-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2024; 14(7): 1902-1906
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20241407.37
Received: Jun. 22, 2024; Accepted: Jul. 21, 2024; Published: Jul. 25, 2024

Peculiarities of Patients with Spinal Cord Stroke in Elderly Patients
Ikromov Sh. B.1, Gaybiyev A. A.2
1Doctoral Student of the Department of Neurology, Samarkand State Medical University, Uzbekistan
2Doctor of Medical Sciences, Associate Professor of the Department of Neurology, Samarkand State Medical University, Uzbekistan
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Application of new methods of treatment of elderly patients with spinal cord infarction and further improvement of treatment results based on the study of clinical and pathogenetic features of recurrent stroke through rehabilitation measures.
Keywords: Spinal cord stroke, Spinal cord dysfunction, Critical, Changes, Rehabilitation measures, Treadmill therapy
Cite this paper: Ikromov Sh. B., Gaybiyev A. A., Peculiarities of Patients with Spinal Cord Stroke in Elderly Patients, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 14 No. 7, 2024, pp. 1902-1906. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20241407.37.
1. Introduction
- Stroke is an acute cerebral circulatory disorder (ACCD) causing damage and death of nerve cells. The name itself comes from the Latin word ‘insultus’, translated as ‘blow, attack’. Previously, the pathology was called apoplexy (apoplectic stroke), as the Greeks called paralysis - one of its main symptoms and consequences [1,6].The disease is more common than acute myocardial infarction. More than 15 million cases are registered annually in the world. They are associated with 10% of all fatalities (almost 6 million per year), which makes stroke the ‘No. 2 cause of death’ on the planet after coronary heart disease (CHD). But in the majority of episodes, the consequence of STEMI is not death, but limitation of life activity, which is the leading cause of disability among older people [2,7].About 60% of patients who have suffered a stroke have persistent neurological disorders that interfere with their full lifestyle. Among the typical abnormalities noted are impaired movement and mobility, difficulty swallowing, high risk of speech and visual disorders, falls, fractures. Emotional (depression) and cognitive (up to the stage of dementia) disorders are often observed [3,8].Acute circulatory disturbance is possible not only in the brain. Occlusion (disturbance of blood circulation) of the vessels of the spinal cord leads to spinal stroke. Compared to brain strokes, such cases are quite rare (1-1.5% of the total number of strokes), but they occur, as a rule, in people aged 30-50 years [5]. Blood to the spinal cord is supplied by three main arteries. If there are problems with blood flow in these arteries and their branches, this is the cause of a spinal stroke [4].Purpose of the study: to investigate the patient features of patients with spin insult in elderly people.
2. Materials and Methods
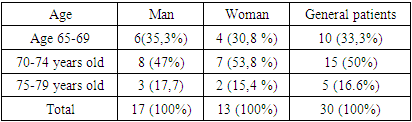
- For older people, the problem of spinal stroke is especially relevant. Men and women over the age of 60 have a twice-increasing risk of developing spinal strokes every 10 years. In addition, 75-89% of strokes develop after the age of 65, 50% after the age of 70, and 25% in patients over the age of 85. In 30 patients treated in the neurology department of Samarkand State Medical University Clinical Hospital No. 1, the features of spinal stroke were studied. Also, patients were selected to receive a course of rehabilitation measures, and later participated in the rehabilitation treatment of 16 patients on the basis of the Rehabilitation Department of the Clinical Hospital No. 1 of Samarkand State Medical University.Special attention is paid by specialists to the problem of their social and physical rehabilitation through physical education in order to restore the health of people with disabilities, to attract them to socially useful work. It is extremely rare to fully restore the working capacity of people with disabilities and their return to professional activities. In this regard, the problem of physical rehabilitation of people with disabilities is especially acute. Physical education always remains one of the most effective means of Health and character development. Exercise helps to learn the skills and abilities necessary in life, helps to restore motor activity and helps to form positive character traits. Adaptive physical rehabilitation as a type of adaptive physical culture satisfies the disabled person's need to recover their healing and temporarily lost functions. The goal of adaptive physical rehabilitation is to form adequate mental reactions of a disabled person to the disease, to use natural rehabilitation tools that stimulate the rapid recovery of the body. 1. The problem of physical rehabilitation of individuals with spinal cord injuries using adaptive physical culture. Spinal cord injury due to spinal cord injury (picture) has serious consequences in the form of disorders of the motor, sensory, trophic and pelvic organs. Social, labor and physical rehabilitation of patients in conditions of increased trauma is a complex and urgent task. Every year in Uzbekistan, the number of people with disabilities of this profile increases by 1.3 thousand people. [1]. Physical rehabilitation of disabled people with spinal dysfunction solves the most important task - the restoration of vital motor skills and abilities, the formation of functional compensation mechanisms [3,6]. Physical rehabilitation is an integral part of medical and socio-labor rehabilitation using the means and methods of physical education, massage and physical factors. Flexible physical education includes the formation of vital and professionally necessary motor skills and abilities in people with disabilities, the development and improvement of physical, mental, functional and volitional qualities and abilities, the means, techniques and methods of physical education that allow them to achieve independence every day. and psychological independence. The main tools of physical rehabilitation are elements of exercise and sports, the use of which is always a pedagogical, educational process. All means and opportunities for physical education should be aimed at increasing the physical activity of people with disabilities, which is a crucial condition for the integration of people with disabilities into society (comprehensive rehabilitation and social adaptation). 2. General rules for the implementation of the process of physical rehabilitation of disabled people with spinal dysfunction. Physical rehabilitation of disabled people with spinal dysfunction should be considered as a medical-pedagogical system, the effectiveness of which depends on the completeness of the manifestation of the factors that shape the system. Physical rehabilitation, which includes therapeutic physical education depending on the stage, correctional training, labor, daily life and individual physical exercises in the resting conditions of people with disabilities, ensures the normalization of the patient's motor activity and mental state. the necessary conditions at the initial stages, then the formation, development and improvement of functional compensation mechanisms of a local nature. In the process of physical rehabilitation of disabled people with spinal dysfunction, a positive result can be achieved by successively solving the following tasks:
|
|
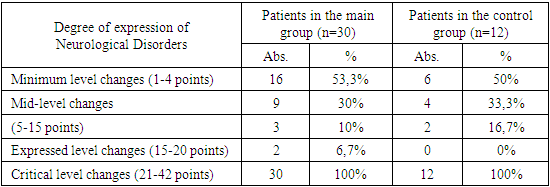
3. Results
- The results show that, rehabilitation tactics are based on the general principles of long-term, continuous and systemic exposure to a complex of restorative means, the leading place among which is the education of the needs necessary for physical exercise (kinesitherapy) and systemic physical education. Methodological techniques have been developed that allow you to force the patient to perform the action and believe in the possibility of rehabilitation. These methods include: - performing ideomotor exercises; - isometric muscle tension; - exercise in water; - selection of starting exercises; - passive and active-passive exercises; - the use of various devices that reduce weight. Only 10-15% of patients with spinal cord injuries are able to take care of themselves, 25-35% partially take care of themselves, and in the rest the ability to self-care is completely lost. In the acute stage of the early stage of spinal traumatic disease, only patients with a low level of injury and lower paraparesis are able to partially provide basic self-care; in the rest this ability is lost. One of the effective recovery tools is occupational therapy. However, this tool can retain such a role in the rehabilitation Arsenal only with a rational approach to its use. The use of labor in treatment is a pathogenetic effect that restores impaired motor functions. In its essence, occupational therapy is therapeutic Gymnastics, including labor movements. Labor activity aimed at the result combines the achieved actions, develops them in every possible way, uses movements as a physiological stimulator, helps to increase the amplitude of movements, develop automatism, reduce muscle stiffness, increase muscle strength and plasticity. In the process of performing certain works, contact with various materials that differ from each other in shape, size and elasticity stimulates the restoration of sensitivity. Different labor processes involve muscles that work with different levels of activity. Therefore, when prescribing occupational therapy, it is necessary to separately select labor operations, focusing on a functional defect, taking into account the clinical characteristics of the work and the motor capabilities of the patient, taking into account the biomechanical characteristics of a particular technology. The effectiveness of kinesiotherapy increases if it is used in combination with physical methods of treatment and targeted drugs. The restoration of lost functions under the influence of exercise can be achieved only in patients who have had spinal compression eliminated, the anatomical integrity of the spinal canal has been restored, and the spine has stabilized. In other cases, it is possible to adapt only to the defect, in the table shows, as an example, the differential application of kinesiterapia for relaxed and spastic paralysis. The combination of vertical drop and treadmill (treadmill) training in a suspension system developed by Canadian orthopedic doctors was revolutionary. This was partially called treadmill therapy with vertical discharge. For training, the paralyzed patient is placed in a suspension system located above the treadmill; vertical discharge is provided by a block or pneumatic system. Two methodologists are located on the right and left side of the patient, passively "stepping" the patient's legs; the duration of the procedure is 40 minutes. In training, the passive "step" is replaced by a series of passive-active, active with assistance, and then active walking. The training effect of Treadmill therapy is associated with the systematic activation of spinal musculoskeletal generators by afferent input by receptors (muscles, skin, joints) of the legs that perform rhythmic movements [7]. A comparative analysis of the use of new technologies by existing methods shows positive dynamics in the complex therapy of patients. The main criterion for the effectiveness of rehabilitation can be only functional recovery, complete or partial. Only active tactics can ensure the success of the rehabilitation of patients with spinal cord injuries. The main criterion for the effectiveness of rehabilitation can be only functional recovery, complete or partial. Only active tactics can ensure the success of the rehabilitation of patients with spinal cord injuries. Due to the development of Medicine, the mortality rate from spinal injuries decreased from 90% during the first three months of the disease in the early and mid-20th century. currently up to 28.9%. About 50% of spinal cord injury patients survive, living for more than 25 years, but most of them are deeply disabled. This necessitates the improvement of the methods of rehabilitation of such patients, which is of great practical importance. The activation of work with people with disabilities in the field of physical education and sports helps to humanize society, change its attitude to this group of the population, and therefore has great social significance. It should be recognized that the problems of physical rehabilitation and social integration of people with disabilities through physical education and sports are being solved slowly. The main reasons for the poor development of physical education and sports among persons with disabilities are specialized physical education, wellness and the almost complete absence of sports facilities, lack of equipment and inventory, lack of physical education and sports clubs, underdevelopment of the youth sports network. schools and departments for people with disabilities in all types of further education institutions focused on physical education and sports. There is a lack of Professional personnel. The need for physical wellness among people with disabilities is insufficiently expressed, which is due to the lack of special promotion that encourages people with disabilities to engage in physical education and sports. In the field of physical rehabilitation of people with disabilities, there is still a lack of adequate assessment that physical education and sports are much more important for people with disabilities than people who are comfortable in this regard. Active physical education and sports training, participation in sports competitions is a very necessary form of communication, restores mental balance, relieves the feeling of loneliness, restores the feeling of self-confidence and self-esteem, gives the opportunity to return to an active life.
4. Conclusions
- Improving the system of measures for the modern treatment and rehabilitation of elderly patients with spinal stroke disease is the restoration or compensation of impaired functions, correction of deformities associated with them, solving the problems of the maximum adaptation of these patients to society (social, professional), achieving the maximum level. Including economic and professional, improving the quality of life.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML