-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2024; 14(2): 458-465
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20241402.60
Received: Jan. 31, 2024; Accepted: Feb. 20, 2024; Published: Feb. 22, 2024

Characteristics of the Thyroid Profile in Various Clinical Forms of Glomerulonephritis and Correlations with the Cytokine System
Khamdamov Bakhtiyor Zarifovich1, Eshbekov Murodilla Abdumusayevich2, Khamdamov Ilxom Bakhtiyorovich1
1Bukhara State Medical Institute, Bukhara, Uzbekistan
2Samarkand State Medical University, Samarkand, Uzbekistan
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

When the cytokine cascade reaction is stimulated and the factors of innate and adaptive immunity are activated under pathogenic conditions, the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis is activated simultaneously. The process of activation of this axis is a manifestation of the adaptive ability of the body, which is aimed at maintaining homeostasis in response to external stimuli, such as exposure to various microorganisms or psychological stress. The purpose of our study was to determine the pituitary-thyroid status in patients with various forms of glomerulonephritis and to study the relationship between indicators of thyroid status with indicators of cytokine, immune status, as well as other clinical and laboratory parameters in patients with glomerulonephritis. Results and conclusions. an analysis of the study of the state of thyroid status and the available correlations with the rest of the studied indicators of patients with various forms of GN revealed that 88.1% of patients with nephrotic form of GN and 56.3% with mixed form of GN revealed changes in the level of hormonal status of the pituitary-thyroid system characteristic of hypothyroidism. In the hypertensive form of GN, only 17.2% of patients were diagnosed with a hypothyroid condition. The indicators of thyroid status in the group of patients with latent GN did not differ from these indicators in the healthy group. After analyzing the correlations, it is possible to conclude about the negative effect of TSH hormone and autoantibodies to TPO on the functional state of the kidneys, while the positive effect of thyroid hormones – free T4 and free T3 on kidney function has been determined.
Keywords: Glomerulonephritis, Thyroid hormones, Hypothyroidism, Cytokines, Interleukins
Cite this paper: Khamdamov Bakhtiyor Zarifovich, Eshbekov Murodilla Abdumusayevich, Khamdamov Ilxom Bakhtiyorovich, Characteristics of the Thyroid Profile in Various Clinical Forms of Glomerulonephritis and Correlations with the Cytokine System, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 14 No. 2, 2024, pp. 458-465. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20241402.60.
1. Introduction
- The neuro-immune-endocrine system is a complex and multifunctional system with various regulatory mechanisms. It is believed that various diseases have common pathogenetic connections in this regulatory system, despite various clinical manifestations. It is known that many mediators produced by immunocompetent cells, such as lymphokines, interferons and interleukins, have hormonal properties [1,2,31,32,33,34,35]. The hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal system controls the synthesis of antibodies and the release of mature B lymphocytes from the bone marrow. It should be noted that neuropeptide receptors have been found on cells of the immune system, through which the endocrine system can participate in regulating the body's immunoreactivity and vice versa, which shows how the immune and endocrine systems are interconnected with each other. When the cytokine cascade reaction is stimulated and the factors of innate and adaptive immunity are activated under pathogenic conditions, the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis is activated simultaneously. The process of activation of this axis is a manifestation of the adaptive ability of the body, which is aimed at maintaining homeostasis in response to external stimuli, such as exposure to various microorganisms or psychological stress [1,3,5,7,9,11,13,15,17,19,21,23,25,27,29].Thanks to a number of studies, it is known about the mutual influence of the metabolism of thyroid, pituitary hormones and the functioning of the urinary system [2,4,6,8,10,12,14,16,18,20,22,24,26,28,30]. Considering the above, the study of thyroid status in patients with glomerunephritis (GN) is of practical interest, especially depending on its forms and the level of pituitary-thyroid hormones.Based on the above, the purpose of our study was to determine the pituitary-thyroid status in patients with various forms of GN and to study the relationship between indicators of thyroid status with indicators of cytokine, immune status, as well as other clinical and laboratory parameters in patients with glomerulonephritis.
2. Materials and Methods
- Our study involved 103 patients with GN, aged 16 to 58 years (average age 35.6±2.8). The average duration of GN in the examined patients was 3.8±1.1 years. The diagnosis was established on the basis of the results of a clinical examination, data from laboratory and instrumental research methods. Depending on the clinical form of GN, patients were divided into four groups: group I (n=28) – patients with latent form of GN; group II (n=25) – patients with nephrotic form of GN; group III (n=25) – patients with hypertensive form of GN; Group IV (n = 25) – patients with a mixed form of GN.To determine the cytokine content in the blood serum of the studied groups, a three–stage "sandwich" method was used - this is a type of three-phase ELISA. The concentration of interleukin-IL-1β, IL-8, IL-10, IFN-γ was determined using a set of reagents from the company Vector-Best (Novosibirsk).
3. Results and Discussion
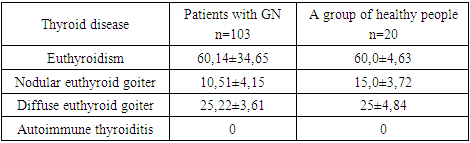
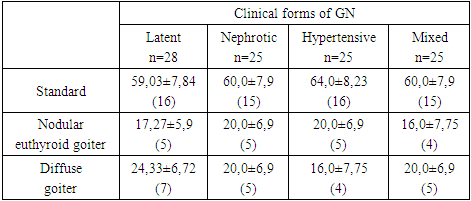
- First, we decided to study the prevalence of thyroid pathology in GN, in which it was found that they did not have significant differences from the healthy group (Table 1). The unchanged euthyroid state of the thyroid gland was noted in most patients with GN and in the healthy group.
|
|
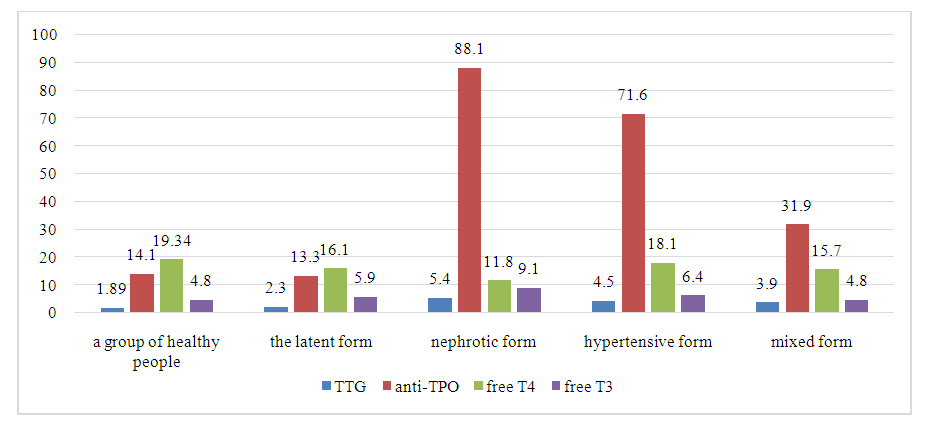 | Figure 1. Thyroid hormone levels in various forms of GN before inpatient treatment |
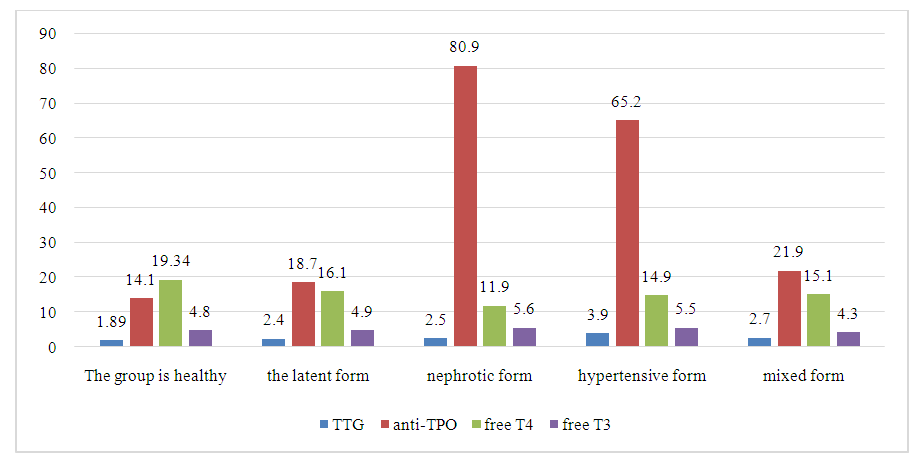 | Figure 2. Thyroid hormone levels in various forms of GH after inpatient treatment |
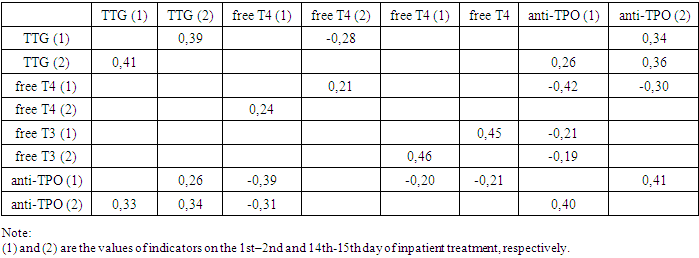
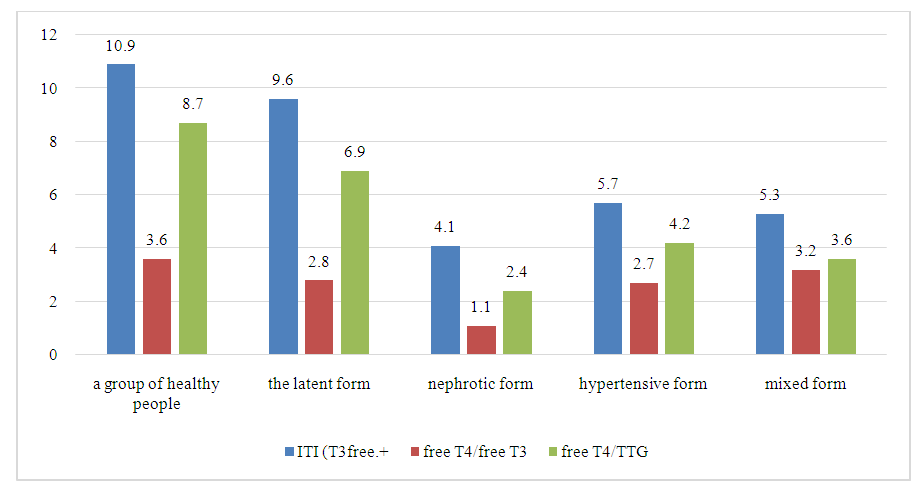 | Figure 3. Integral indicators of thyroid status in various forms of GN before inpatient treatment |
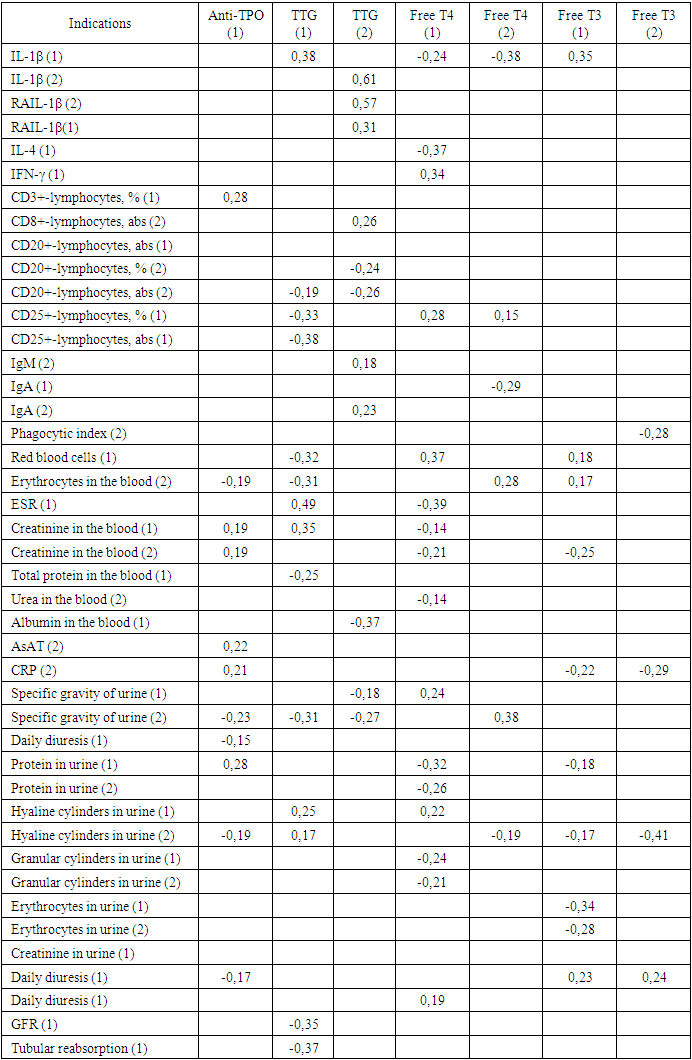
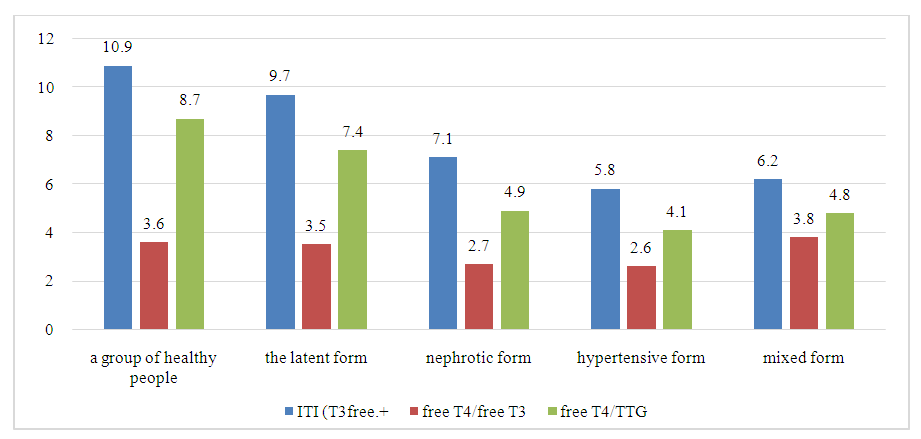 | Figure 4. Integral indicators of thyroid status in various forms of GN after inpatient treatment |
|
|
4. Conclusions
- 1. Studying the state of thyroid status and the available correlations with the rest of the studied indicators of patients with various forms of GN, revealed that 88.1% of patients with nephrotic form of GN and 56.3% with mixed form of GN revealed changes in the level of hormonal status of the pituitary-thyroid system, characteristic of hypothyroidism. 2. In the hypertensive form of GN, only 17.2% of patients were diagnosed with a hypothyroid condition. The indicators of thyroid status in the group of patients with latent GN did not differ from these indicators in the healthy group. After analyzing the correlations, it is possible to conclude about the negative effect of TSH hormone and autoantibodies to TPO on the functional state of the kidneys, while the positive effect of thyroid hormones – free T4 and free T3 on kidney function has been determined.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML