-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2024; 14(6): 1629-1631
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20241406.33
Received: May 14, 2024; Accepted: Jun. 2, 2024; Published: Jun. 19, 2024

Pathomorphological Characteristics of Gallbladder Adenoma
Jumanov Ziyadulla Eshmamatovich1, Khamidov Obid Abdurakhmanovich2, Beknazarova Xolniso Nurillo Kizi3
1Associate Professor of the Department of Pathological Anatomy of Samarkand State Medical University, Doctor of Medical Sciences (DSc), Uzbekistan
2Head of the Department of Medical Radiology, Faculty of Postgraduate Education, Samarkand State Medical University, Doctor of Philosophy (PhD), Associate Professor, Uzbekistan
31st Year Basic Doctoral Student of the Department of Medical Radiology, Faculty of Postgraduate Education, Samarkand State Medical University, Uzbekistan
Correspondence to: Jumanov Ziyadulla Eshmamatovich, Associate Professor of the Department of Pathological Anatomy of Samarkand State Medical University, Doctor of Medical Sciences (DSc), Uzbekistan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

In order to determine the morphological features of the gallbladder adenoma, revealed by ultrasound examination, fragments of the gallbladder adenoma taken during the operation of 26 patients were subjected to morphological examination. It has been established that the frequency of meeting tubular, papillary and tubular-papillary adenomas in the gallbladder clearly differs from each other. It is noted that the gallbladder adenoma consists mainly of prismatic epithelium.
Keywords: Bile bubble, Adenoma, Morphology, Aspect
Cite this paper: Jumanov Ziyadulla Eshmamatovich, Khamidov Obid Abdurakhmanovich, Beknazarova Xolniso Nurillo Kizi, Pathomorphological Characteristics of Gallbladder Adenoma, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 14 No. 6, 2024, pp. 1629-1631. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20241406.33.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- In recent years, a sharp increase in the number of patients suffering from the formation of good-quality polypoid formations of the gallbladder has been observed all over the world. According to the literature, the prevalence of this pathology is 4-6% [1]. The percentage of surgical interventions performed for the safe derivatives of the gallbladder is 10-15.8% of the total number of cholecystectomies [5]. From 57% to 80% of benign gallbladder tumors are cholesterol "polyps" with a histologically heterogeneous structure [6]. Among gall bladder polyps, papillomas make up 25.5%, adenomas - 11%, they are usually small in size, and in 72% of cases they can affect ducts in addition to the gallbladder [7]. Diagnosis of gallbladder polyps is primarily based on ultrasound. In addition, this method allows you to diagnose this pathology with high frequency. One or more exogenous formations of polyps are diagnosed, which, unlike gallstones, do not move when the patient turns from one side to the other. In addition, there will be no acoustic shadowing of polyps [2].
2. The Purpose of the Study
- To determine the morphological characteristics of the adenoma of the gallbladder detected by ultrasound examination.
3. Materials and Methods
- In the surgical department of the multidisciplinary clinic of Samarkand State Medical University, tissue fragments were taken from the changed part of the gallbladder, which was surgically removed from 26 (23 women, 3 men) patients with gallbladder adenoma. Histological sections prepared from the slices were stained with hematoxylin and eosin.Hematoxylin and eosin staining procedure:It is the most widely used method for staining histological sections.Sections are deparaffinized in chloroform, washed in distilled water, then a solution of hematoxylin is dripped onto the surface of the section and fixed for 3 minutes. It is washed in running water for 10 minutes and stained with eosin for 0.2 to 3 minutes. Dehydrated in 70° and 96° alcohol, transferred to carbol-xylene and xylene and covered with balsam.Result: cell nuclei are stained blue-black, cytoplasm - dark purple.Histological preparations were studied and photographed using a LeicaGME microscope (Leica, India) coupled with a LeicaEC3 digital camera (Leica, Singapore) and a Pentium IV computer. Photo processing was carried out using Windows Professional applications.Gallbladder adenoma was morphologically evaluated in prepared micropreparations.
4. Results and Discussion
- Gallbladder of 26 patients, who were surgically removed due to the diagnosis of gall bladder formation detected by ultrasound, were examined by macroscopic examination. Microscopic examination revealed tubular adenoma of the gallbladder in 18 patients (Fig. 1). They are women with an average age of 58±4.0. Papillary type was identified in 6 people, their average age was 51±3.0, of which 4 were women and 2 were men. Tubular-papillary type was noted in the remaining 2 (their average age is 45±5.0. 1 (50%) female and 1 (50%) male).
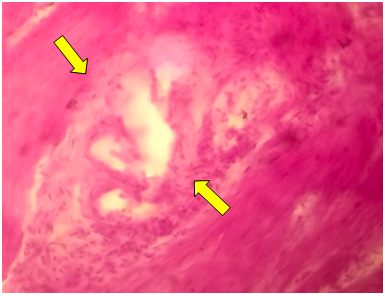 | Figure 1. Tubular adenoma of the gallbladder. Prismatic epithelium located in pyloric glands. Stained in hematoxylin-eosin. Ob.40, ok.10 |
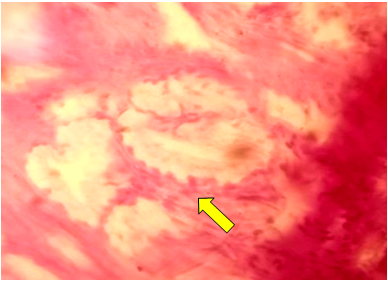 | Figure 2. Tubular adenoma of the gallbladder. Cystic changes of the pyloric type. Stained in hematoxylin-eosin. Ob.40, ok.10 |
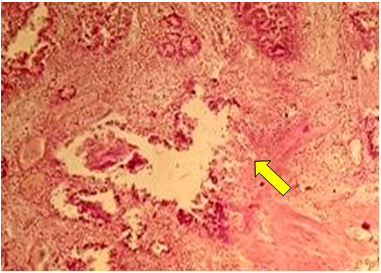 | Figure 3. Tubular adenoma of the gallbladder. Single cystic enlargement of the gland. Stained in hematoxylin-eosin. Ob.40, ok.10 |
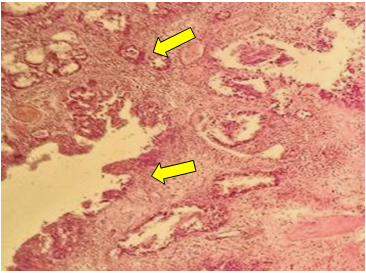 | Figure 4. Papillary adenoma of the gallbladder. Metaplasia of some epithelia in the peripheral area. Stained in hematoxylin-eosin. Ob.40, ok.10 |
5. Conclusions
- Thus, the frequency of meeting tubular, papillary and tubular-papillary adenomas in the gallbladder is clearly different from each other. In particular, the incidence of tubular adenoma of the gallbladder is higher. Gallbladder adenomas, regardless of type, are made up of more prismatic epithelium, and dysplasia and metaplasia are observed in them. It is necessary to eliminate these pathological processes in time before they turn into adenocarcinoma, and a comparative analysis of the obtained adenomas with adenocarcinoma of the gallbladder must be carried out.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML