-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2024; 14(7): 1777-1780
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20241407.10
Received: Jun. 16, 2024; Accepted: Jul. 6, 2024; Published: Jul. 9, 2024

Optimization of Surgical Treatment for Rectal and Rectosigmodal Forms of Hirsprung's Disease in Preschool Children
Odilbek T. Ollabergenov, Bilim A. Terebaev, Alisher Sh. Nematov
Department of Pediatric Surgery, Tashkent Pediatric Medical Institute, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Backdround: Surgical correction of Hirschsprung's disease in children is one of the most difficult and pressing problems in pediatric surgery, since the number of unsatisfactory functional results in the long-term postoperative period is about 30% among all operated patients. Determination of surgical tactics, improvement of existing ones and development of new minimally invasive modified methods and methods for treating rectal and rectosigmoid forms of Hirschsprung's disease are the basis of scientific and practical research carried out by many leading clinics in the world. Methods: In the pediatric surgery clinic of the Tashkent Pediatric Medical Institute, from 2017 to 2023, 95 preschool children with rectal and rectosigmoid forms of Hirschsprung’s disease were treated as inpatients. Results: A comparative analysis of surgical interventions for Hirschsprung's disease showed that traditional methods (Soave-Lenyushkin: 17.9%, Swenson: 12.6%) had higher complication rates. Minimally invasive techniques (Swenson-like: 18.9%, De la Torre-Mandragon: 50.5%) were more effective, with fewer complications. Preoperative antibacterial prevention and colon decompression were crucial for successful outcomes. Conclusion: The studies carried out allowed us to conclude that in the treatment of rectal and rectosigmoid forms of Hirschsprung's disease in children, minimally invasive endorectal methods of surgical intervention are more effective and physiological; when they are carried out, the immediate and long-term results of treatment are significantly higher compared to traditional open interventions.
Keywords: Hirschsprung's disease, Chronic colostasis, Diagnosis, Surgical treatment, Children
Cite this paper: Odilbek T. Ollabergenov, Bilim A. Terebaev, Alisher Sh. Nematov, Optimization of Surgical Treatment for Rectal and Rectosigmodal Forms of Hirsprung's Disease in Preschool Children, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 14 No. 7, 2024, pp. 1777-1780. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20241407.10.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Surgical correction of Hirschsprung's disease in children is one of the most complex and pertinent issues in pediatric surgery. Significant progress has been made in recent decades through the introduction of high-tech surgical treatment methods [1-4,8,10,12,13]. However, despite advancements in many surgical techniques, approximately 30% of operated patients experience unsatisfactory functional outcomes in the long-term postoperative period. The main reasons for these unsatisfactory results, which prevent achieving good functional outcomes, include the patient's age, secondary changes due to prolonged colostasis affecting both the intestines and the body as a whole, inappropriate timing of defect correction, choice of surgical method and technique, associated developmental anomalies, inadequate preoperative preparation and postoperative management, as well as insufficient patient rehabilitation [5-7,9,11,14].Many issues related to early diagnosis, choice of surgical tactics, development of new modified minimally invasive techniques, and improvement of existing treatment methods form the basis of in-depth scientific research aimed at addressing this critical problem. Years of accumulated experience in treating this severe patient population have allowed us to revise traditional surgical correction methods for Hirschsprung's disease in children and implement new minimally invasive techniques, significantly improving immediate and long-term treatment outcomes. At the same time, these alternative treatment methods are not a panacea and remain controversial, requiring resolution and recognition by many specialists dealing with this complex pathology.Research Objective: To improve and implement minimally invasive surgical methods for treating rectal and rectosigmoid forms of Hirschsprung's disease in children.
2. Material and Methods
- Study design and participantsIn the pediatric surgery clinic of the Tashkent Pediatric Medical Institute, from 2017 to 2023, 95 preschool children with rectal and rectosigmoid forms of Hirschsprung’s disease were treated as inpatients. We divided these patients into two comparison groups: the first control group included 29 (30.5%) patients who underwent traditional open surgical interventions and the second main group consisted of 66 (69.5%) patients who underwent the Swenson video-assisted transanal endorectal method -like with resection of the aganglionosis zone.Clinical manifestations of rectal and rectosigmoid forms of Hirschsprung's disease in both compared groups were varied and largely depended on the length of the aganglinar zone and the degree of suprastenotic expansion of the colon, the duration of chronic colostasis and fecal intoxication, as well as the presence of concomitant pathology. The compensated stage of the disease was detected in 84 (88.4%) patients, subcompensated in 7 (7.4%) and decompensated in 4 (4.2%) cases. The objectives of our research included not only a comparative assessment of surgical correction of rectal and rectosigmoid forms of Hirschsprung's disease in preschool children, but also the development of effective and optimal methods of conservative therapy and rehabilitation of patients aimed at achieving positive long-term functional results and full social adaptation of children in society.ProceduresDepending on the anatomical and functional state of the colon in patients with rectal and rectosigmoid forms of Hirschsprung's disease, we used the optimal diagnostic protocol.
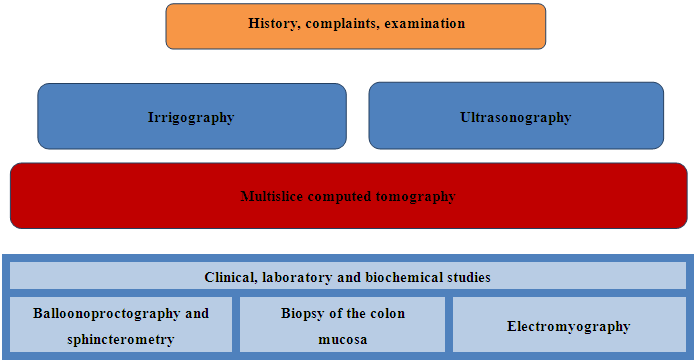 This protocol included clinical, laboratory, and biochemical studies, ultrasound scanning of the external anal sphincter muscles, barium enema, balloon proctography, multislice computed tomography (MSCT), and mucosal biopsy of the colon. The barium enema was performed to identify the transitional pathological section of the colon. Balloon proctography was used to assess the functional integrity of the puborectalis muscle and the anorectal angle. The aim of MSCT was to determine the anatomical integrity of the pelvic muscles. A mucosal biopsy was conducted to identify the aganglionic and dilated zones of the colon. This diagnostic protocol outlines the sequence and advantages of each method, enabling differential diagnosis with various colon pathologies associated with chronic colostasis. It is important to note that these standardized diagnostic methods for children with Hirschsprung's disease provide critical information that directly influences the choice of surgical tactics, methods, and techniques.
This protocol included clinical, laboratory, and biochemical studies, ultrasound scanning of the external anal sphincter muscles, barium enema, balloon proctography, multislice computed tomography (MSCT), and mucosal biopsy of the colon. The barium enema was performed to identify the transitional pathological section of the colon. Balloon proctography was used to assess the functional integrity of the puborectalis muscle and the anorectal angle. The aim of MSCT was to determine the anatomical integrity of the pelvic muscles. A mucosal biopsy was conducted to identify the aganglionic and dilated zones of the colon. This diagnostic protocol outlines the sequence and advantages of each method, enabling differential diagnosis with various colon pathologies associated with chronic colostasis. It is important to note that these standardized diagnostic methods for children with Hirschsprung's disease provide critical information that directly influences the choice of surgical tactics, methods, and techniques.3. Results and Discussion
- A comparative analysis of surgical interventions performed for rectal and rectosigmoid forms of Hirschsprung's disease was carried out on the basis of a differentiated approach to the choice of method and method for correcting the defect. Open traditional surgical interventions were performed using the Soave-Lenyushkin method in 17 (17.9%) patients and O. Swenson in 12 (12.6%) cases. The rationale for choosing these open techniques was that in preschool children with rectal and rectosigmoid forms of Hirschsprung's disease, submucosal dissection is easy, even in the presence of a significant aganglinar zone of the colon. Minimally invasive video-assisted transanal endorectal interventions with resection of the aganglionic zone of the colon in the rectal and rectosigmoid forms of Hirschsprung's disease were performed using the Swenson-like method in 18 (18.9%) patients and the De la Torre - Mandragon method in 48 (50.5%) patients. It should be noted that important importance in preparing patients for surgical intervention was given to the timely implementation of preoperative antibacterial prevention of possible complications in the field of surgical exposure and normalization of the biocenosis in patients with rectal and rectosigmoid aganglionosis of the colon, as well as decompression of the colon and its complete emptying, which was carried out by performing daily and regular cleansing or siphon enemas.Traditional surgical intervention according to the Soave-Lenyushkin method, performed in 17 (17.9) patients, was carried out with mobilization of the sigmoid colon at a level of at least 4 cm to the transitional fold of the peritoneum with preservation of the superior rectal artery. This distinctive feature was a fundamental point of surgical intervention, since when crossing the sigmoid colon, the venous outflow should not be disrupted and the vascularization of the muscle cylinder should be preserved. The next stage of the operation was complete demucosation of the submucosal layer of the rectosigmoid region, which ended at a level of up to 2 cm above the mucocutaneous junction, since excessive mobilization of the mucous membrane is always fraught with damage to the nerve receptors located in the area of the morganian ridges and anal crypts. Then the mobilized intestine is brought down through the seromuscular sheath, on top of which lies the rectal mucosa. The excess intestine protruding through the anus is left hanging freely in the form of a stump, and 2 weeks after the formation of the muff, the stump is circularly excised, while the edges of the mucous membrane and the muff are connected with interrupted sutures, which helps restore the anatomical and topographic relationships in the terminal part of the rectum.The O. Swenson operation using the classical method in our studies was performed in 12 (12.6%) patients with an extended aganglionic zone. The main principle of this intervention was that in the case of the rectal form, the sigmoid arteries were intersected; in the case of the rectosigmoid form, the left colic artery was additionally dissected. Then, the mobilized colon was evaginated through the anus and a complete resection of the aganglionic zone was performed with dissection of the rectum along its outer wall to the upper border of the external sphincter while maintaining the venous outflow in the pelvis. After that, the rectum was transected in an oblique direction with the imposition of a sealed coloanal anastomosis.The results of traditional surgical interventions were monitored in the immediate and long-term observation periods, and it was found that when performing abdominal-perineal proctoplasty using the Soave-Lenyushkin method, despite the control of complete demucosation and the absence of nerve damage during rectal dissection, an unsatisfactory result was noted in 8 patients in the form: postoperative anal incontinence in 3 cases and stenosis of the colorectal anastomosis in 5 observations. The cause of postoperative anal incontinence in these 3 patients was due to an increase in pressure in the anal canal, due to the created duplication of the seromuscular layer of the rectum and rectum, as well as incomplete synergism of the fibers of the internal and external sphincters of the rectum, which ultimately led to accumulation and prolonged stagnation fecal matter, which was accompanied by involuntary release of intestinal contents. The occurrence of stenosis of the colorectal anastomosis in 5 patients was due to a postoperative inflammatory process at the site of fixation of the reduced intestine in the anus, as well as diastasis between the mucous membrane of the reduced intestine and the rectal stump.Similar complications were noted during the O. Swenson operation, which were noted in 6 patients. Despite observing all the principles of the classical implementation of the O. Swenson technique, the treatment results in our studies were not reassuring, which was expressed in a high percentage of complications, such as: stenosis of the anastomotic zone - in 2 patients, postoperative anal incontinence - in 4 observations.The video-assisted transanal endorectal Swenson-like method with resection of the aganglionosis zone was performed in 18 (18.9%) patients with rectal and rectosigmoid forms of Hirschsprung's disease. The essence of this intervention was that after intra-abdominal isolation of the rectum, a circular incision was made from the mucous membrane of the anal canal (1 cm above the dentate line) through the entire thickness of the intestinal wall, and then the seromuscular sheath, which retains the aganglionic fibers, was excised. The peculiarity of this technique is that the rectosigmoid part of the colon is isolated as high as possible, while fixation of the descending colon allows this, and reliable ligation of the vessels is necessary. The use of the Swenson-like correction method has shown its effectiveness from the point of view of the fact that this technique is performed without prior application of a sigmostoma, and the results obtained in our observations were assessed as good and satisfactory in 90% of patients.The endorectal method of proctoplasty De la Torre - Mandragon with resection of the aganglionic zone of the colon was performed in 48 (50.5%) patients with rectal and recto-sigmoid forms of Hirschsprung's disease. This method of surgical intervention was performed mainly in children of the younger age group, since the most important stage of the De la Torre - Mandragon method - transanal demucosation of the mucous membrane of the seromuscular cylinder of the rectum from the perineum, in the technical aspect, proceeds more favorably in them. The next stage of the operation was the isolation of the mucous membrane of the anal canal in the proximal direction to the peritoneum, followed by mobilization of the rectum and sigmoid colon for their removal through the anus. Then, above the area of aganglionosis above the transitional expanded zone of the pathological area, the large intestine was crossed and a coloanal anastomosis was performed. The advantage of this method is: surgical intervention without laparotomy, minimal trauma during mobilization of the sigmoid and rectum, the possibility of early rehabilitation in the postoperative period, good and functionally satisfactory treatment results. In the immediate postoperative period and follow-up observation showed that the De la Torre - Mandragon method is effective, but it is not without certain disadvantages, such as pain that appears for a certain time during defecation, identified in 9 observations. One patient had a fatal outcome, the cause of which was the divergence of the anastomotic sutures, which led to the development of diffuse purulent fecal peritonitis.A retrospective analysis of traditional and minimally invasive surgical interventions performed by us in the treatment of rectal and rectosigmoid forms of Hirschsprung's disease showed fundamental differences not only in the technique of execution, but also in the immediate and long-term results obtained after surgery. Treatment of complications that arose directly in the immediate and long-term periods of time was carried out comprehensively using rehabilitation measures aimed at normalizing the function of the colon and the entire digestive tract. Stenosis of the colorectal anastomosis after traditional open interventions was resolved as a result of daily bougienages (the duration of which depended on the severity of the stenosis). In case of unsatisfactory treatment results in the form of postoperative anal incontinence, a set of conservative therapy measures was used, in which an individual program was determined depending on the degree of anal incontinence, the presence of severity of deformities in the anal area, as well as the nature of the stool and the consistency of stool. Most often, rehabilitation measures were aimed at restoring impaired neuro-reflex connections in the anal area, which was performed by contact intraanal electrical stimulation of the sphincter apparatus, therapeutic herbal training enemas, vitamin therapy, physical therapy and selection of a diet that reduces stool frequency.
4. Conclusions
- Our studies clearly allow us to conclude that in the treatment of rectal and rectosigmoid forms of Hirschsprung's disease in children, preference should be given to minimally invasive transanal endorectal reduction methods, since they are less traumatic, gentle and the most effective in terms of the radicality and physiology of the intervention. Traditional extensive surgical interventions are characterized by technical complexity, insufficient functionality and relatively worse immediate and long-term treatment results, sometimes requiring repeated surgical corrections and long-term rehabilitation measures. Conservative therapy and rehabilitation measures in patients with complications after previously performed surgical interventions for rectal and rectosigmoid forms of Hirschsprung's disease in children require an integrated approach to obtain a positive result in the form of restoration of the multifactorial mechanism of the rectal obturator apparatus.
Conflict of Interest
- The authors declare no conflict of interest.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML