-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2024; 14(4): 819-824
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20241404.04
Received: Mar. 12, 2024; Accepted: Mar. 27, 2024; Published: Apr. 2, 2024

Current Factors Determining the Distraction Potential of Limb Segments in Patients with Congenital and Acquired Polysegmental Shortening and Deformation of Lower Limb Segments
Iskandar Khodjanov1, Khabibjon Mirzamurodov2, Konstantin Novikov3, 4, 5, Oleg Klimov3, Marat Sayfutdinov3
1Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, Scientific Director of the Department of General Orthopedics of the Republican Specialized Scientific and Practical Medical Center of Traumatology and Orthopedics, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
2Assistant, Department of Traumatology and Neurosurgery, Bukhara State Medical Institute, Bukhara, Uzbekistan
3Doctor of Medical Sciences, National Medical Research Center for Traumatology and Orthopedics named after Academician G.A. Ilizarov, Kurgan, Russia
4Doctor of Medical Sciences, Tyumen State Medical University, Tyumen, Russia
5Doctor of Biological Sciences, Samarkand State Medical University, Samarkand, Uzbekistan
Correspondence to: Iskandar Khodjanov, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, Scientific Director of the Department of General Orthopedics of the Republican Specialized Scientific and Practical Medical Center of Traumatology and Orthopedics, Tashkent, Uzbekistan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Polysegmental shortenings and deformations of the lower extremities are a severe orthopedic pathology, during the surgical treatment of which, in order to reduce the stages and duration of treatment, polysegmental osteosynthesis of the limb is used, which entails an increase in the volume of surgical trauma and the achievement of the maximum possible treatment result, which requires an assessment of the distraction potential of the limb segments. The work was to study the dependence of the dynamics of bioelectrical activity of muscles on the volumetric characteristics of the lengthened segments of the lower extremities and the possibility of using this dependence to assess the distraction potential of the limb. During the study, two comparison groups were formed, each of which consisted of 10 patients of the same age who underwent polysegmental monolateral osteosynthesis of the lower limb. The first group included patients with systemic damage to the musculoskeletal system as a result of the genetically determined disease achondroplasia, the second group included patients with acquired damage to segments of the lower limb. In general, the study of the dynamics of bioelectrical activity and volumetric parameters in patients of different nosological groups made it possible to identify the characteristics of the response of the soft tissue apparatus to limb lengthening, as well as to evaluate the diagnostic value of the research methods usedsoft tissue conditionsfor ratedistraction potential of the extended limb.The use of these research methods in clinical practice has shown their objectivity and high information content for personalizing the tactics of using transosseous osteosynthesis techniques, in the context of choosing the lengthening value and the rate of distraction, as well as avoiding neurological complications and predicting treatment results.
Keywords: Ilizarov method, Limb lengthening, Polysegmental osteosynthesis, Volume of soft tissues of lower limb segments, Achondroplasia, Electromyography
Cite this paper: Iskandar Khodjanov, Khabibjon Mirzamurodov, Konstantin Novikov, Oleg Klimov, Marat Sayfutdinov, Current Factors Determining the Distraction Potential of Limb Segments in Patients with Congenital and Acquired Polysegmental Shortening and Deformation of Lower Limb Segments, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 14 No. 4, 2024, pp. 819-824. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20241404.04.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Polysegmental shortenings and deformations of the lower extremities are a severe orthopedic pathology, during the surgical treatment of which, in order to reduce the stages and duration of treatment, polysegmental osteosynthesis of the limb is used, which entails an increase in the volume of surgical trauma and the achievement of the maximum possible treatment result, which requires an assessment of the distraction potential of the limb segments [1,5,9,19].According to the biological effect discovered and studied by G.A. Ilizarov, during distraction osteosynthesis, the same type of process occurs on the part of the bone structures and soft tissue apparatus of the limb, this is tissue growth in response to their dosed stretching. Based on this scientific fact, it is obvious that in order to obtain a positive treatment result, this process must occur in the bone structures and soft tissue apparatus of the limb segments within their adaptive capabilities, otherwise, the exhaustion of the regenerative capabilities of one of them is fraught with a number of serious complications that can influence the final clinical and functional outcome of treatment [3,9].Thus, the overall distraction potential of the limb is determined not only by the activity of reparative osteogenesis, but also by the state of the soft tissue apparatus of the limb [2,3,4,18].As is known, during surgical reconstruction of the lower extremities ODS, the process of reparative osteogenesis occurs from the bone structures, which is the reaction of the bone structure to the movement of bone fragments in the area of osteotomy. The soft tissues of the limb segment being lengthened, in response to distraction efforts, are subject to stretching at the initial stage of this process, and after this opportunity has been exhausted, they grow, which is accompanied by an increase in their volume [5,6,7,10,14]. In cases where the distraction potential of soft tissues is exhausted, degenerative phenomena begin to develop in the muscles, which in severe cases result in irreversible fibrous changes. All these phenomena ultimately affectthe state of neuromotor muscle function, which has a decisive influence on the functionality of the lower limb [8,9,11,13,21].The practice of using the Ilizarov method has shown that the main factors that influence the condition of soft tissues under conditions of distraction osteosynthesis are the pace and rhythm of distraction, as well as the magnitude of the cumulative increase in the longitudinal dimensions of limb segments during its lengthening and correction of deformities [8,12,15,16,17,20]. An important factor is the decrease in the functional activity of the limb.
2. Purpose
- The aim of the work was to study the dependence of the dynamics of bioelectrical muscle activity on the volumetric characteristics of the lengthened segments of the lower limbs and the possibility of using this dependence to assess the distraction potential of the limb.
3. Materials and Methods
- During the study, two comparison groups were formed, each of which consisted of 10 patients of the same age who underwent polysegmental monolateral osteosynthesis of the lower limb. The first group included patients with systemic lesions of the ODS as a result of the genetically determined disease achondroplasia, the second group consisted of patients with acquired lesions of segments of the lower limb, which was a consequence of hematogenous osteomyelitis or a congenital malformation of the limb. The average value of the cumulative elongation of the segments of the lower limb in the group with systemic lesions of the ODS was 12 cm + 1.5 cm; in patients with acquired shortening deformity of the segments of the lower extremities, the cumulative value of elongation was 8.3 cm + 2.1 cm.In order to study the nature of the course of compensatory adaptive reactions on the part of soft tissues, calculations of absolute (sm3) and relative volume of soft tissues (cm3/cm limb length) lengthened limb segments. Measurements were performed before surgery, after removal of the device and 2 months after treatment [9].To study changes in the bioelectric characteristics of muscles, we performed cutaneous electromyography of such muscles as m.tibialis anterior, m.gastrocnemius lateralis, m.rectus femoris, m.biceps femoris. During the study, we recorded the dynamics of the measured parameters at maximum voluntary muscle tension using the Viking-2e digital EMG system (Nicolet, USA). The study was carried out before the start of treatment, after removal of the device and two months after osteosynthesis.The examination was carried out according to the traditional method for this type of research, during which the study of EMG indicators was carried out with a bipolar surface electrode, the contact area of which was 8 and 10 mm. During the measurement, voluntary muscle tension was performed smoothly and with maximum effort necessary to overcome the resistance exerted on the limb by the research assistant. The calculation of indicators was carried out using the formula recommended for this study, which took into account the frequency of occurrence of individual electromyographic patterns.
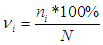 where v is the amplitude, ni is the number of observations of the i-th activity pattern, N is the total number of observations in the group under consideration at the corresponding stage of the study.During the electromyographic study, several types of electromyographic profiles of indicators obtained in a state of tension and relaxation were identified, which were divided into six types:The first, main electromyographic profile, was characterized by an EMG amplitude of more than 100 microvolts, with an average frequency in the range of 150-300 Hz.The second type of electromyographic profile was a high-amplitude indicator of more than 300 microvolts, which was the result of interference of measured indicators and was characterized by EMG with high amplitude indicators and frequency values of more than 300 Hz.The third type of EMG can be characterized as low amplitude interference of indicators, the maximum value of which did not exceed 100 microvolts;The following three types of EMG can be characterized as atypical forms; they included ultra-low indicators and EMG that had a reduced character, the main characteristic of which was low activity with periods of silence.
where v is the amplitude, ni is the number of observations of the i-th activity pattern, N is the total number of observations in the group under consideration at the corresponding stage of the study.During the electromyographic study, several types of electromyographic profiles of indicators obtained in a state of tension and relaxation were identified, which were divided into six types:The first, main electromyographic profile, was characterized by an EMG amplitude of more than 100 microvolts, with an average frequency in the range of 150-300 Hz.The second type of electromyographic profile was a high-amplitude indicator of more than 300 microvolts, which was the result of interference of measured indicators and was characterized by EMG with high amplitude indicators and frequency values of more than 300 Hz.The third type of EMG can be characterized as low amplitude interference of indicators, the maximum value of which did not exceed 100 microvolts;The following three types of EMG can be characterized as atypical forms; they included ultra-low indicators and EMG that had a reduced character, the main characteristic of which was low activity with periods of silence.4. Results
- According to the data obtained during the study, it was established that the main difference in the comparison groups was in the anthropometric parameters of the musculoskeletal system of patients, and was that the absolute volume of soft tissues of the segments of the lower extremities in patients with systemic lesions of the musculoskeletal system was almost 15% less than the volume of soft tissue of a healthy limb in a patient with acquired shortening and deformities of the lower extremities, and at the same time, according to this indicator, was on average 10% greater than the volume of segments of the affected limb in patients of the second group (Fig. 1).
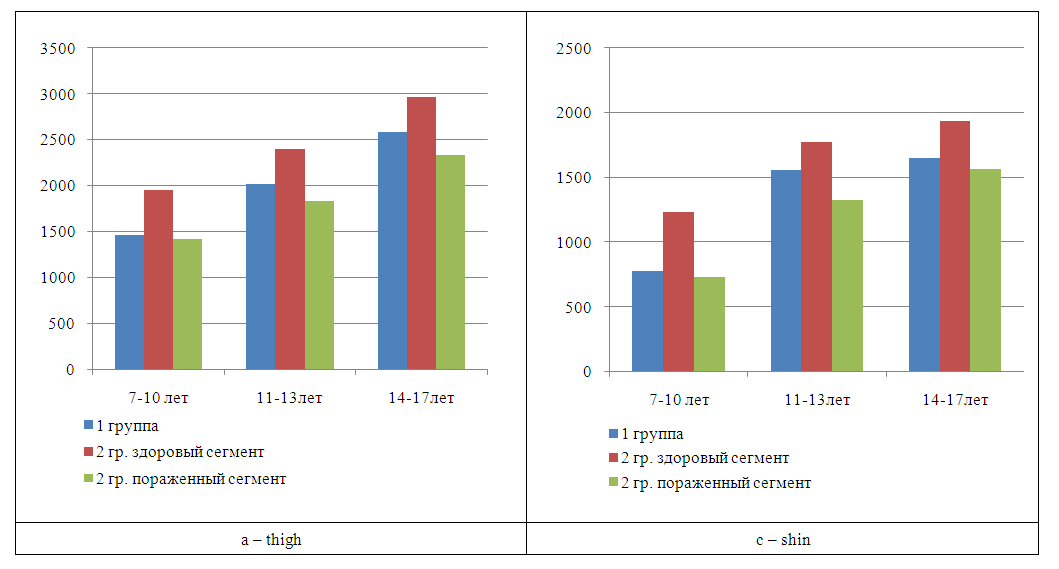 | Figure 1. The absolute value of the segment volume (cm3) in the comparison groups: a – thigh, c – lower leg |
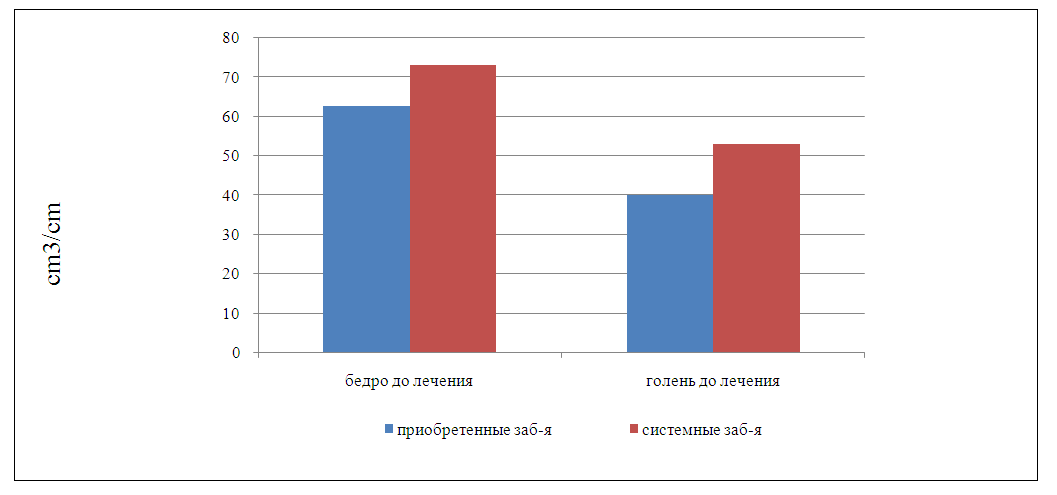 | Figure 2. Indicator of the relative value of the segment volume in the comparison groups |
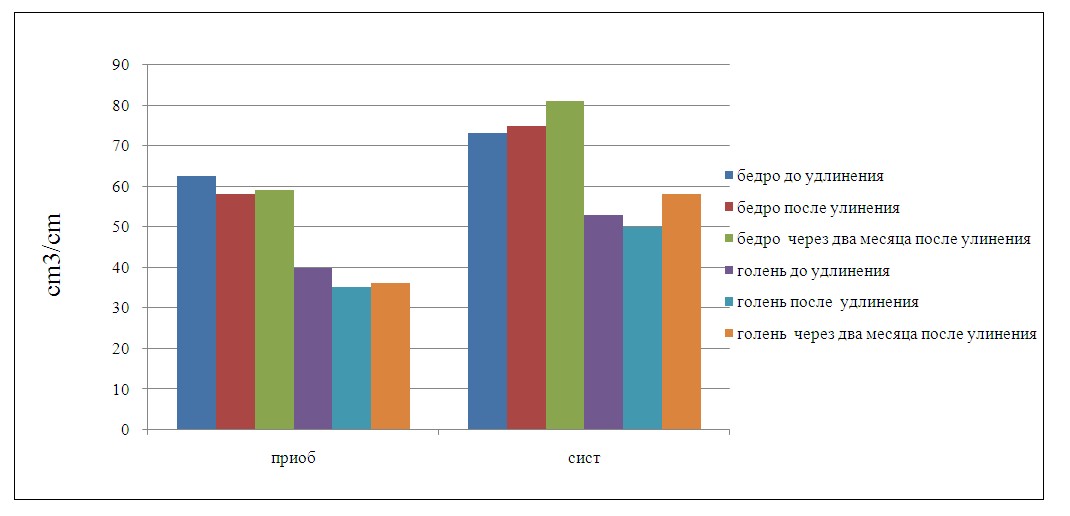 | Figure 3. Indicator of the relative value of the segment volume in the comparison groups at the stages of treatment |
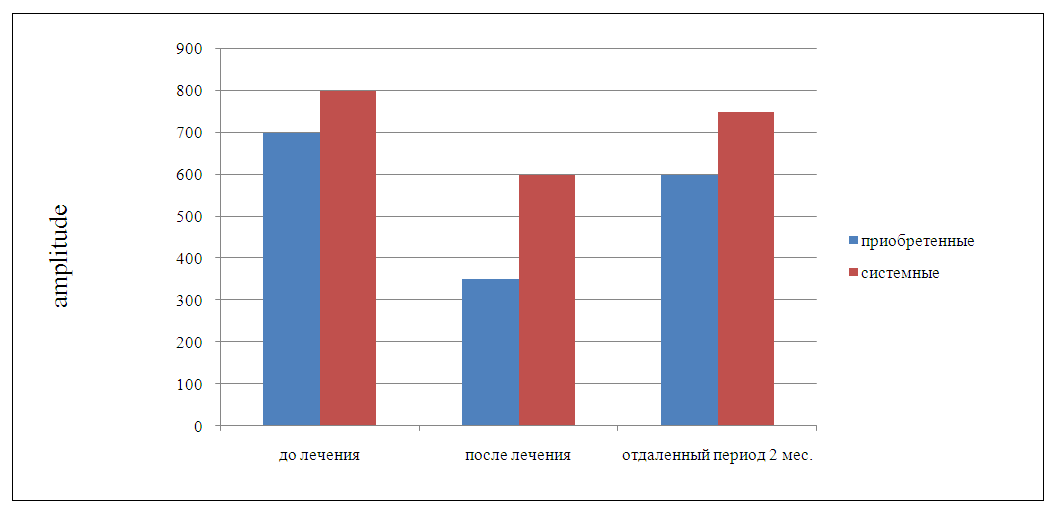 | Figure 4. Dynamics of electromyographic parameters in the comparison groups at different stages of treatment |
5. Discussion
- The results of the study showed that the distraction potential of the limb is in a statistically significant dependence on the volumetric characteristics and bioelectrical activity of the neuromuscular structures of the limb being extended.The data obtained also allow us to conclude that in patients with symptoms of hypotrophy of the soft tissue structures of the limb, its distraction potential is reduced.Based on statistical and anthropometric data obtained during the study, we came to the conclusion that when segments are lengthened, neurological complications consist of a statistically substantiated dependence on the amount of lengthening and the relative volume of soft tissues, which reflects the state of their trophism. We would like to emphasize that these conclusions do not apply to cases of increased nutrition of patients.
6. Conclusions
- In general, the study of the dynamics of bioelectrical activity and volumetric parameters in patients of different nosological groups made it possible to identify the characteristics of the response of the soft tissue apparatus to limb lengthening, which made it possible to determine their diagnostic value and formulate recommendations that will prevent neurological complications.Thus, we can conclude that the distraction potential of the limb largely determines the condition of the soft tissues of the lengthened limb.The use of these research methods in clinical practice has shown their objectivity and high information content for personalizing the tactics of using transosseous osteosynthesis techniques, in the context of choosing the lengthening value and the rate of distraction, as well as avoiding neurological complications and predicting treatment results [15].
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML