology, Intima, Connective tissue fibers, Metabolic syndrome, Sunchoke
Cite this paper: B. L. Khoshimov, An Analysis of the Structural Characteristics of the Carotid Artery in Individuals with Metabolic Syndrome, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 14 No. 8, 2024, pp. 2111-2115. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20241408.34.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Currently, metabolism is a pressing issue in both modern basic and clinical medicine [2,3,10]. Metabolic syndrome adversely affects the functioning of organs and systems in the body due to disruptions in carbohydrate and lipid metabolism, insulin resistance, and dysfunction of the endothelium in blood vessel walls. The phrase “metabolic syndrome” was coined in the 1980s. It is a prevalent health issue in numerous places worldwide. Recently, the prevalence of metabolic syndrome has expanded beyond the senior population, with a rising proportion of young individuals being affected by it [1,4,9,12]. Metabolic syndrome is a metabolic condition that increases the chance of developing vascular disorders, which are closely associated in terms of their underlying causes and mutually strengthen each other. Given these factors, including the high prevalence in the population and the significant rise in the incidence of metabolic syndrome projected by the WHO, along with its association with aging, this issue is a top priority in modern medicine [5,6,7].Hypokinesia refers to a reduction in movement activity, which can be linked to the physiological immaturity of the organism, specific working conditions in a small space, and various other factors. In certain instances, there may be a total absence of movement or akinesia, which poses greater challenges for the body. A reduction in physical activity results in a disruption of the coordinated operation of the muscular system and internal organs. Hypokinesia is characterized by alterations in the composition of skeletal muscles and myocardium, a decrease in immunological activity, and a reduced ability of the organism to withstand extreme temperatures and oxygen deprivation. After being immobile for a period of 7–8 days, individuals experience apathy, increased sleepiness, difficulty focusing on important tasks, disrupted sleep patterns, significant decrease in muscle strength, impaired coordination for both complex and simple movements, deterioration in the contractility of skeletal muscles, alteration in the physic–chemical properties of muscle proteins, and functional disturbances such as reduced calcium levels in bone tissue. The development of these metabolic alterations includes multiple intricate pathways and numerous unresolved issues [4,8,11]. Arterial blood arteries have a crucial function in delivering blood and nutrients to organs. Arteries consistently operate at elevated pressure. In order to handle this pressure, they possess a substantial quantity of elastic tissue and a minimal amount of smooth muscle. The body contains two primary categories of arteries: elastic arteries and muscular arteries. Muscular arteries, such as the brachial artery, the radial artery, and the femoral artery, are characterized by their anatomical designations. Muscular arteries possess a greater number of smooth muscle cells in the interstitial layer compared to elastic arteries. Elastic arteries, such as the aorta and pulmonary arteries, are the arteries that are located closest to the heart. These arteries have a higher amount of elastic tissue in their innermost layer (intima) compared to muscular arteries. The elastic nature of arteries allows for the maintenance of a consistent pressure gradient against them, even with the continuous contracting (pumping) action of the heart.Considering the information provided, our objective was to examine the structural alterations in the carotid artery caused by experimental hypokinesia and metabolic problems.
2. Research Materials and Methods
- The study utilized white laboratory rats with a weight range of 180–200 grams. The experiments and decapitation of animals were conducted in compliance with the European Convention for the Protection of Vertebrate Animals Used for Experimental and Other Scientific Purposes (Strasbourg, 1985). The white rats used for the experiment were categorized into 3 groups. Each group consisted of 20 rats.The initial group consisted of healthy rats without any observable symptoms of somatic or infectious illnesses, serving as the control group. The control group of rats had a consistent diet consisting of standard food and water, which was available to them at all times.The second group was referred to as the experimental hypodynamia and metabolic syndrome model. A hypodynamia model was created using specialized cage pens. In this instance, the size of the cages was maintained at a minimum of 150 cm2. Rats that were in good health and showed no evidence of infectious or somatic disorders were placed in specialized cages and provided with a diet that had high levels of fat and carbohydrates. The rats' diet comprised 60% laboratory feed, 20% sheep fat, and 20% fructose. Instead of consuming water, a solution containing 20% fructose was administered. The rats were euthanized 60 and 90 days post–experiment.In the third group, the rats were subjected to hypokinesia and metabolic syndrome modeling. Starting from the 60th day of the experiment, the rats were taken out of the experiment, removed from the panel–cage, and transferred to a regular cage. The feeding ration commences with the appropriate nutritional composition, consisting of 24% protein, 6% fat, and 44% carbohydrates. This composition is provided by the use of “Delta Fids” feed, specifically the Biopro brand from RF. In order to rectify antioxidant and metabolic imbalances, Topinambur Danikafarm (0.4) tablets were dissolved in water and administered twice day via a subcutaneous catheter.The rats in both the control and experimental groups are maintained under identical circumstances in the vivarium. The body weight of the rats in both the control and experimental groups was assessed. In order to conduct morphological study, a carotid artery that had a mixture of different components was extracted. Histological slices were then made using a rotor microtome, with each section having a thickness of 8–10 microns. These sections were stained using the hematoxylin and eosin, Van Gion, and Weigert procedures. The histological preparations are used to determine the structure of the cytoplasm of the blood vessel wall and the condition of the collagen elastic fibers. To conduct a morphometric analysis of blood vessels, preparations were prepared from four sections of the common carotid artery. A morphometric examination was performed to determine the average values of the evaluated parameters. In the morphometric investigation, we calculated the following parameters: the thickness of the common carotid artery wall, the thickness of the intima, the individual thickness of the media, the overall thickness, the ratio, the diameter of the blood vessel, and the relative volume of the intima as a percentage.The G.G. Avtandilov approach and the NanoZoomer (REF C13140–21.S/N000198/HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS/431–3196 JAPAN) Hamamatsu (QuPath–0.4.0, NanoZoomer Digital Pathology Image) morphometric computer program are utilized for performing morphometric analyses. The data was analyzed using the statistical functions of Microsoft Excel 2010 to get the arithmetic mean (M), the average error (m) of the relative sizes, and the accuracy coefficient. The CX40 type OD400 camera microscope is used to capture photomicrographs from histology preparations.Over the initial 10–day period of the experiment, the sedentary rats exhibited a decline in their consumption of food and water. However, in the subsequent days, they adjusted to their lack of physical activity and displayed an increased level of activity in their intake of food and water. Throughout the investigation, the rats in the experimental group exhibited an increase in body weight, indicating a heightened adaption to a state of inactivity. The mean body weight of neonatal rats was 10 grams, and by day 30, the body weight of rats increased by a consistent factor of 9.5 compared to neonates, with an average of 95.8 grams. Multiplied by a factor of 1.8 and had an average of 175.4 grams. The mean body mass of rats at 90 days of age was 260.6 grams, representing a 1.4–fold increase compared to rats at 60 days of age. The results indicated that the body weight of the 30–day–old rat in the experimental group was 11.5 times more than that of the newborn.At the 60–day mark, there was a 2.1–fold rise in body weight, resulting in a total weight of 245.3 grams. At the end of a 90–day period, the body weight had increased by a factor of 1.6, resulting in an average body weight of 416.5 grams (Fig. 1).
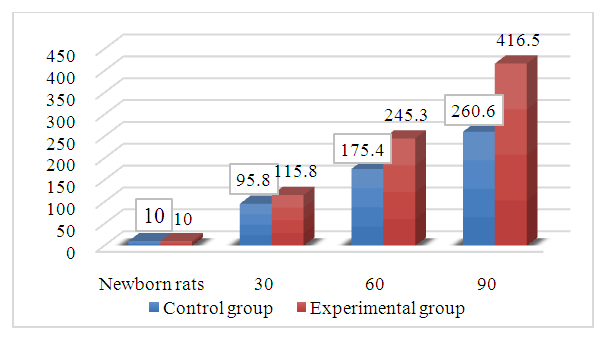 | Figure 1. Changes in body weight of rats in the control and experimental groups |
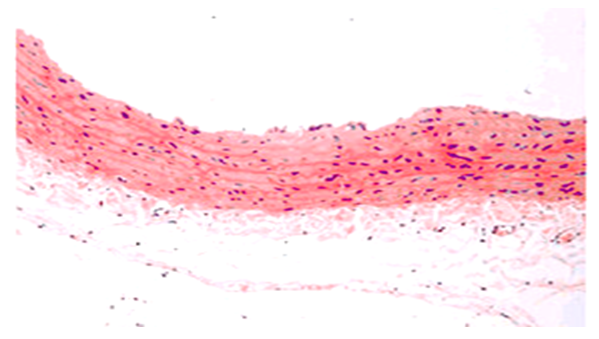
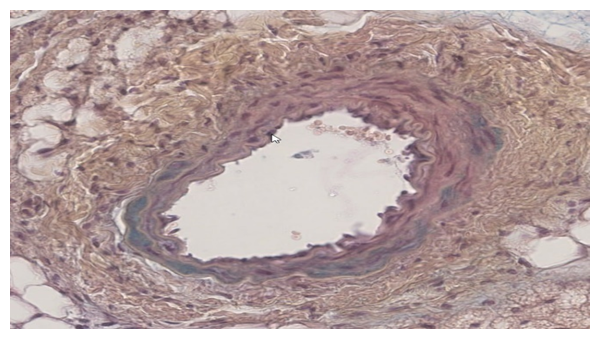 | Figure 5. The histological appearance of the carotid artery in the experimental group of 60–day–old newborn rats. Staining method used: hematoxylin–eosin. Magnification level: 10x40 |
3. Results and Discussions
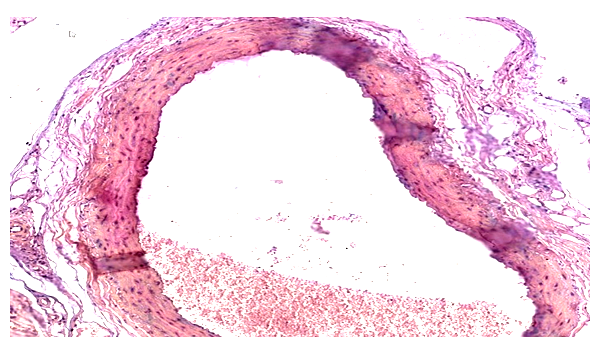
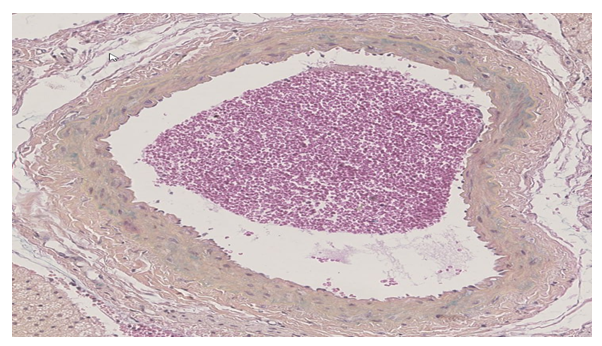
- The analysis of the collected data revealed that the experimental conditions of hypodynamia and hypokinesia led to an increase in the thickness of the internal elastic membrane and middle layer of the thoracic aorta wall, in comparison to the control group. The examination of the results showed that the thickness of the internal elastic membrane rose by 11% on day 30, 16% on day 60, and 18% on day 90 of the experiment. The central layer’s thickness exhibited a growth rate of 7% in 30 days, 49% in 60 days, and 47% in 90 days. An increase in the number of smooth muscle cell lines was consistently detected at 30 and 60 days compared to the control group. However, by the end of the 90–day trial, there was a 6% drop in the number of smooth muscle cell lines.Furthermore, it was seen that the elastic membrane underwent a process of smoothing, and there was evidence of fibration in certain branches. An increase in the thickness of collagen fibers was observed in the intermediate layer, namely near the exterior elastic membrane. During the initial stages of the experiment, there was an observed rise in the quantity of smooth muscle cells, which subsequently declined by the 60th day of the trial. Therefore, it can be concluded that experimental hypokinesia and metabolic syndrome lead to alterations in all layers of the carotid artery wall, with significant modifications primarily occurring in the middle and inner layers.
4. Conclusions
- Metabolic syndrome is a prominent and socially significant medical issue that has garnered the interest of a diverse group of experts worldwide. Regarding this matter, the issue of comprehending the pathophysiology of metabolic syndrome and its rectification is significant. Therefore, in cases of experimental hypokinesia and metabolic syndrome, there was an observed thickening of the internal elastic membrane of the carotid artery wall, a reduction in the thickness of the middle layer, and a decrease in the number of smooth muscle cells in the vascular wall. Metabolic syndrome was associated with documented endothelial degradation, stasis, and fibrosis in the carotid artery wall. When treated with sunchoke, the intima thickness on the carotid artery wall decreases, tumors in the muscle layer dissipate, and the thickness becomes similar to that of the control group.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML