-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2024; 14(5): 1346-1350
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20241405.42
Received: Apr. 28, 2024; Accepted: May 17, 2024; Published: May 21, 2024

To Assess the Effectiveness of Preoperative Preparation and Postoperative Management of Patients with Pelvic Organ Prolapse in the Retrospective and Prospective Groups
Nazarov B. B., Niyazmetov R. E.
Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Bukhara State Medical Institute, Bukhara, Uzbekistan
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Genital prolapse remains one of the unsolved problems of modern gynecology. The aim of the study is to improve the preoperative preparation and postoperative management of patients with grade III pelvic organ prolapse, using modern innovative technology in combination with drugs to reduce postoperative complications and relapses. Materials and methods of research. The object of the study was 217 patients with grade III pelvic organ prolapse who underwent surgical treatment. Results and discussion. 110 women with grade III PG received an improved method of preoperative preparation, including irrigation with cavitated low-frequency ultrasound with an aqueous 0.05% chlorhexidine solution in the amount of 200.0, up to 4 times, locally conjugated estrogen, and in the presence of urinary tract infection, acute cystitis - once fosfomycin trimetabol 3.0 grams orally, in recurrent forms of phytopreparation (Canephron N) for 14.5 ±2.5 days. Conclusion: The improved method of preoperative preparation of patients with PTO of the III degree contributed to the reduction of the days of preoperative preparation by 6.0±0.5 days, reduced interoperative blood loss by 2.0 times, reduced the duration of the operation by 37.0±6.35 minutes, the hospital stay decreased by an average of 3.5±0.5 days, and postoperative recurrences after 1 year decreased by 2.4 times and after 2 years by 2.8 times.
Keywords: Pelvic organ prolapse, Genital prolapse, Irrigation, Conjugated estrogen, Relapse
Cite this paper: Nazarov B. B., Niyazmetov R. E., To Assess the Effectiveness of Preoperative Preparation and Postoperative Management of Patients with Pelvic Organ Prolapse in the Retrospective and Prospective Groups, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 14 No. 5, 2024, pp. 1346-1350. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20241405.42.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Genital prolapse (PH) is a pathological process characterized by the prolapse and prolapse of the internal genitalia to or beyond the vaginal opening. PH is both a medical and social problem, leading to a reduced quality of life [1,4]. This pathology creates discomfort, causes urinary incontinence, constipation, leads to a decrease in libido, i.e. problems associated with sexual dysfunctions arise. In more advanced cases of genital prolapse, Trophic ulcers of the mucous membrane of the anterior wall of the vagina and cervix appear. [3,10]. One of the relevances of this pathology is due to its high prevalence, high index of infectious and inflammatory diseases against the background of a pronounced violation of the vaginal microbiocenosis and urinary tract infection, as well as a high frequency of recurrences in the postoperative period [1,2,9].According to the WHO, there has been a significant increase in the number of patients suffering from genital prolapse worldwide in recent years. Today, between 6.5% and 64.6% of women suffer from PH of varying severity at different stages of life and in postmenopause, and their number in the world could reach 63 million by 2030. According to the American Association of Urology (AUA), one in nine women in the general population needs surgical treatment of genital prolapse and/or stress urinary incontinence. Every year, approximately 400,000 women in the United States in an economically developed country undergo surgery for PH, however, the incidence of long-term postoperative recurrences is up to 30%, and early postoperative purulent infectious complications are 4 to 9%, which requires a new search for a solution to this problem [9].The ongoing scientific study of optimization of preoperative preparation and postoperative management of patients with genital prolapse, the use of modern innovative technologies reduces interoperative, early, long-term complications and relapses in this pathology.The aim of this study is to improve the preoperative preparation and postoperative management of patients with grade III pelvic organ prolapse by using modern innovative technology in combination with drugs to reduce postoperative complications and relapses.
2. Material and Methods of Research
- The object of the study was 217 patients with grade III pelvic organ prolapse who underwent surgical treatment. The collection of materials, analysis and evaluation of the results of preoperative preparation and postoperative management of patients with pelvic organ prolapse in a comparative aspect was also carried out in the period from 2019 to 2022 on the basis of the gynecological department of the Bukhara district maternity hospital, the regional perinatal center and the private clinic "Lorastom". General clinical, biochemical, instrumental and statistical research methods were used in the study.
3. Discussion of the Results
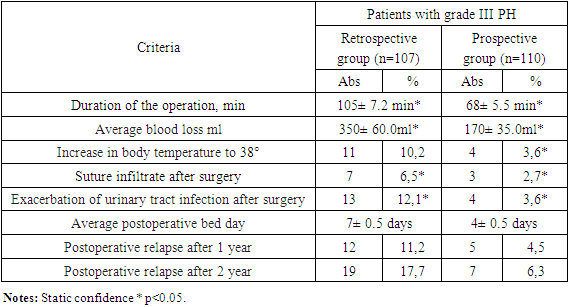
- To assess the effectiveness of preoperative preparation and postoperative management of patients with grade III pelvic organ prolapse retro and prospective group, the object of the study was 217 women with grade III prolapse. All 217 patients with grade III pelvic organ prolapse were divided into two groups depending on the method of preoperative preparation and postoperative management.Group I A (1A) – (retrospective-control) – 107 women with grade III PG, who received traditional preoperative preparation: vaginal debridement with a 1% alcohol solution of chlorophyllipt, ointment tamponade with Levomycol and Ovestin (micronized estriol 0.5 mg, vaginal suppositories 1 suppository per night) for 10±1.5 days. In the presence of urinary tract infection, recurrent and acute cystitis, the antibiotic Ceftriaxone was received 1.0x2 times for 7.0±2 days. Rehabilitation of gynecological and somatic diseases.The first B group (1B) – (prospective) – 110 women, also with stage III PH, who received an improved method of preoperative preparation and postoperative treatment. In the preoperative preparation, the FOTEC AK 101 device was used with cavitated low-frequency ultrasound with an aqueous 0.05% chlorhexidine solution in the amount of 200.0, up to 4 times, the level of ultrasonic vibrations was 50 units and the duration of exposure was 3 minutes. After 8 hours, 1.0 g of conjugated estrogen cream (femistron) was smeared on the entire prolapsed surface of the vaginal and uterine mucosa once a day, for 4.0±0.5 days. In the postoperative period, a three-component drug was received (Metostyl, 1 in the vagina at night for 5 days). In the presence of urinary tract infection, acute cystitis, a single dose of phosfomycin trimetabol 3.0 grams orally was given, in recurrent forms of phyto preparation (Canephron N) for 14.5 ±2.5 days. Studying the causes of PTO of the third degree in the retrospective and prospective groups from a comparative perspective, the following factors played a significant role: the number of pregnancies and births, concomitant somatic diseases, estrogen deficiency in the menopausal period, profession and age. The peak incidence of PTO grade III occurred at the age of 40 to 59 years. At this age, this pathology occurred in the retrospective group in 62 (57.9%), in the prospective group in 74 (67.2%) p<0.05. It should be noted that in patients with PTO of the third degree of both groups, this pathology was mainly observed after the third birth. In the retrospective group after III-IV births, PTO grade III was detected in 72 (67.2%), and in the prospective group in 81 (73.6%) p<0.05. 88 (82.2%) in the retrospective group and 89 (80.9%) p<0.05 in the prospective group gave birth through the vaginal canal, which is one of the main risk factors for the development of PT. As indicated in the literature review, the influence of this factor is reflected in studies aimed at studying the so-called "bloating" phenomenon: 3D ultrasound after childbirth with the Valsalva test, in which a "swelling" of the muscle suspending the anus is detected [4,6].In the menopausal period, grade III PTO was observed in 63 (58.8%) in the retrospective group and in 71 (64.5%) p<0.05 in the prospective group. During this period of life, there is not only a decrease in the systemic concentration of estrogens and their receptors for estrogens, which are located in the nuclei of connective tissue cells, all this leads to a change in the properties of collagen. The observed estrogen deficiency in tissue and serum depends not only on the concentration of the hormone, but also on the level of expression and the receptor group. In the preoperative preparation, we paid special attention to the prescription of conjugated estrogens. In 31 (28.9%) patients in the retrospective group and in 24 (21.8%) in the prospective group with stage III PTO, chronic cough was observed, i.e. chronic pathology of the bronchopulmonary system, and, accordingly, in 15 (14.0%) p<0.05 and in 11 (10%) complications after a coronavirus infection, which caused frequent dry cough. All these conditions lead to an increase in intra-abdominal pressure and deterioration of the functional capacity of the pelvic tissue, which contributes not only to the development of PTO, but also to the deterioration of its course. The most common somatic pathology and complication in patients with stage III PTO was UTI, i.e. cystitis and pyelonephritis, which occurred in 42 (39.2%) cases in the retrospective group and in 48 (43.6%) p<0.05 cases in the prospective group, as well as cardiovascular diseases, such as stage I-II hypertension, in 21 (19.6%) in the retrospective group and in 19 (17.2%) cases in the prospective group. Vegetative-vascular dystonia in 16 (14.9 %) and 12 (10.9%) cases, respectively<, and mild iron deficiency anemia in 62 (57.9%) in retrospective and in 71 (64.5%) p<0.05 cases in the prospective group, in a moderate-severe form, did not occur. The onset of PTO and pelvic organ prolapse does not occur immediately, this pathology develops slowly, patients pay attention when clinical symptoms appear, especially from the urinary tract. In the retrospective group, the first signs of clinical manifestation began after 3.5 years, i.e. the duration of PTO grade III ranged from 3.5 to 9 years with an average of 6.5±0.5 years p<0.05, And in the prospective group from 4 to 10 years, the average is 7.0±0.7 years, p<0.05. During this long time, due to the defect in the closure of the genital cleft (Fig. 1., Fig. 2., and Fig. 3), the obstetric trauma of the perineum or vagina is the main cause of the violation of the vaginal biocenosis. Changes in the biocenosis of the cervical canal are accompanied by inflammation, vaginosis and a decrease in local immunity with the subsequent formation of decubital ulcers (Fig. 2), and all this requires thorough preoperative preparation. In 34 (31.7%) patients with stage III PTO in the prospective group, it was complicated by trophic ulcers of the mucous membrane of the anterior wall of the vagina and cervix. Before the start of debridement, the size of the ulcers varied from 2.0 to 6 cm2 and was characterized by pale vitreous granulations and flaccid epithelialization, purulent discharge from the ulcer, and infected margins. The chronicity of vaginal inflammatory processes, the development of dysplasia and recurrent changes in the biocenosis have an extremely negative effect on the technique of the operation, the healing process increases the frequency of early and distant postoperative recurrences.
 | Figure 1. Cervical prolapse after amputation |
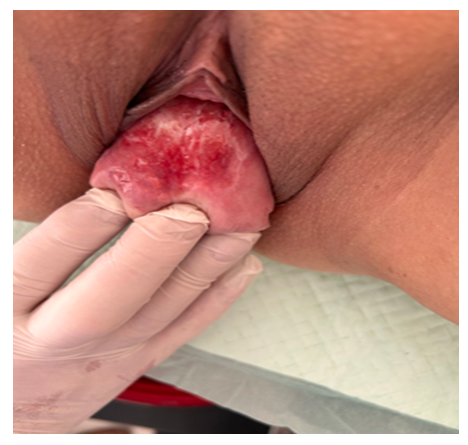 | Figure 2. Initial stage of decubital ulcers |
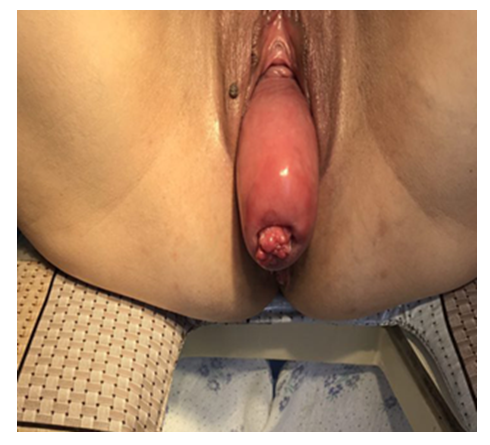 | Figure 3. Cervical polyps of the uterus |
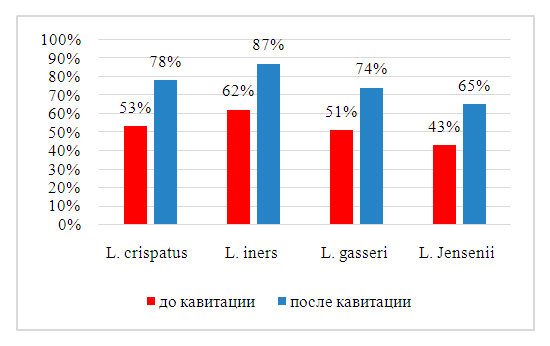 | Diagram 1. Changes in the vaginal biotope after cavitated irrigation with chlorhexidine in patients with grade III PH |
|
4. Conclusions
- 1) The improved method of preoperative preparation of patients with PTO of the III degree contributed to the reduction of the days of preoperative preparation by 6.0±0.5 days, reduced interoperative blood loss by 2.0 times (by 180.0±32.0 ml), this method reduced the duration of the operation by 37.0±6.35 minutes, reduced the stay in the hospital by an average of 3.5±0.5 days, and reduced early postoperative purulent infectious complications by 2.1 times.2) Postoperative recurrences decreased by 2.4 times after 1 year and by 2.8 times after 2 years, and at the same time the quality of life improved in all patients.3) The economic efficiency of preoperative preparation of the recommended method was 72.1% and postoperative – 40.6% p<0.05.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML