-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2024; 14(6): 1627-1628
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20241406.32
Received: May 15, 2024; Accepted: Jun. 3, 2024; Published: Jun. 19, 2024

Morphological Characteristics of Pituitary Gland Adenomas
Khamidov Obid Abdurakhmanovich1, Jumanov Ziyadulla Eshmamatovich2, Gaybullaev Sherzod Obid Ugli3
1Head of the Department of Medical Radiology, Faculty of Postgraduate Education, Samarkand State Medical University, Doctor of Philosophy (PhD), Associate Professor, Uzbekistan
2Associate Professor of the Department of Pathological Anatomy of Samarkand State Medical University, Doctor of Medical Sciences (DSc), Uzbekistan
31st Year Basic Doctoral Student of Medical Radiology of the Faculty of Postgraduate Education of Samarkand State Medical University, Uzbekistan
Correspondence to: Khamidov Obid Abdurakhmanovich, Head of the Department of Medical Radiology, Faculty of Postgraduate Education, Samarkand State Medical University, Doctor of Philosophy (PhD), Associate Professor, Uzbekistan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

In order to determine the pathomorphology of pituitary gland adenomas detected by magnetic resonance imaging, the pieces of pituitary gland adenoma taken from 14 patients during neurosurgery were subjected to morphological examination. It was found that a low level of polymorphism is observed in eosinophilic adenoma of the pituitary gland. This is manifested by the different size of the cells, the different sizes of their nuclei and their irregular arrangement. It is noted that the cells of chromophobe adenoma are small in size, the cytoplasm is dim, their cells sometimes grow into the epidural area, sometimes they erode the bone tissue where they are located and grow into the brain tissue.
Keywords: Pituitary gland, Eosinophilic adenoma, Chromophobe adenoma, Pathomorphology
Cite this paper: Khamidov Obid Abdurakhmanovich, Jumanov Ziyadulla Eshmamatovich, Gaybullaev Sherzod Obid Ugli, Morphological Characteristics of Pituitary Gland Adenomas, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 14 No. 6, 2024, pp. 1627-1628. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20241406.32.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Pituitary adenomas are one of the most common primary intracranial tumors. Usually benign, they account for 10–15% of all intracranial neoplasms [1,5]. Pituitary adenomas are very diverse, and among all brain tumors, pituitary adenomas account for 18% of all brain tumors in adults and occur equally in men and women. 50% of all pituitary adenomas occur in people aged 30-50 [3]. Magnetic resonance imaging remains the leading method for X-ray diagnosis of pituitary tumors. However, in the practice of neurosurgery, the pathomorphological justification of removed pituitary adenomas is important [4].
2. The Purpose of the Study
- Determination of the pathomorphology of pituitary gland adenomas detected by magnetic resonance imaging.
3. Materials and Methods
- Tissue fragments of 1x1x0.5 cm were taken from 14 (10 of them male, 4 female) patients who were diagnosed by magnetic resonance imaging in the multidisciplinary clinic of the Samarkand State Medical University. Hematoxylin and eosin for histological sections prepared from slices.Hematoxylin and eosin staining procedure:It is the most widely used method for staining histological sections.Sections are deparaffinized in chloroform, washed in distilled water, then a solution of hematoxylin is dripped onto the surface of the section and fixed for 3 minutes. It is washed in running water for 10 minutes and stained with eosin for 0.2 to 3 minutes. Dehydrated in 70° and 96° alcohol, transferred to carbol-xylene and xylene and covered with balsam.Result: cell nuclei are stained blue-black, cytoplasm - dark purple.Histological preparations were studied and photographed using a LeicaGME microscope (Leica, India) coupled with a LeicaEC3 digital camera (Leica, Singapore) and a Pentium IV computer. Photo processing was carried out using Windows Professional applications.
4. Results and Discussion
- In our study, eosinophilic type of surgically removed pituitary adenoma was detected in 8 cases, and chromophobe type was detected in the remaining 6 cases. Microscopically, these adenomas have the following structure: in the chromophobe adenoma of the pituitary gland, in the preparations prepared for our study, the cell body is oval, and in other preparations, the cell body is polygonal, and the nucleus is oval and round. A state of necrosis of some cells is observed. It is noted that the cytoplasm is stained light pink. Remains of small blood vessels are visible between tumor cells and diapedesis hemorrhages are detected (Fig. 1).
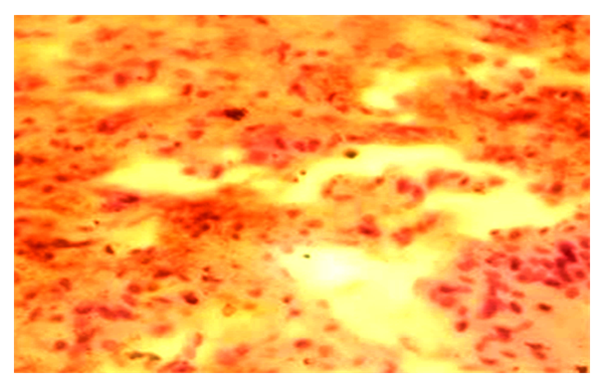 | Figure 1. Chromophobe adenoma of the pituitary gland. Diapedesis bleeding. Stained in hematoxylin-eosin. Ob.40, ok.10 |
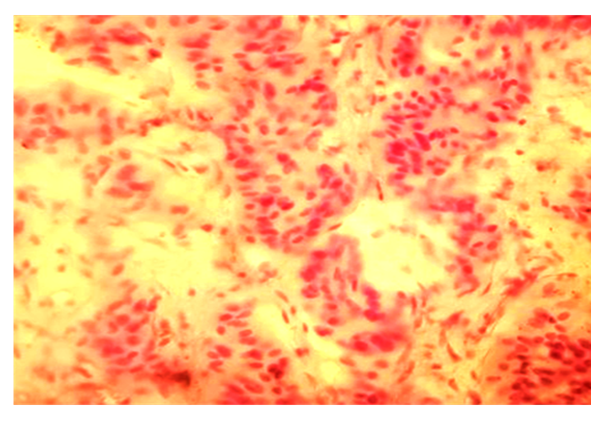 | Figure 2. Chromophobe adenoma of the pituitary gland. Stained in hematoxylin-eosin. Ob.40, ok.10 |
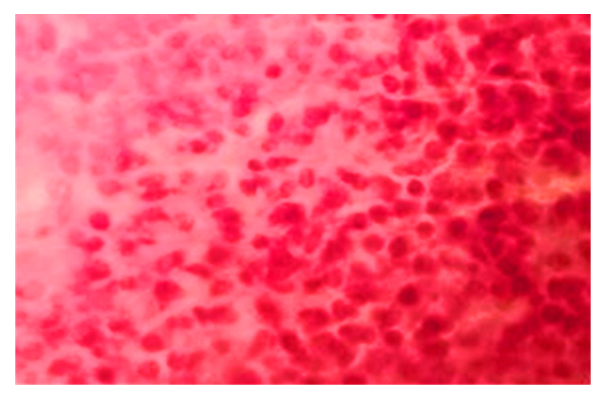 | Figure 3. Eosinophilic adenoma of the pituitary gland. Stained in hematoxylin-eosin. Ob.40, ok.10 |
5. Conclusions
- Thus, a low level of polymorphism is observed in eosinophilic adenoma of the pituitary gland. This is manifested by the different size of the cells, the different sizes of their nuclei and their irregular arrangement. It is noted that the cells of chromophobe adenoma are small in size, and the cytoplasm is dim. Tumor cells sometimes grow into the epidural area, sometimes they erode the bone tissue where it is located. In particular, the detection of neurons in the peripheral areas of chromophobe adenoma indicates the possibility of shallow growth into the brain tissue.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML