-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2024; 14(4): 805-807
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20241404.01
Received: Dec. 10, 2023; Accepted: Jan. 7, 2024; Published: Apr. 1, 2024

Immunological Aspects in Young Children with Congenital Heart Defects
Tairova Sakina Bakhodirovna1, Mukhamadiyeva Lola Atamuradovna2
1Assistant, Samarkand State Medical University, Uzbekistan
2Doctor of Medical Sciences, Associate Professor, Samarkand State Medical University, Uzbekistan
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

In this article, we examined indicators of immune status in children with septal congenital heart defects (CHD). Young children with septal congenital heart disease were prospectively recruited between 2021 and 2022. The examination included 138 young children with septal congenital heart disease, of whom 73 (52.3%) were boys and 65 (47.7%) were girls. The concentration of immunoglobulins - Ig A, Ig M, Ig G in the blood serum was determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), and the determination of the pro-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-6 (IL-6) in the blood serum was based on the sandwich ELISA method. A study of the concentrations of the main classes of immunoglobulins G, A and M showed a decrease in IgA synthesis in septal congenital heart disease in children - 0.17±0.01 g/l. Analysis of the cytokine status of sick children showed a slight increase in IL-6 titer. The presented results made it possible to identify the main immunological features of septal congenital heart disease in young children. Thus, the data obtained characterize a decrease in the body’s reactivity against the background of circulatory disorders.
Keywords: Congenital heart disease, Immune status, Children, Interleukin, Immunoglobulin
Cite this paper: Tairova Sakina Bakhodirovna, Mukhamadiyeva Lola Atamuradovna, Immunological Aspects in Young Children with Congenital Heart Defects, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 14 No. 4, 2024, pp. 805-807. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20241404.01.
1. Introduction
- Congenital heart disease (CHD) represents a significant global health and economic burden-despite advances in the treatment of CHD that have reduced the risk of mortality, CHD accounts for approximately 300,000 deaths annually worldwide [3,5,6,12]. Children with congenital heart disease experience both acute and chronic cardiac complications. Although treatment options have improved, some remain extremely invasive. Some studies indicate an immune contribution to the development of congenital heart disease; however, the role of the immune system is not well understood [2,9,11].According to M.F. Zinkovsky et al. [1,4,8], the existing immune imbalance in children with congenital heart disease consists of suppression of all parts of the immune system. Thus, the humoral link of the immune system is characterized by a tendency to reduce the amount of certain immunoglobulins [7,10,13]. When proinflammatory cytokines released during infection are dysregulated, a systemic inflammatory response can occur, potentially leading to adverse outcomes [14].Thus, identifying the role of immune and inflammatory responses in CHD holds promise for elucidating the mechanisms underlying these disorders and improving current diagnostic and treatment options.In connection with this, we set a goal to study the indicators of immune status in children with septal congenital heart disease based on the analysis of data from the pediatric cardiac surgery department of the Regional Children's Multidisciplinary Medical Center (ODMMC) in the city of Samarkand, in order to improve the treatment of children with congenital heart disease.
2. Materials and Methods
- A survey was conducted of 138 children aged from 1 month to 3 years with septal congenital heart disease, who were treated as inpatients in the cardiac surgery department at the Children's Medical Center in Samarkand in the period from 2021 to 2022.During the study, all children (n=138) were divided into three groups: the main group included 108 children (78.2%), and this group was divided into 2 subgroups: Ia (n=73) (operated children with correction of comorbidities) flow (CS)) and Ib (n=35) (operated children without correction of CS); The comparison group (CG) included 30 children, consistent by gender and age, who, due to some differences, were not operated on. (Fig. 1.).
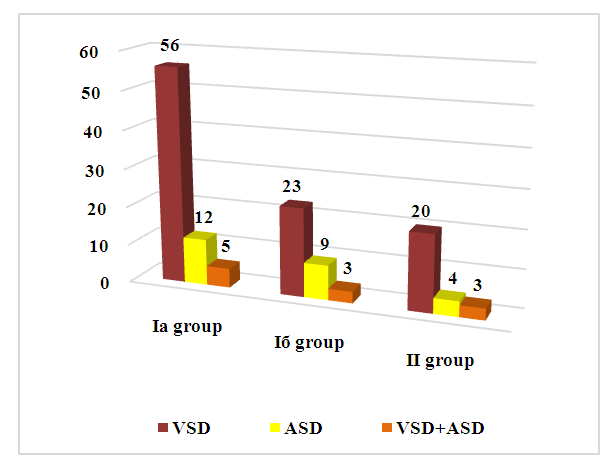 | Figure 1. Distribution of examined children with septal congenital heart disease by study groups |
3. Results
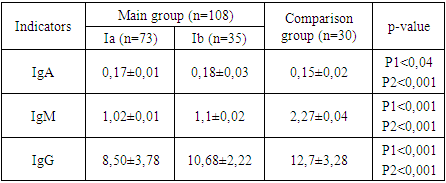
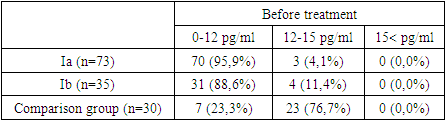
- When studying the indicators of immune status in young children with septal congenital heart disease, according to immunological data, it was found that children with congenital heart disease more often have manifestations of immune imbalance syndrome.It is known that specific factors of humoral immunity are produced by B lymphocytes and these include immunoglobulins. A study of the concentrations of the main classes of immunoglobulins G, A and M was carried out. A study of the concentrations of the main classes of immunoglobulins G, A and M showed a decrease in IgA synthesis in septal congenital heart disease in children – 0,17±0,01 g/l (normally 1-12 months. 0,15-0,55 g/l, 1-2 years 0,26-0,74 g/l, 2-3 years 0,34-1,11 g/l). In children with congenital septal heart defects, an isolated decrease in serum IgA was detected in the blood serum of 8 children (5,9%)). Thus, the data obtained characterize a decrease in the body’s reactivity against the background of circulatory disorders (Table 1).
|
|
4. Conclusions
- The development of immune imbalance in children with cardiovascular diseases leads to increased susceptibility to intercurrent infections, a tendency to develop chronic forms of any disease, allergic and autoimmune processes. These changes in inflammatory responses in children with septal congenital heart disease in the perioperative period may contribute to various clinical outcomes, including sepsis, and over time, autoimmune failure. In addition, they may influence the pathogenesis and outcome after surgery in the long term. Characterization of the inflammatory response in the perioperative period may pave the way for individualized management of children with septal congenital heart disease using new treatment modalities, including immunomodulation.The presented results made it possible to identify the main immunological features of septal congenital heart disease in young children. Thus, the data obtained characterize a decrease in the body’s reactivity against the background of circulatory disorders.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML