-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2024; 4(2): 282-286
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20241402.25
Received: Jan. 12, 2024; Accepted: Feb. 1, 2024; Published: Feb. 8, 2024

Methods of Increasing the Effectiveness of Detection of Covid-19-Related Preeclampsia by Biochemical Markers in the Formation of a Complex of Symptoms
Nishanova F. P., Karimova L. A., Nadirkhanova N. S., Asatova M. M.
Republican Specialized Scientific and Practical Medical Center for Maternal and Child Health, Uzbekistan
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

The article presents methods for increasing the efficiency of detection during the formation of the symptom complex of preeclampsia using biochemical markers associated with COVID-19.
Keywords: Preeclampsia, COVID-19, HELLP-syndrome, Elimination of pneumonia
Cite this paper: Nishanova F. P., Karimova L. A., Nadirkhanova N. S., Asatova M. M., Methods of Increasing the Effectiveness of Detection of Covid-19-Related Preeclampsia by Biochemical Markers in the Formation of a Complex of Symptoms, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 4 No. 2, 2024, pp. 282-286. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20241402.25.
1. Introduction
- Preeclampsia remains one of the most common complications of pregnancy today, which causes serious disorders in the mother and fetus [1,3,5]. Most researchers agree that preeclampsia ranks third in terms of maternal and perinatal complications and mortality, accounting for 11-16% compared to birth [8,12,18]. According to studies, more than 8 million complications of preeclampsia are recorded annually worldwide, which is the leading cause of maternal and perinatal death, taking the lives of 60,000 young women each year [2,4,6].So far the pathogenesis of preeclampsia remains unclear. Some researchers believe that the placenta plays an important role in the occurrence and development of preeclampsia, since after removal of the placenta, the symptoms in patients are significantly reduced [2,6,10]. In addition, its development may be closely related to endothelial dysfunction and immune disorders [13,19,25].Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) is the most widespread infectious virus in the world. Due to its rapid development and the lack of specific treatment strategies, it has become a global pandemic. The primary effects of COVID-19 are on the lungs, followed by liver damage, followed by thrombocytopenia, hypertension, and kidney damage. Pregnant women may be more susceptible to COVID-19 due to immunological and physiological adaptive remodeling that occurs during pregnancy [14,15,16].In addition, COVID-19 also causes hypoxic damage to the placenta, which may contribute to the development of preeclampsia.In order to evaluate the relationshipbetween COVID-19 and preeclampsia, scientists from School of Medicine at Wayne University conducted a meta-analysis of 28 studies, which included data on 790,900 women in childbirth, 15,500 of whomwere infected with the coronavirus. In infected women, the risk of developing this condition was 62% higher than in uninfected pregnant women [7,9,11,13].In addition, during pregnancy, COVID-19 is associated with a significant increase in the risk of severe preeclampsia, eclampsia and HELLP-syndrome are considered to be a severe pathology that develops in the first week after delivery, accompanied by increased jaundice and liver failure.According to the researchers, the risk of preeclampsia increases with asymptomatic carriage and symptomatic disease, but women with severe COVID-19 have the greatest chance of complications from preeclampsia.According to the results of the study, after the elimination of pneumonia, the typical preeclampsia was preserved in only one patient, in whom the concentration of LDH increased, the ratio of sFlt-1/PlGF>110 exceeded, and the disorder of blood flow in the uterine arteries remained [17,20,23].These indicators directly show the disruption of angiogenesis and placental hypo perfusion, which are diagnostically valuable signs that allow distinguishing true preeclampsia from a number of diseases that can imitate it.It is known that remodeling of the uterine spiral artery and disruption of trophoblast invasion play a key role in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia, which subsequently leads to decreased perfusion and reactive oxidative stress in the placenta. As a result, the pulsation index in the uterine arteries increases, the ratio of angiogenic and antiangiogenic factors is disturbed: the concentration of sFlt-1 increases and the production of PlGF decreases [4,14,22].From the findings of the studies, it can be assumed that true preeclampsia occurs only in pregnant women who are at risk for the development of preeclampsia, and in a pregnant woman complicated by COVID-19, the characteristic symptoms were caused directly by the severe course of COVID-19 or the drugs prescribed for its treatment. Normal values of sFlt-1/PlGF ratio, LDH concentration, and absence of uterine blood flow disorders were confirmed in pregnant women complicated by COVID-19 [16,24,26].It is noted that COVID-19 and preeclampsia have similar clinical symptoms, which can make it difficult to make an accurate diagnosis. Doctors state that studying preeclampsia-like symptoms in pregnant women with COVID-19 can help avoid misdiagnosis and premature birth [21].Differential diagnosis of preeclampsia in pregnant women with COVID-19 is performed by assessing placental vascular development using VEGF, PlGF, and the anti-angiogenic factor sFlt-1. This imbalance may also be due to inflammatory mediators, including cytokines (eg, IL-1, INF-γ, TNF) and the complement cascade. The ratio of sFlt-1/PlGF can also be altered by infectious conditions, but dysregulated levels of these mediators are associated with placental insufficiency, placental hypoxia, and poor transport of nutrients to the fetus, leading to poor neonatal complications.The purpose of the research. To identify preeclampsia and the symptom complex of preeclampsia associated with COVID-19 and the biomarkers which are important for diagnosis, to develop differential diagnosis.
2. Materials and Methods
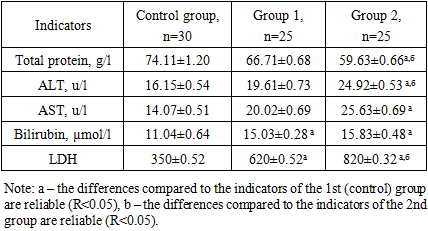
- Scientific research was carried out at the Zangiota infectious disease clinic, “Immunogenic test” private clinic, as well as at Republican Specialized Scientific and Practical Medical Center for Maternal and Child Health. 80 women involved in the study were complicated by preeclampsia. 25 of them were women complicated by preeclampsia and had COVID-19, 25 women were complicated by COVID-19 and had a symptom complex of preeclampsia, and the control group consisted of 30 women whose pregnancy was uncomplicated.The method of biochemical research was carried out by Hegay T.R., the author, head of the departmentin the private clinic “Immunogen test”inthe Republic of Uzbekistan. Examinations were carried out using the "Mindray MR-96A" immunoenzyme analyzer. Biomarkers such as sFlt-1, PlGF, their ratio sFlt-1/PlGF, LDHwere examined in the plasma of pregnant women involved in the study.sVEGF-R1FMS-related tyrosine kinase-1 (sFLT-1)-human sVEGF-R1 ELISA kit is an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the determination of VEGFR1. Catalog number: BMS268-3 and BMS268-3TEN. Developed in 2019 by Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. Soluble VEGF-R1 (sFLT-1) is a naturally occurring endogenous form of VEGF-R1 that was originally discovered in human vascular endothelial cell supernatant. It is formed as a result of differential proteinization of the flt-1 gene. In vitro, VEGF-R1 indirectly inhibits VEGF-A-mediated signaling in endothelial cells and can be used to block physiological angiogenesis in several organs in vivo.The reagent kit should be stored at 2°C to 8°C. Reagents remaining after use should be stored in a refrigerator at 2°C to 8°C.PLGF (placental growth factor) ELISA – Angiogenesis and vascular transformation are important processes in the normal development of the placenta. Anomalous angiogenesis and changes in blood vessels are one of the main factors for preeclampsia and fetal growth restriction. Placental growth factor (PLGF), a member of the VEGF family, is mainly produced by the placenta and is a potent angiogenic factor. A related receptor, soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase-1, is believed to have angiogenic properties.This biochemical assay is an enzyme immunoassay used to measure human placental growth factor in serum. This reagent can be used as a diagnostic tool to assess the possibility of preeclampsia in pregnant women.This reagent is manufactured in Demeditec Diagnostics GmbH. Lise-Strabe2/ 24145 Kiel (Germany). The Demeditec PLGF ELISA Kit is an enzyme immunoassay based on the sandwich principle (ELISA).This reagent should also be stored at 2-8°C until the expiration date.All patients underwent a clinical and laboratory examination, including general analysis of blood and urine, fibrinogen, aPTT, PTI, thrombin time, INR, D-dimer, etc.The age of all the women under observation was around 18-42 years. Average age in group 1 was 28.2±0.8 (17-42) years; It was 29.8±0.8 (42-19) in group II, and 25.7±0.7 (20-37) in the control group.
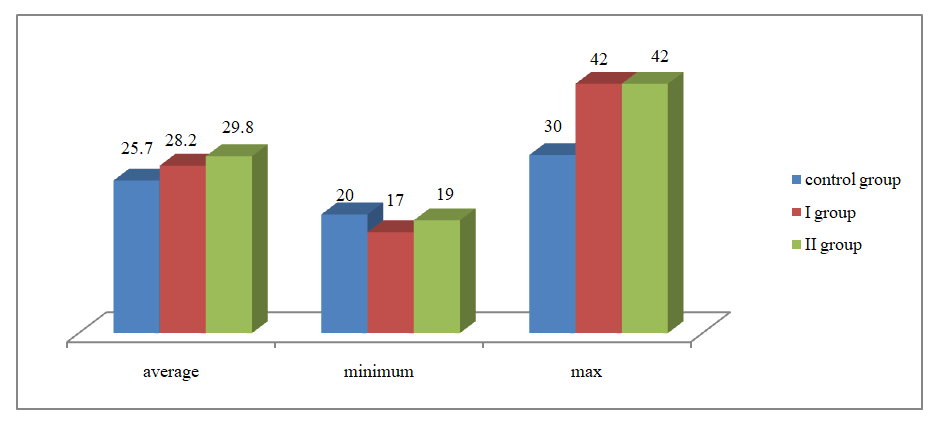 | Figure 1. The average age of the examined women |
 | Figure 2. The duration of the menstrual cycle of women participating in the study |
3. The Findings of the Research
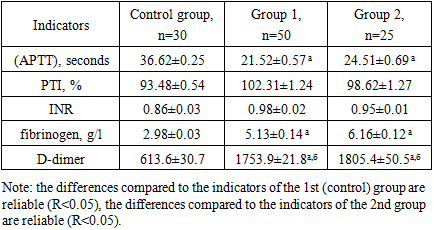
- In pregnant women complicated by PE and COVID-19, activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT) in plasma was reduced and was 21.52±0.57 seconds in pregnancy group 1 and 24.51±0.69 seconds in group 2, that is, 1.70 (R< 0.05) and 1.49 (R<0.001) times decreased. The results obtained show that (APTT)decreases with increasing gestational age in pregnant women with PE and COVID-19, and this, in our opinion, indicates an increased risk. In the control group, (APTT)was 36.62±0.25 seconds. The prothrombin index was calculated using a special formula and it was 93.48±0.54% in the control group. This indicator was 102.31±1.24% in pregnant women complicated by PE, and 98.62±1.27% in pregnant women with COVID-19. This indicates the presence of hypercoagulation in pregnant women.As can be seen from Table 1, there was a tendency to lengthen the international normalized ratio in pregnant women with PE: in group II, INR was 0.95±0.01 and in group 2it made up 0.98±0.02. In the control group, this indicator was 0.86±0.03. The obtained results showed a significant shift of blood towards hypercoagulability in the second stage of blood coagulation in pregnant women with PE and COVID-19.
|
|
|
4. Conclusions
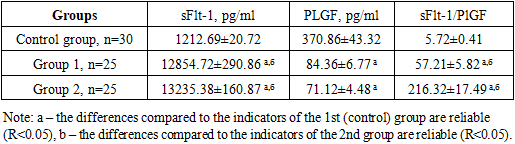
- • an increase in biochemical indicators is observed with increased complications of preeclampsia in pregnant women, which, in turn, can lead to a fetal growth restriction and complications.• In pregnant women complicated by preeclampsia and COVID-19, a tendency to hypercoagulation was observed at all stages of coagulation hemostasis, especially in pregnant women with severe PE, and mainly hyperfibrinogenemia and a progressive increase in D-dimer levels were observed.• it has been proven that in the blood serum of pregnant women complicated by preeclampsia and COVID-19 the amount of sFlt-1 increases rapidly, the amount of PlGF decreases, and the ratio of sFlt-1/PlGF increases progressively.• When all the above methods of treatment are used together, the cost associated with this disease decreases and the effectiveness of the treatment increases.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML