-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2024; 14(7): 1873-1879
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20241407.32
Received: Jun. 28, 2024; Accepted: Jul. 20, 2024; Published: Jul. 22, 2024

Bronchial Asthma – A Practical Approach to Diagnosis, Adaptation to the Primary Health System
Ruzikulov Azamat Qurbanmurodovich, Irsalieva Fatima Khusniddinovna
Department Of Allergology, Clinical Immunology and Nursing, Tashkent Medical Academy, Uzbekistan
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

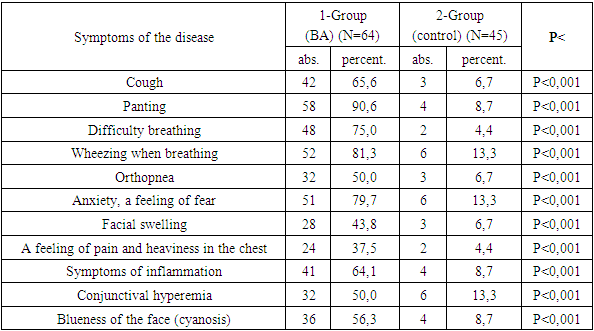
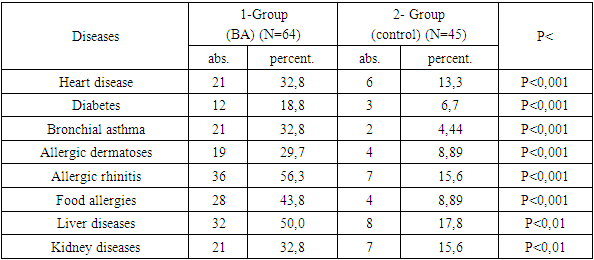
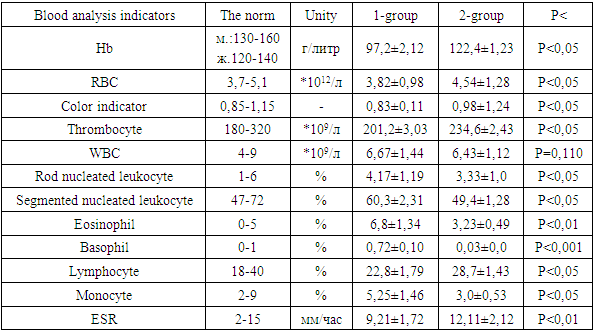
Bronchial asthma is one of the pressing problems of modern health care. Today, an estimated 358 million people worldwide suffer from asthma, accounting for 4 to 10 percent of the adult planet's population, and according to some other sources, it was suspected that by 2025 this figure would reach 400 million people. The goal is to develop an early diagnostic method for timely detection of bronchial asthma, prevention of possible complications, early approach to treatment, selection of preventive treatments. The goal is to develop an early diagnostic method for timely detection of bronchial asthma, prevention of possible complications, early approach to treatment, selection of preventive treatments. Research material and methods. The study was carried out in people with bronchial asthma in various regions of Surkhandarya region. According to the study, 64 (100 percent) patients with bronchial asthma participated in the tests, of which 23 (35.9 percent) were male and 41 (64.1 percent) were female. The study carried out methods for collecting objective and subjective materials, in-depth analysis of Anamnesis data, statistical data of disease outbreaks in Surkhandarya region, General blood analysis, serological-Idem examination, method of enhanced radiological examination of the lungs, examination of polymorphism alleles and genotypes of genes IL17A, IL23R, IL17F, spirometry. Results. The most common areas of bronchial asthma are Sarosian, next are the city of Termez, jargon, Sandgrouse, Goldinsoe districts. We were convinced that the main symptoms of bronchial asthma are higher in the level of salinity when compared with the control group, which is observed in almost all patients. It should be noted that during the period of sensitivity, patients experienced a lot of psychopathological conditions, faced with anxiety, fear of death, insecurity, and in the absence of sensitivity, mainly with a state of depression. among those participating in the study, we found that the mother, father or close relatives have these diseases, the most interesting is that in patients with an allergic or hereditary predisposition to one of the parents, the clinical course of the BA is mild or moderate, but in both the father and mother, their presence has led to the development of severe and In the pathology of the lungs and bronchi according to spirometry, especially in severe types of bronchial asthma, the vital capacity of the lungs, the maximum Examiner flow and the maximum volume of forced breathing decrease sharply in full-fledged breathing volume, which negatively affects not only the lungs themselves, but the brain, heart, blood and general body, completely damaging tissue performance.
Keywords: Bronchial asthma, Eatra diagnosis, Spirometry, Genetic analysis, Serological examination
Cite this paper: Ruzikulov Azamat Qurbanmurodovich, Irsalieva Fatima Khusniddinovna, Bronchial Asthma – A Practical Approach to Diagnosis, Adaptation to the Primary Health System, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 14 No. 7, 2024, pp. 1873-1879. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20241407.32.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- As an open system, the respiratory organs provide a direct opportunity for complex damage to the body, at the same time, it is also considered a protective organ of the whole body, a filter. Environmental, weather, climatogeographical changes can significantly affect the structural and functional damage of the body. Diseases of the respiratory tract develop and pass depending on the conditions of the regional area, based on this, the clinical manifestations of this disease also change according to the mentioned factors. Bronchial asthma (BA) is a heterogeneous disease characterized by chronic inflammation of the lower airways and characterized by airway obstruct ion that differs in duration and intensity (wheezing, shortness of breath, cough). BA formation is a disease based on chronic inflammation, airway hyperreactivity and excessive contraction of bronchial smooth muscles in response to specific stimuli, as well as their structural restructuring [1,9].Bronchial asthma is one of the urgent problems of modern health care. Today, more than 358 million people worldwide suffer from asthma, which is 4 to10 percent of the adult population of the planet, and according to some other sources, this number is suspected to reach 400 million people by 2025 [2,13]. BA is common in most countries such as the United Kingdom, USA, Israel, Ireland, Central American countries, New Zealand and Australia [3,18]. At the same time, in recent years in many countries of the world, the incidence of asthma, including the manifestation of this disease in early childhood, has increased significantly [4,21].Among the elderly population in the Russian Federation, BA is spread from 5.6 to 7.3 percent, this indicator means that it is more common than stroke, UIK, breast can cer, AIDS [5,11]. Mild forms of BA have the highest rate, from 50 to 75 percent, and timely diagnosis and proper treatment can dramatically stop the progression of the disease. The economic and social damage from BA is decreasing due to the use of new methods of diagnosis and treatment, but today this indicator still shows an amount higher than 37 billion Russian rubles [6,18]. However, despite this, the disease is diagnosed too late, and more optimal treatment strategies are often sought after the onset of complications. Bronchial asthma develops regardless of gender and age, timely diagnosis and early treatment can prevent the development of the disease and complications [7,20].Among them, one of the most common diseases, the first mention of bronchial asthma is found in ancient Indian doctors. In the 18th century, the doctor James Anderson, who worked in one of the West Indian clinics, introduced the method of treating bronchial asthma with datura plant to Europe for the first time. The term "asthma" was first used in the four aphorisms of Hippocrates [8,12]. By this term, the author meant "heavy breathing" accompanied by wheezingornoisein "breathing". Hippocrates described this condition as more severe than dyspnea and less severe than orthopnea (dyspnea when lying down). This disease was considered a paroxysmal manifestation of respiratory distress [10,22].Galen's contemporary, Arephaeus of Cappadocia, left amanuscript on bronchial asthma (BA) that remained largely unknown until it was published in Paris in 1554. Accor ding to the manuscript, asthma was more common in women compared to men and observed more severe sleep disturbances [13,24].A different view of the disease began at the beginning of the 19th century, since it is a chronic disease that requires constant monitoring. In most patients with asthma, the widespreaduse of recommendations in standard protocols helps to achieve its control and serves as a key element of a practical health care system. The manage ment of patients with asthma is regulated by two main documents: the Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) and the Russian clinical recommendations for the treatment of BA. Based on these 2 recommendations, two updated documents on the control of bronchial asthma were published in 2019б GINA guidelines for the treatment and prevention of bronchial asthma [8,14,23] and clinical guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of BA of the Russian Federal Respiratory Society [15]. GINA (2019) collected the treatment protocols accumulated over the years and presented a new approach to BA, a modified strategy based on strong evidence, the most updated methods of clinical application, of course, these treatment procedures cannot be carried out with out diagnosing bronchial asthma or without early detection of its presence [8,9,19].In general, the latest international and federal clinical guidelines for the treatment and diagnosis of bronchial asthma serve as a practical guide for specialists.Mamasoliev N.S. and all. (2023) identified epidemiological signs such as smoking, al cohol abuse, severe heredity, dietary habits of the population, insufficient consumption of vegetables and fruits, as well as low physical activity according to WHO criteria as risk factors for bronchial asthma (WHO, 1996) [20,21]. By the authors, the diagnosis of bronchial asthma was determined on the basis of clinical data: typical symptoms of sideropenic and trophic diseases, a decrease in hemoglobin level, changes in the color indicator index (hypochromic type of anemia) and blood serum indicators were considered as generally accepted methods. In general, in 2018-2019, the prevalence of respiratory diseases decreased by 100,000 in the Republic of Uzbekistan. During this period, the prevalence of asthma also decreased by 0.1% in absolute terms and by 3.5% per 100,000 population. In addition, the incidence of asthma and other respiratory diseases decreased both in absolute terms (16.3% and 1.9% reductions, respectively) and per 100,000 population (18.7% and 4.8% reductions, respectively). The dangerous situation regarding the spread of asthma is typical for Tashkent, Andijan, Jizzakh, Kashkadarya, Tashkent, Khorezm regions, and if we take into account the possibility of infection, the dangerous situation is typical for Andijan, Kashkadarya, Surkhandarya, Fergana, Khorezm regions and the Republic of Karakalpakstan [22].Among the factors that cause this trend, urbanization and environmental weather, the destruction of the ecosystem in general, especially in large cities and megacities, are of great importance. An increase in the number of patients with severe asthma leads to a significant decrease in labor productivity and requires an increase in the costs of the health care system. In addition, asthma is one of the main causes of disability and a decrease in the quality of life of patients [4].Taking into account the given data, studying the problem of bronchial asthma, establishing an early and timely diagnosis, early treatment, improvement of the prevention direction is urgent and important, and determines the importance and necessity of studying the subject. The purpose of writing the article is to develop an early diagnosis method for timely detection of bronchial asthma, prevention of possible complications, early approach to treatment, and selection of preventive procedures.
2. Research Material and Methods
- The study was conducted in patients with bronchial asthma in different regions of Surkhandarya region. According to the research results, 64 (100 percent) patients with bronchial asthma participated in the examinations, 23 (35.9 percent) of them were men, 41 (64.1 percent) were women. The average of the patients participating in the study was 46.4±1.43, and they ranged from 16 to 70 years. Patients were examined and monitored at the multidisciplinary medical center in Termez. In order to ensure the transparent conduct of scientific research and patient safety, contracts were drawn up between patients and clinics, and letters of consent were obtained from patients confirming whether or not they could participate in the study. We defined the criteria for selecting or rejecting patients to participate in the study, according to which:Patient selection criteria-patient consent; presence of BA diagnosis; mental health; absence of severe somatic disease; those over 16 years old. The criteria for rejecting patients are those with mental inadequacy, severe genetic disease, smokers (cigarettes, tobacco), severe somatic pathology, those under 16 and over 70 years old.In order to achieve objective and real results, 64 (100 percent) patients with bronchial asthma were interpreted as group 1, and 45 practically healthy people were selected as a comparison group and recognized as group 2 (Fig. 1).
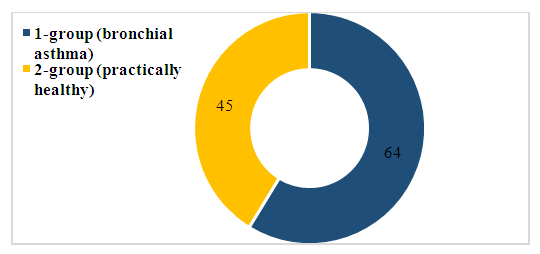 | Figure 1. Group allocation and number of study participants |
3. Methods and Materials of Research
- The research includes collecting objective and subjective materials, in-depth analysis of anamnesis data, statistical data on the prevalence of the disease in the Surkhandarya region, general blood analysis, serological-IgE testing, enhanced X-ray examination of the lungs, spirometry, methods of checking polymorphism alleles and genotypes of IL17A, IL23R, IL17F genes. was conducted. The obtained results were compared between patients with bronchial asthma and practically healthy people.
4. Results and Their Discussion
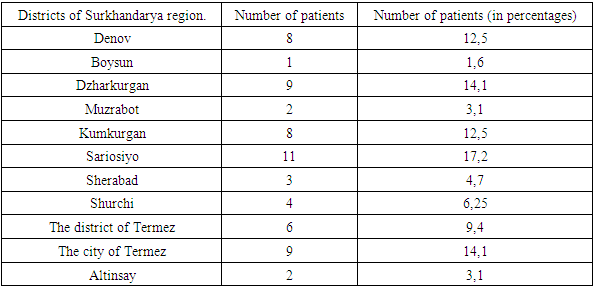
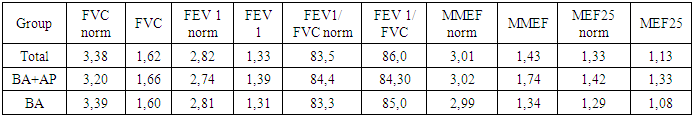
- Based on the conducted research, the prevalence of the disease was analyzed in the Surkhandarya region, and according to it, the most common area of bronchial asthma is Jarqo ‘rgon district 9 (14.1 percent), Kumkurgan district 8 (12.5 percent), Sariosiyo district 11 (17.2 percent), Termiz city 9 (14.1 percent), Denov district 8 (12.5 percent) (Table 1). At this point, it is worth saying that in the Surkhandarya region, we are witnessing the development of severe clinical manifestations of bronchial asthma, which has an allergic basis, in the districts where the environment, weather, and the ecosystem in general are disturbed.
|
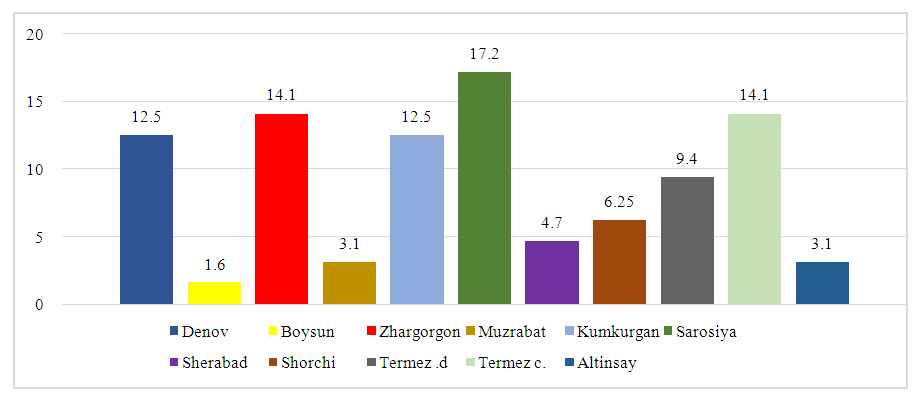 | Figure 2. Distribution of the disease in the regions |
|
|
|
|
5. Medical Effectiveness of the Study
- Medical effectiveness is the level of achieving the result of restoring human health. On the example of a specific patient, we inter pret about restoring health, improving mental and social health, restoring damaged functions in organs and tissues. Medical efficiency at the level of healthcare institutions and the industry as a whole is measured by many specific indicators: the number of people, the number of correct and timely diagnoses, the percentage of patients treated, the duration of bronchial asthma, the reduction of transition to severe complications, the prevention of death from this disease, etc. By applying the above mentioned complex diagnosis method, medical efficiency increases with real relativity, and as a simple, convenient method, it can be used by doctors in remote rural medical centers, early diagnosis can be referred to narrow specialists, and constant monitoring can be carried out, and these actions do not require additional effort and funds. Through this comprehensive examination-diagnostic method, correct and early diagnosis was made in 64 (63.3 percent) of 101(100 percent) patients. Inpatient treatment was recommended. Timely treatment of 54 (84.4%) patients reduced the duration, recurrence, intensity and number of attacks, and eliminated symptoms such as breathing, vegetative changes, fear, restlessness, swelling of the face, shortness of breath, sleep disorders.
6. Social Significance
- If we study the epidemiology of bronchial asthma, we can be sure that it is a huge problem in the health system -Today, more than 358 million people worldwide suffer from asthma, which is 4 to 10 percent of the adult population of the planet, and according to some other sources, by 2025 it is suspected that by the year this indicator will reach 400 million people. In general, in 2018-2019, the prevalence of respiratory diseases decreased by 100,000 in the Republic of Uzbekistan. During this period, the prevalence of asthma also decreased by 0.1% in absolute terms and by 3.5% per 100,000 population. In addition, the incidence of asthma and other respiratory diseases decreased both in absolute terms (16.3% and 1.9% reductions, respectively) and per 100,000 population (18.7% and 4.8% reductions, respectively). The dangerous situation regarding the spread of asthma is typical for Tashkent, Andijan, Jizzakh, Kashkadarya, Tashkent, Khorezm regions, and if we take into acco unt the possibility of infection, the dangerous situation is typical for Andijan, Kashkadarya, Surkhandarya, Fergana, Khorezm region sand the Republic of Karakalpakstan.Among the factors that cause this trend, urbanization and environmental weather, the destruction of the ecosystem in general, especially in large cities and megacities, are of great importance. An increase in the number of patients with severe asthma leads to a significant decrease in labor productivity and requires an increase in the costs of the health care system. In addition, asthma is one of the main causes of disability and a decrease in the quality of life of patients, severe bronchial asthma is explained by the frequent occurrence of attacks, a sharp decrease in breathing, a decrease in saturation, damage to the heart, vascular system, and finally death. In practice, early detection, prevention, preventing the development of complications and timely initiati on of preventive therapy allow to reduce premature death and disability.
7. Conclusions
- 1. The result of the analysis showed that the developed method of early diagnosis of bronchial asthma makes it possible to detect the disease early and start treatment as early as possible;2. As a result of early diagnosis and early treatment, medical, social and economic efficiency of disease treatment is achieved;3. Subjective, objective, anamnestic, instrumental, and laboratory examinations of patients will be carried out systematically, early diagnosis of the disease and referral to narrow specialists and selection of differential treatment procedures will be sys tematically implemented.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML