Murotov Nurshod Farkhodovich
Assistant, Department of Microbiology, Virology and Immunology of the Bukhara State Medical Institute, Uzbekistan
Correspondence to: Murotov Nurshod Farkhodovich, Assistant, Department of Microbiology, Virology and Immunology of the Bukhara State Medical Institute, Uzbekistan.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Abstract
Cytokines are studied as differential diagnostic criteria for evaluating immune status in pregnant women. The purpose of the study. The purpose of this study was to study the status of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines in the blood serum of pregnant and lactating women living in rural areas. 92 women involved in scientific research were of fertile age (19-49 years old), permanent residents of Kuchak, Chibogoni, O'glan, Bog'imusa, Saraycha, Sadir mahallas of Peshko district of Bukhara region. The result obtained was the study of the concentrations of cytokines in the blood serum of pregnant women with anemia (grade I-II) and AIT and the evaluation of the obtained results showed that the amount of studied IL-1b, IL-4, IL-6 and IL-10 was healthy in both nosological units. was reliably higher than the parameters of pregnant women. (R<0.05-R<0.001). This difference is 1.39 and 1.29 times according to Сц-1b, 1.24 and 1.80 times according to IL-4, 1.43 and 1.20 times according to IL-6, 1, according to IL-10 28 and up to 1.51 times were convincingly reported.
Keywords:
Pregnant, Lactating, Assessment, Cytokine, Immunity, Humoral immunity
Cite this paper: Murotov Nurshod Farkhodovich, Pro- Inflammatory and Anti-Inflammatory Cytokines in the Blood Serum of Pregnant and Lactating Women, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 14 No. 4, 2024, pp. 840-843. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20241404.08.
1. Introduction
In recent decades, attention to humoral immunity has increased, its role in the pathogenesis of many pathological entities has been raised, it has been proved that their quantitative indicators have diagnostic and prognostic value in various pathological conditions. [3] As for cellular immunity (T- and V-joints of the immune system, others), they undergo the same changes in various pathologies, inconsistency between their absolute and relative amounts is determined, their quantitative indicators are inextricably linked to the total number of leukocytes, the diagnostic and prognostic value of some representatives of cellular immunity is low, in addition, their determination requires a lot of money and labor, special conditions, and the ability of qualified specialists to work with these methods make it difficult to determine these indicators, complicate their interpretation, and make their introduction into healthcare practice practically impossible. [4] It is known that cytokines provide immunoregulation of the body's protective function, control the duration and amplitude of immune response and inflammatory processes. They are endogenous peptide molecules with molecular masses of 5-25 kDa. [1] They are synthesized, released to the cell surface and interact with a nearby cell receptor. In this way, information (signal) is given from cell to cell and its subsequent reaction takes place, so cytokines are mediators of intercellular communication. They have the property of being activated when pathogens enter the body or in other immunopathological conditions. [5] Cytokines include interferons, interleukins, colony-stimulating factors, transforming growth factors, tumor necrosis factor, interleukins, and other endogenous mediators. It is mainly produced by lymphocytes [2].Cytokine balance studies are important for assessing the direction of the immune response as well as pregnancy outcomes for both mother and fetus. Excessive stimulation of the systemic humoral immune response as a result of increased activity of peripheral anti-inflammatory cytokines and low secretion of anti-inflammatory cytokines is one of the main mechanisms of PR development. [6]The purpose of the study. to study the status of pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines in serum of pregnant and lactating women living permanently in rural areas.
2. Research Material and Method
For this, 145 pregnant women and 145 lactating women involved in the study were selected for the nosological units of I-II degree anemias (n=36) and autoimmune thyroiditis (n=36) identified and confirmed during the screening process. They were compared with parameters of healthy pregnant women (n=20) and healthy lactating women (n=20). For the purpose of adequate interpretation, sick women were combined into a common group and presented in comparison with the indicator of healthy women.For this, blood serum of female patients was taken and studies were conducted using IFA. The test systems produced by "Cytokin" LLC (SPb, RF) were used. With their help, the concentration of interleukin-1 b (IL-1 b), interleukin-6 (IL-6), interleukin-10 (IL-10), as well as lactoferrin in blood serum was determined.
3. Results Obtained and Discussion
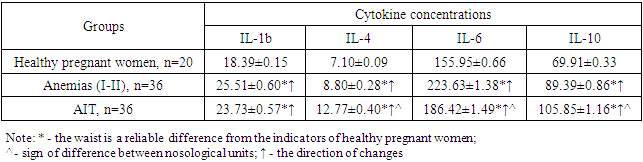
Changes in cytokine status were studied between nosological units. The obtained results are shown in Table 1.Table 1. Comparative indicators of cytokine parameters in blood serum of pregnant women diagnosed with anemia and AIT, ng/ml
 |
| |
|
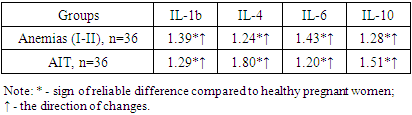
The analysis of the obtained results showed that IL-1β was higher in anemia (25.51±0.60 ng/ml) and AIT (23.73±0.5 ng/ml) than in healthy pregnant women (18.39±0.15 ng /ml) was characterized by a reliable increase of 1.39 and 1.29 times, respectively (R<0.05). If we take into account that IL-1β is a mediator of inflammation and the immune system, it is synthesized by activated macrophages, β-cells, and fibroblasts. It was shown that this condition is a consequence of pathological processes (anemias, AIT).Therefore, IL-1 b tends to increase in pregnant women living in rural areas with these diseases. This condition can help in assessing the immune status of pregnant women and provide information about the pathologies that develop in them. It is noteworthy that the difference between nosological units was not determined.Similar studies were conducted on IL-4. In this case, a trend similar to the above was observed. In pathological cases, parameters of these cytokines were reliably increased by 1.24 (R<0.05) and 1.80 times (R<0.001) compared to healthy pregnant women. If we consider that IL-4 induces the differentiation of primary T-helpers (ThO-cells) into Th2-cells, its increase indicates the level of activation of the T-cell of the immune system. T-joint activation indicates that the immune system has an adequate response to the pathological process. The detection of this cytokine is recommended for use in the first line of health care as an indicator of immune system T-cell activation.Similar studies were conducted on IL-6. The concentration of this cytokine in blood serum was 155.95±0.66 ng/ml in healthy pregnant women, while its amount increased by 1.43 times to 223.63±1.38 ng/ml in women diagnosed with I-II degree anemia. (R<0.05). A similar tendency remained for AIT, but less intense, that is, the increase in IL-6 concentration was 1.20 times compared to healthy pregnant women - up to 186.42±1.49 ng/ml (R<0.05). It should be recognized that a reliable difference was found between both main groups, the amount of this cytokine was determined in anemia compared to AIT (up to 1.20 times, R<0.05). This condition is associated with the pathogenetic features of these diseases. If we take into account the fact that IL-6 acts as a pro-inflammatory cytokine, stimulates the immune response, is synthesized by macrophages and T-cells, we can be sure that it is of great importance for the evaluation of the immune status.Among other cytokines, serum concentrations of IL-10, an anti-inflammatory cytokine that activates the STAT3-dependent signaling pathway, were also detected. The obtained results showed that the amount of this cytokine was statistically significantly higher (R<0.05) in cases where pathological conditions were observed compared to healthy pregnant women. Indicators increased by 1.28 times (R<0.05) in anemias, 1.5 times (R<0.001) in AIT. Given that the expression of IL-10 is usually minimal, it can be activated by normal, pathogenic or conditional-pathogenic microflora, the reasons for its increase even in the absence of inflammatory symptoms become clear.The level of detection of studied pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines, the difference compared to healthy pregnant women, the ratio of differences between nosological units are presented in Table 2.Table 2. Parameters of the difference ratio of cytokines in the blood serum of pregnant women diagnosed with anemia and AIT compared to healthy pregnant women, times
 |
| |
|
It can be seen from Table 2 that all cytokines, regardless of their functions, were reliably higher than the parameters of healthy pregnant women, in other words, although the intensity of changes was slightly different, the trend of changes was the same. At the same time, differences between nasological units were also shown (figure).As can be seen from the cited figure 1, nosological unit differences were found for the concentration of all cytokines. This situation shows that cytokines are the most sensitive molecules among the parameters of the immune status and allows them to be used as prognostic criteria for the evaluation of the immune status and the prognosis of various pathological conditions.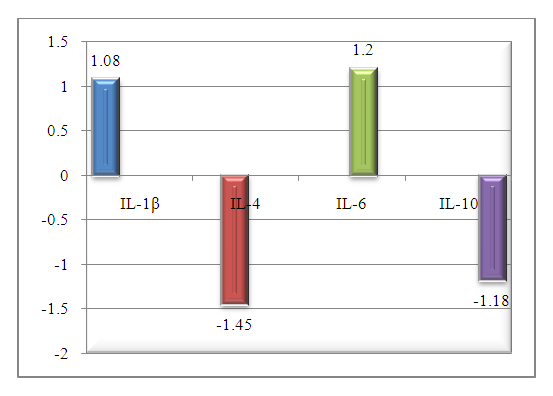 | Figure 1. The ratio of differences in the concentrations of cytokines in anemia compared to pregnant women with AIT, times (a negative sign means that the concentration of this cytokine is higher in AIT) |
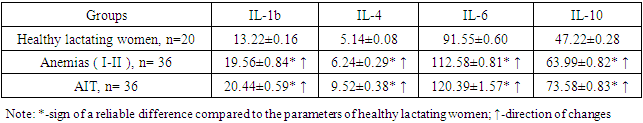
Thus, the study of the concentrations of cytokines in the serum of pregnant women with anemia (grade I-II) and AIT and the evaluation of the obtained results showed that the studied amount of IL-1b, IL-4, IL-6 and IL-10 in both nosological units was reliably higher than the parameters of healthy pregnant women. (R<0.05-R<0.001). This difference is 1.39 and 1.29 times according to Сц-1b, 1.24 and 1.80 times according to IL-4, 1.43 and 1.20 times according to IL-6, 1, according to IL-10 28 and up to 1.51 times were convincingly reported. This situation showed that the activity of the immune system increased, the immune response increased, even if the symptoms of inflammation were not clearly manifested in these pathologies. The presence of differences between nosological units showed that the changes were in different directions. The occurrence of such changes in pregnant women living in rural areas requires the identification of these indicators during the screening of their health protection. The same is true for primary health care.It was also interesting to study the status of cytokines in the studied contingent. In this case, the 4 cytokines listed above were also studied. The obtained results are shown in Table 3. It was observed that the obtained data showed a trend of parameters changes in lactating women similar to pregnant women.Table 3. Comparative analysis of the results of the study of the cytokine status of lactating women, ng/ml
 |
| |
|
In contrast to serum immunoglobulins and non-specific protective factors, cytokine values remained stably elevated. All 4 studied cytokines were statistically significantly higher in pathological cases compared to healthy lactating women (R<0.05 - R<0.001).IL-1b was statistically significantly higher (R<0.001) in lactating women with anemia up to 1.48 times than in healthy lactating women, and in those diagnosed with AIT by 1.55 times. A similar trend was observed for IL-4 - significantly higher by 1.21 and 1.85 times, respectively (R<0.05-R<0.001). It can be seen in the given table that the concentrations of IL-6 and IL-10 in blood serum are also high - 1.23 and 1.32 times (R<0.05) and 1.36 and 1.56 times (R<0.001), respectively. It can be seen that the information provided by cytokines was specific and specific, unlike the parameters of humoral immunity and non-specific resistance factors. This situation was also observed in pregnant women. The level of changes in the studied contingent is presented in Table 4.Table 4. Cytokine status of pregnant and lactating women compared to the indicators of healthy pregnant and lactating women
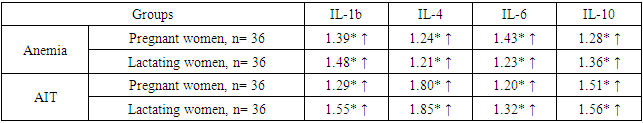 |
| |
|
From the obtained results, it can be seen that the indicators of cytokines studied in the same trend and intensity in both pathologies. Remarkably, pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines were found to be remarkably increased at the same rate. Such a condition is the effect of a pathological condition formed in the body, and indicates that the inflammatory process has not been extinguished.These cytokine changes were observed in pregnant and lactating women alike, and were recommended for use in health screening of lactating women living in rural areas. These indicators were recommended as immunological prognostic criteria for predicting the condition of healthy and pathological pregnant and lactating women.
4. Conclusions
1. The amount of IL-1b, IL-4, IL-6 and IL-10 in the blood serum of pregnant women with anemia (grade I-II) and AIT was significantly higher than the parameters of healthy pregnant women in both nosological units. IL-1 This difference according to β was 1.39 and 1.29 times, according to IL-4 1.24 and 1.80 times, according to IL-6 1.43 and 1.20 times, according to IL-10 1.28 and 1 It was noted that there was a convincing increase of.51 times;2. An increase in the amount of cytokines in these pathologies showed that the activity of the immune system increased, the immune response increased, even if the symptoms of inflammation were not evident. The presence of differences between nosological units showed that the changes were in different directions. The occurrence of such changes in pregnant women living in rural areas requires them to determine these indicators during health screening, which is the same term for the first link of health care;3. In both pathologies, cytokines studied in the same trend and intensity, reliably increased in the same ratio. Such specific and concrete changes were recommended for their use in health screening of lactating women living in rural areas. These indicators were recommended as immunological prognostic criteria for predicting the condition of healthy and pathological pregnant and lactating women.
References
| [1] | Pfefferle P. I. et al. Cord blood cytokines are modulated by maternal farming activities and consumption of farm dairy products during pregnancy: the PASTURE Study // Journal of allergy and clinical immunology. – 2010. – Т. 125. – №. 1. – С. 108-115. e3. |
| [2] | Pertsov S. S. i dr. Dynamics of concentrations of tsitokinov and blood mice with different behavioral characteristics of poste ostroy stressornoy nagruzki. IM Sechenova. - 2015. - T. 101. - no. 9. - S. 1032-1041. |
| [3] | Hindle L. J. et al. Effect of multiple micronutrient supplementation during pregnancy on inflammatory markers in Nepalese women // The American journal of clinical nutrition. – 2006. – Т. 84. – №. 5. – С. 1086-1092. |
| [4] | Coussons-Read M. E., Okun M. L., Nettles C. D. Psychosocial stress increases inflammatory markers and alters cytokine production across pregnancy // Brain, behavior, and immunity. – 2007. – Т. 21. – №. 3. – С. 343-350. |
| [5] | Montagnana M. et al. Serum pro-inflammatory cytokines in physiological and pre-eclamptic pregnancies // Gynecological Endocrinology. – 2008. – Т. 24. – №. 3. – С. 113-116. |
| [6] | Cemgil Arikan, Deniz, et al. "Plasma IL-4, IL-8, IL-12, interferon-γ and CRP levels in pregnant women with preeclampsia, and their relation with severity of disease and fetal birth weight." The Journal of Maternal-Fetal & Neonatal Medicine 25.9 (2012): 1569-1573. |


 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML



