-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2024; 14(8): 1985-1990
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20241408.08
Received: Jul. 12, 2024; Accepted: Jul. 29, 2024; Published: Aug. 8, 2024

Importance of Rehabilitation on Children with Down Syndrome
Saodatkhon Salikhova1, 2, Kamala Salikhova3, Botirkhon Salikhov4
1Tashkent Pediatric Medical Institute, 223 Bagishamal Street, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
2Alfraganus University, 2v Yukori Karakamish Street, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
3Republican Specialized Scientific-Practical Medical Center of Pediatrics, 3 Talant Street, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
4Republican Specialized Scientific and Practical Medical Center for Therapy and Medical Rehabilitation, 4 Khurshid Street, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
Correspondence to: Saodatkhon Salikhova, Tashkent Pediatric Medical Institute, 223 Bagishamal Street, Tashkent, Uzbekistan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Background. Down syndrome is the predominant recognized factor leading to intellectual disability, responsible for over 30% of cases. Children diagnosed with Down syndrome often have issues related to their neurological and somatic health. Currently, many children with DS struggle to learn sufficient number skills in the classroom, which hinders their ability to function in everyday life. Numicon is an essential and helpful tool for teaching children with DS how to count. To enhance attention, focus, cognition, and conduct EEG-Neurofeedback therapy was used for individuals with DS. Methods. The results of assessing cognitive sphere in children with DS, used the Schulte diagnostic scale before and after applying the Numicon program and EEG-NFB practice. Results. The findings of this study demonstrate that cognitive function, particularly attention, was greatly enhanced with the use of Numicon and EEG-NFB rehabilitation, with no observed adverse effects. Additionally, this treatment facilitated a decrease in impulsivity and hyperactivity. Conclusion. Rehabilitation enhances self-care and assists children with Down syndrome in adjusting to social life.
Keywords: Down syndrome, Cognitive impairment, Neurology
Cite this paper: Saodatkhon Salikhova, Kamala Salikhova, Botirkhon Salikhov, Importance of Rehabilitation on Children with Down Syndrome, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 14 No. 8, 2024, pp. 1985-1990. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20241408.08.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Children diagnosed with Down syndrome (DS) often experience difficulties with attention [1], concentration [2], learning, memory [3], speech, language, behavior [4], and physical coordination [5]. Their lack of focus on certain stimuli can significantly and negatively impact their capacity to acquire knowledge [6]. Common speech and language concerns encompass difficulties in fluency, social communication in both formal and informal settings, articulation and expression [7]. These children have a high frequency of behavioral problems [8]. Common concerns include aggression, excessive noise [9], hyperactivity, and difficulty adhering to rules [10]. Also, these children are more prone to encountering health complications such as, congenital heart defects [11,12], hearing loss [13,14], hypothyroidism [15], obstructive sleep apnea [16], and epilepsy are examples of common health issues in these children [17]. Furthermore, the most commonly observed physical traits are decreased or poor muscle tone [18]; short neck, with excess skin at the back of the neck; flattened facial profile and nose; macroglossia [19]; small head, ears, and mouth; epicanthal folds; Brushfield spots spaced around the periphery of the iris [20]; wide, short hands with short fingers; single transverse palmar crease [21]. The majority of individuals with DS experience varying degrees of intellectual disability, which can range from mild to severe [22]. On average, the amount of disability is often modest to moderate [23]. There exist discrepancies in cognitive abilities [24]. Verbal short-term memory capacities often exhibit significant weakness [25]. The learning processes that depend on the prefrontal cortex, cerebellum, and hippocampus regions are widely recognized, and they may be particularly impaired in individuals with DS [26]. It is important to acknowledge that youngsters with DS encounter significant challenges when studying mathematics [27]. This is primarily because mathematical operations necessitate a considerable level of abstract thinking, proficient short-term memory, and the capacity to manipulate multiple concepts simultaneously [28]. Proficiency in comprehending cause and effect relationships, understanding the relativity of concepts, making comparisons, and utilizing mathematical terminology is necessary [29], however children with DS struggle with these skills. Numicon, which utilize a visual approach to the number system, have the potential to make a valuable contribution to the teaching strategies [30]. Numicon’s forms are designed so that children can manipulate them, learn to recognize patterns and relate them to the corresponding numbers [31].Numicon is an essential and helpful tool for teaching children with DS how to count [32]. In fact, it is a comprehensive educational program specifically created to teach numerical concepts to children in preschool and primary school who are developing ordinarily [33]. Due to the enhanced visual abilities observed in many children with DS, it is believed that Numicon could serve as a beneficial tool to help them develop their numerical skills [34,35].Aggression and hyperactivity, which are behavioral issues, can also be treated with the non-invasive treatment called EEG-Neurofeedback (EEG-NFB) therapy [36]. This therapy aims to enhance attention, focus, cognition, and conduct in individuals with DS [37]. The primary goal of the EEG-NFB, especially in the context of a clinical setting, is to teach the patient how to regulate the neurophysiological parameter or parameters that exhibit the greatest degree of variation from the population as a whole [38]. It is predicated on the causation hypothesis, which postulates that behavioral manifestations of neuropsychological problems are caused by abnormalities in brain functioning [39]. Through operant conditioning—a learning process in which the strength of behavior is adjusted using rapid feedback and positive reinforcement—the subject is taught how to augment or inhibit certain, abnormal electrophysiological parameters [40].Children with DS commonly exhibit signs of coexisting conditions related to brain dysregulation [41]. EEG-NFB can significantly reduce these symptoms by utilizing the brain’s natural ability to self-regulate, therefore improving its functioning and relieving the related manifestations [42].EEG-NFB has been found to be effective in addressing conditions such as DS by helping to improve brain regulation through self-regulation training using brainwaves [43].EEG-NFB has been extensively utilized in the past ten years as a primary therapeutic approach for psychiatric and neurological disorders [44,45]. EEG-NFB utilizes the patients' capacity to acquire the skill of regulating and harmonizing their cerebral functions by manipulating brain waves in specific regions of focus [46,47]. EEG-NFB is an operant conditioning method for retraining brainwave (EEG) patterns [48]. The goal of neurofeedback is to initiate and maintain instrumental learning. This requires proper and consistent rewards during ongoing learning - EEG-NFB provides this [49].Decades of EEG-NFB practice have proven that children with DS can be effectively trained to selectively regulate their brain activity, thus potentially improving performance [50,51].
2. Methods
- A study has been conducted following the number skills developed by 27 children with DS aged between 6 and 10 years in Tashkent, Uzbekistan in 2023, with using the Numicon materials and approach. For each child we used the Numicon program during 8 months. Also, EEG-NFB training sessions, according to the β-rhythm program, were carried out in 20 sessions lasting 10–30 minutes. The control group comprised 10 children with DS who did not utilize Numicon program and EEG-NFB training. EEG-NFB practice was carried out using Neyron-Spektr-1/NFB (Neurosoft, Russia) equipment. The positioning of electrodes is done in accordance with particular brain processes and symptoms.All cases had confirmed genetically; all had complete trisomy on chromosome 21 (karyotype analyzes had performed at the Republican Screening Center, Tashkent, Uzbekistan).The results of assessing concentration in children with DS and effects of procedures, the Schulte diagnostic table used before and after applying the Numicon program and EEG-NFB practice. Schulte tables are commonly regarded as effective tools for enhancing peripheral vision, attention, and memory. Accordingly, they facilitate rapid reading comprehension, efficient information retrieval, and the cultivation of cognitive resilience against external distractions during tasks. The tables are constructed with randomly arranged numbers or letters of varying colors, which correspond to the level of difficulty. Parents of each child were given a questionnaire designed by a neurologist that included questions about behaviors, learning ability, speech and language skills, and concentration. Throughout the course of treatment, no medication was used in any of the sessions.Exclusion criteria: severe vision impairment, profound impairment including deafness, children under 6 years old, severe mental retardation. The statistical analysis involved the use of variation statistics techniques in Microsoft Office Excel 2019 to calculate measures of standard deviation and arithmetic mean error using the methods (M±m), standard deviation (s), median, mode, and interquartile range. Student's criterion (t) was then used to assess the statistical significance of these measures, along with determining the level of confidence (P). This analysis was performed on data that followed a normal distribution. Differences were considered significant at a confidence level of 95% (P<0.05).
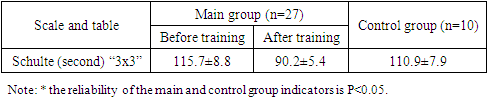
3. Results
- Children with DS often struggled with visual skills, making it crucial for them to focus on improving in this area. By including graphic assignments into our lessons and assigning them as homework, we enhanced the fine motor abilities of children and reinforced the skills they obtained through practical activities with Numicon. During the subsequent phase, children with DS were introduced to Numicon, a mathematical manipulative. They engaged in extensive manipulation and play with the components, observing them, physically manipulating them, placing them on their fingers, and engaging in actions such as knocking and throwing. It was essential for the children to thoroughly inspect and physically interact with the objects in order to vividly remember their appearance and texture. It is crucial to acknowledge that, over time, the youngsters gained experience and became saturated with sensory input from Numicon. As a result, their non-specific manipulations decreased. During the midpoint of the initial year of study, children were capable of transitioning to mathematical problems utilizing this material.Consequently, children experienced and engaged in many stages and types of behaviors using Numicon shapes. This allowed them to develop a comprehensive understanding of these forms, including their visual and tactile properties, as well as the association between these shapes and their corresponding numbers. Specifically, the youngsters started to envision the shapes of Numicon and numbers, and subsequently, the activities associated with them, even without having tangible visual references.At the beginning and ending of our research, we conducted an assessment of cognitive advancement in all children.According to the findings from the Schulte table, prior to their initial instruction, all children with DS struggled to complete the “3x3” and “4x4” tables, making a certain number of errors. This group was unable to successfully finish the “5x5” multiplication tables. In the initial training session, the duration required to locate numbers ranging from 1 to 10 in a sequential order (with a total of 5 sets of “3x3” tables executed consecutively) was recorded as 115.7±8.8 seconds, while the average number of errors made was 3.5±1.0. After completing all training session, the indicator for finding numbers in the proper sequence improved to 90.2±5.4 seconds and 1.5±0.5 mistakes. This indicates that children’s ability to locate numbers has significantly increased in terms of speed and efficiency. Following the training, the control group did not show any improvement in their indicators compared to the main group (with indicators of 110.9±7.9 seconds and 4.0±0.5 mistakes).
|
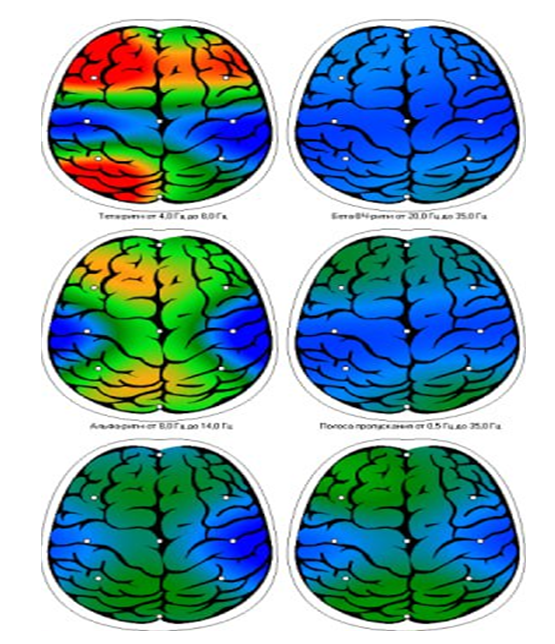 | Figure 1. Patient A.Tairov. EEG-NFB - after 1st training |
4. Discussion and Conclusions
- In this research, we reviewed the clinical applications of EEG-NFB and method Numicon. In EEG-NFB is usually recorded, and various brain-activity components are extracted and feed backed to subjects. The Numicon technique facilitates the development of fine motor skills and cognitive abilities in children. Numicon was just one component of the child’s numerical education. Each activity card included recommendations for establishing links with other activities that enhance learning and assist the youngster in utilizing and applying their newfound comprehension. Crucially, it is essential for youngsters to start learning and practicing their counting skills right from the start, while engaging in all Numicon activities. Furthermore, the findings of this study demonstrate that cognitive function, particularly attention, was greatly enhanced with the use of EEG-NFB rehabilitation, with no observed adverse effects. Additionally, this treatment facilitated a decrease in impulsivity and hyperactivity. Notably, favorable improvements, such as a reduction in theta waves in EEG parameters, were also seen. It should be noted that, rehabilitation helps children adapt to social life and improves self-care.
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
- All parental consent was obtained. Voluntarily of the participation.
Consent for Publication
- Not applicable.
Availability of Data and Materials
- The datasets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Competing Interests
- The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ Contributions
- SS, KS, BS were the initiators of the proposed concept and made significant contributions to the final manuscript. The first author was responsible for the development of the theoretical framework and provided support in data collection. The second and the third authors conducted a thorough review of the final manuscript, played a role in the conceptual development, and made valuable additions. All authors made substantial contributions to the article and have given their approval for the submitted version.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- We would like to thank and acknowledge all patients and their parents for their consent to participate in this study to improve research. The used figures are original, and belong to the authors of this manuscript.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML