-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2024; 14(2): 201-205
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20241402.07
Received: Jan. 6, 2024; Accepted: Jan. 26, 2024; Published: Feb. 4, 2024

The Role of the Contribution of Optical Coherence Imaging Studies in Children with the Consequences of Perinatal Hypoxic Central Nervous System Disorder
Niyazov Shukhrat Toshtemirovich1, Ergashev Suhrob Sayidovich2, Djurabekova Aziza Takhirovna3
1Doctor of Medical Sciences, Associate Professor, Department of Neurology, Samarkand State Medical University
2Basic Doctoral Student of the Neurology Department, Samarkand State Medical University
3Doctor of Medical Sciences Professor, Head of the Department of Neurology, Samarkand State Medical University
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Perinatal lesions of the central nervous system (PNS) or hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy is a group of pathological conditions associated with brain damage in the perinatal period.
Keywords: Optical coherence imaging, Studies in children, Perinatal hypoxic disorder, Central nervous system
Cite this paper: Niyazov Shukhrat Toshtemirovich, Ergashev Suhrob Sayidovich, Djurabekova Aziza Takhirovna, The Role of the Contribution of Optical Coherence Imaging Studies in Children with the Consequences of Perinatal Hypoxic Central Nervous System Disorder, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 14 No. 2, 2024, pp. 201-205. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20241402.07.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Scientists of modern paediatrics, paediatric neurology, paediatric neurorehabilitation have achieved high successes in the field of medicine dealing with the problem of consequences of perinatal damage of the central nervous system (CNS) in children. The main task of specialists is conditioned by prevention of disability formation from childhood [1,5,9]. Over the last ten years, researchers have argued that the basis of all CNS lesions in children is initially based on a variety of morphofunctional shifts in the brain associated with individual neuroontogenesis [2,6,10]. If we consider all disorders associated with hypoxic CNS disorders as a consequence of perinatal damage, a variety is noted, including delayed motor development up to the formation of cerebral palsy, delayed psycho-speech development, cognitive deficiency, seizure syndromes, hydrocephalus, attention deficit and hyperactivity disorder, visual and auditory deficits, dysythonia [3,7,11]. Literature sources of recent years indicate that the formation involves not only cerebral changes at the level of cells, but also the formation of destructive diffusion in the area of the blood-brain barrier, and this occurs instantly (a few minutes), or in a subsequent stage with slow progression [4,8,12]. This fact leads to the cause of release of neurospecific factors into the blood, which leads to neuro-conflict or pathomechanical triggering of the autoimmune process in the CNS directly related to cell migration, which is important in the formation of the growing and developing brain [13,17]. Given the huge potential of scientific works, the issue of clinical features of the consequences of cerebral ischaemia in the perinatal period remains controversial, which makes it difficult to determine the true incidence of perinatal encephalopathies. The issues of differentiation criteria and transition from the level of normative indicators to pathological ones have not been fully resolved. Practical experience of doctors shows that it is not uncommon to find severe CNS defects in case of minor abnormalities when collecting anamnesis, and the opposite is true, in case of severe and obvious catamnestic factors, normal development of the child [5,9,11]. All this is due to the fact that mainly the diagnostic value is based on clinical and anamnestic data and traditionally on neurosonographic indicators, which can show only already formed structural disorder, besides it is limited by age [6,10]. Therefore, the issue of finding new criteria for diagnosis and prognosis of brain deficit remains relevant. A promising direction is the study of optical coherence tomography, laboratory indices of pyruvic acid [3,7,15], which is a link in the complex chain of energy exchange of methochondrial structures [8,12].Thus, perinatal encephalopathy and its consequences remain a controversial problem, the urgency of the problem is not decreasing, but increasing due to the growth of child neurological disability, thus reducing the level of socio-economic development of the country as a whole.Purpose of the study. To study clinical manifestations of the consequences of perinatal hypoxic encephalopathy in children, with the estimation of the contribution of optical-coherent imaging of the central nervous system lesions.
2. Material and Methods of Research
- There were 40 children aged from 1 to 2 years with the consequences of perinatal hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy (main group) under observation. 16 children from them were observed in dynamics from the moment of the newborn period. A separate questionnaire was administered to the mothers of the main group, where the anamnesis of somatic status before pregnancy, obstetric and gynaecological status during pregnancy and the outcome of delivery were carefully studied. The comparison group consisted of 20 healthy children of identical age (1-2 years). All patients underwent standard traditional examination by a neurologist, neonatologist, paediatrician, and ophthalmologist. Additional examination combined laboratory methods (blood biochemistry, urinalysis); all children underwent neurosonographic examination (but the indicators are not included in the description of this article, given the purpose of the study). Quantitative scales, included the study of levels of psycho-speech behaviour. This work was carried out on the basis of the paediatric neurological department and neonatal pathology department of MK Samarkand State Medical University (Samarkand), for the period 2022-2024.As noted above, retinal OCT was performed in 11 children with perinatal encephalopathy at the age of 6-12 months, who constituted group A. At the same time, 5 patients underwent OCT at an earlier date, respectively, in the dynamics of the examination, where the age from birth was 7-8 weeks. The control group consisted of children of corresponding identical age, healthy, 10 children, who constituted group B. For the examination, parents signed a written voluntary consent for the medical study. The examination was performed on the Cirrus TM. HD-OCT SPECTRAL DOMAIN TECHNOLOGY, Carl Zeiss AG (Zeiss) Germany, where the area and perimeter, retinal thickness, densities of superficial and deep plexus vascular, presence or absence of neovascular complexes were determined. As confirmation of the obtained results, it was necessary to clearly fix the patient in the lateral position, where the results corresponded to the rotation of the obtained images by 90 degrees. It should be noted that the age peculiarity required a quick procedure, in this connection only a high quality image of one eye was taken, and the analysed eye was chosen randomly. Statistical processing of the material was performed on an individual computer, where clinical parameters and quantitative scales were analysed by the traditional method of Spearman's criterion, and OCT parameters, as they have no normative separation, were studied in comparison groups according to the Mann-Whitney (U) criterion, where differences with values p<0.05 were considered reliable.
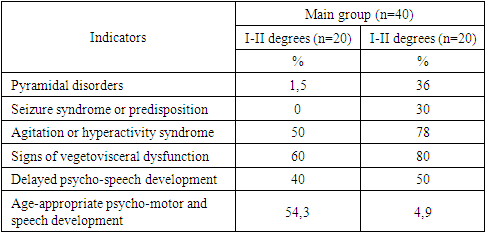
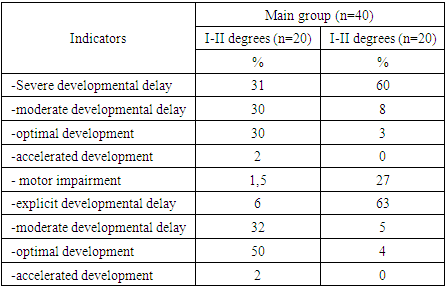
3. Result of the Study
- In accordance with the objective, the study included observation of children with perinatal encephalopathy of hypoxic-ischaemic genesis of different severity using a set of planned clinical and instrumental studies. An important component in the pathology of PEP, is the level of maternal health, the peculiarity of the course of the entire period of pregnancy, childbirth, the impact on the birth of a child with various deviations of organs and systems, which forms in them, in the future, certain functional-organic disorders. Accordingly, the analysis of extragenital changes and the course of anteintrapartum time in mothers is undoubtedly indicative of the examined children. Thus, the result of the analysis showed that among the complications of pregnancy in mothers of the examined children there are many aggravating factors, such as placental insufficiency and chronic intrauterine fetal hypoxia, directly affecting the nature of neurological pathology in children.
|
|
|
 | Figure 1. 7 patients, zones of vascularisation are visible, borders of epiretinal proliferation, with an average size of 36 µm with narrowing at the base, are displayed close to the retinal border |
4. Conclusions
- The main problem in neonatal hypoxic ischaemic encephalopathy is early differential diagnosis, prognosis and classification of the disease, on the results of which the further optimisation of treatment directly depends. The study revealed a direct significant dependence of maternal health before and during pregnancy, quality of labour and complications on the outcome of birth, dependence on the time of the beginning of procedures to compensate for the resulting hypoxia. In recent advances in systemic diagnostics, the use of optical coherence tomography makes it possible to study at an early stage the differentiation and prognosis of children with PEP. As an addition to clinical signs, as well as establishing the relationship with the degree of severity of PEP, especially this fact is necessary taking into account the detection of brain damage in newborns, because it is in the first days of life is difficult to diagnose the impact of hypoxia on the whole organism. The determination of tracing in the dynamics of existing signs of brain damage to clarify not only the diagnosis of PEP (complications), but also to prescribe the correct treatment without polyprogmotism is of interest in this direction.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML