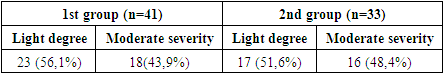
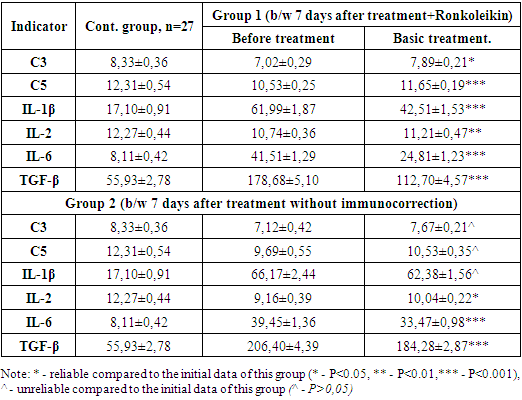
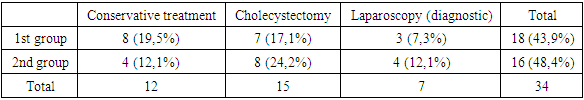
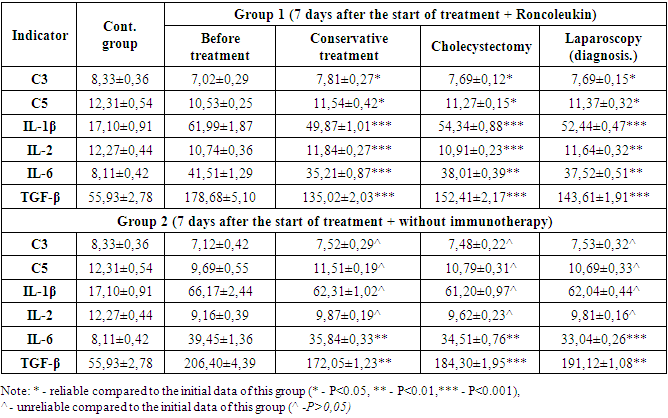
| [1] | Belik, B.M. Intraperitoneal hypertension and intestinal insufficiency syndrome as predictors of the development of early organ dysfunctions and infectious complications in pancreatic necrosis / B.M. Belik, G.M. Chirkinyan, R.Sh. Tenchurin, D.V. Mareev, M.A. Oskanyan, I.V. Dudarev, A.R. Dadayan, A.I. Maslov / Infections in surgery. - 2018. - Vol. 16, No. 1-2. - pp. 46-47. |
| [2] | Bogdanov, S.N. Questions of classification of acute pancreatitis: the point of view of a practical surgeon / S.N. Bogdanov, A.S. Mukhin, V.N. Voloshin, L.A. Otdelnov // Perm Medical Journal. - 2020. - Vol. 37, No. 1. - pp. 102-110. |
| [3] | Rizaev, K.S. Optimization of diagnosis and treatment of acute pancreatitis / K.S. Rizaev, B.K. Altiev, Sh.E. Baymuradov // Proceedings of the XXIV International Congress of the Association of hepatopancreatobiliary surgeons of the CIS countries "Actual problems of hepatopancreatobiliary surgery". – St. Petersburg: B.I., 2017. – pp. 73-74. |
| [4] | Musoyev T.Y., Khamdamov B.Z., Khakimboeva K.A., Usmonova N.U. Direct results of complex traditional treatment of patients with pancreatic necrosis complicated by sepsis. Biology and problems of medicine. – 2023, №3(144). - Pp.150-160. |
| [5] | Musoyev Tohir, Hamdamov Bakhtiyor, Hamdamov Alisherjon. Analysis of the results of complex treatment of patients with pancreatic necrosis complicated by sepsis. Journal Medicine and Innovations 2 (10) June, 2023. –pp. 217-235. |
| [6] | Musoyev T.Ya., Khamdamov B.Z., Ganiev A.A., Khakimboeva K.A. The role and place of laboratory parameters in the diagnosis of acute pancreatitis. Biology and problems of medicine. – 2022, №3(136).- Pp.59-63. |
| [7] | Musoyev T.Y., Khaydarov F.N., Khamdamov B.Z., Khamdamov A.B. Experimental modeling of pancreatic necrosis complicated by sepsis. New day in medicine. - Bukhara, 2023. - № 5 (55). - Pp. 433-438. |
| [8] | Khamdamov B.Z., Musoyev T.Y., Khaydarov F.N., Khamdamov I.B., Comparative clinical and laboratory characteristics of an experimental model of pancreatic necrosis complicated by sepsis // International Conference modern medicine: innovations and current approaches. 2022 Baku, Azerbayjan.- P. 174-175. |
| [9] | Khamdamov B.Z., Musoyev T.Y., Khaydarov F.N., Khamdamov I.B., Development of an experimental model of pancreatic necrosis complicated by sepsis // International Conference MODERN MEDICINE: INNOVATIONS AND CURRENT APPROACHES. 2022 Baku, Azerbayjan. - P. 184-186. |
| [10] | Musoyev T.Y. The effectiveness of the results of complex treatment of patients with pancreatic necrosis complicated by sepsis // “Collection of materials of the scientific and practical conference No. 11 of the Republic on the topic "Current problems of science development and innovative achievements, August 20, 2023 y, pp. 76-80. |
| [11] | Musoyev T.Y. A new experimental model of pancreatic necrosis complicated by sepsis // International scientific and practical conference on “Problems of Modern Surgery" Materials, October 6, 2023, Andijan. - pp. 224-225. |
| [12] | Musoyev T.Y., Khaidarov F.N., Khamdamov B.Z. Characteristics of the course of an experimental model of pancreatic necrosis complicated by sepsis // International scientific and practical conference on “Problems of Modern Surgery" Materials, October 6, 2023, Andijan. - pp. 228-229. |
| [13] | Musoyev T.Y., Ayubov B.M. Complex treatment of acute destructive pancreatitis using minimally invasive technologies // Materials of the XVIII Republican scientific and practical conference "Actual problems of emergency medical care in polytrauma and acute cardiovascular pathology", October 12, 2023, Bukhara. – pp. 135-136. |
| [14] | Musoyev T.Y., Ayubov B.M. Modern approaches to surgical treatment of pancreatic necrosis // Materials of the XVIII Republican scientific and practical conference "Actual problems of emergency medical care in polytrauma and acute cardiovascular pathology", October 12, 2023, Bukhara. – pp. 136-137. |
| [15] | Khamdamov B.Z., Musoyev T.Ya., Khaydarov F.N. New Experimental Model of Pankreonecrosis Complicated with Sepsis // Journal of Education & Scientific Medicine. – Toshkent, 2023. - № 1 (1). – P. 22-27. |
| [16] | Musoyev T.Ya. Comparative Clinical and Labaratory Characteristics of the Course of the Experimental Model of Pankreonecrosis Complicated with Sepsis // Journal of Education & Scientific Medicine. – Toshkent, 2023. - № 1 (2). – P. 7-14. |
| [17] | Khamdamov B.Z., Musoyev T.Ya., Khaydarov F.N., Ganiyev A.A. Morphological and Morphometric Characteristics of the Pancreas in the Dynamics of the Development of the Experimental Model of Pancreatic Necrosis Complicated by Sepsis // Journal of Education & Scientific Medicine. – Toshkent, 2023. - № 2 (1). – P. 10-19. |
| [18] | Khamdamov B.Z., Musoyev T.Ya., Khaydarov F.N., Ganiyev A.A. Immediate and Long-Term Results of Complex Traditional Treatment of Patients with Pancreatic Necrosis Complicated by Sepsis // Journal of Education & Scientific Medicine. – Toshkent, 2023. - № 2 (2). – P. 51-64. |
| [19] | Khamdamov B.Z., Musoyev T.Ya., Khaydarov F.N., Ganiyev A.A., Boboyev K.Kh., Abdurakhmanov F.M., Korikhonov D.N., Khamdamov Sh.A., Bobokulova Sh.A. About the Complexity and Mortality Among Patients with Pancreatic Necrosis // Journal of Education & Scientific Medicine. – Toshkent, 2023. - № 3 (1). – P. 20-31. |
| [20] | Khamdamov B.Z., Musoyev T.Ya., Khamdamov I.B. Development of a new Experimental Model of Pancreatic Necrosis Complicated by Sepsis // Eur.Chem.Bull. 2023, 12(Special Issue 4), - P 7688-7695. |
| [21] | Musoyev Tokhir Yakhoevich Analysis of the results of comprehensive treatment of patients with pancreonecrosis complicated with sepsis // American Journal of Pediatric Medicine and Health Sciences. – USA, Volume 01, Issue 07, 2023, ISSN (E): 2993-2149. – P. 36-47. |
| [22] | Tokhir Musoev Analysis of the Results of Complex Treatment of Patients with Pancronecrosis Complicated with Sepsis // American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 13 No. 10, 2023, pp. 1409-1416. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20231310.11. |
| [23] | Musoyev T.Ya., Khaydarov F.N., Khamdamov B.Z., Khamdamov A.B. Modeling of Pancronecrosis Complicated with Sepsis // International Conference on Advance Research in Humanities Sciences and Education Turkey, Conference June 15th 2023. |
| [24] | Khamdamov I.B. Clinical evaluation of the effectiveness of the traditional approach to the treatment of hernias of the anterior abdominal wall in women of fertile age // Doctor's Bulletin. –Samarkand 2022. No. 2.2 (104). -P.65-70. |
| [25] | Khamdamov I.B., Khamdamov A.B. Differentiated approach to the choice of hernioplasty method in women of fertile age (Clinical and experimental study) // Tibbiyotda yangi kun. – Bukhoro, 2021. -№ 6 (38/1). -С. 112-114. |
| [26] | Khamdamov I.B., Khamdamov A.B. Fertil yoshdagi ayollarda endovideo surgeon hernioplasty // Tibbiyotda yangi kun. Bukhoro, 2021.-No.6 (38/1) -S. 25-27. |
| [27] | Khamdamov I.B.Experimental determination of the extensibility of the anterior abdominal wall tissues at different times of pregnancy using various approaches to hernioplasty // Academicia: An International Multidisciplinary Research Journal Vol. 12, Issue 04, April 2022 SJIF 2022 = 8.252 Р.193-201. |
| [28] | Khamdamov I.B. Improving tactical approaches in the treatment of hernias of the anterior abdominal wall in women of fertile age // Tibbiyotda Yangi kun. Bukhoro, 2022. -№10(48) - pp. 338-342. |
| [29] | Khamdamov I.B. Morphofunctional features of the abdominal press in women of reproductive age // Tibbiyotda Yangi kun. Bukhoro, 2022. -№3(41) - pp. 223-227. |
| [30] | Khamdamova M.T. Ultrasound features of three-dimensional echography in assessing the condition of the endometrium and uterine cavity in women of the first period of middle age using intrauterine contraceptives // Biology va tibbyot muammolari. - Samarkand, 2020. - No. 2 (118). - P.127-131. |
| [31] | Khamdamova M. T. Ultrasound аssessment оf changes in the endometrium of the uterus in women of the first and second period of middle age when using intrauterine and oral contraceptives // Биомедицина ва амалиёт журнали. – Ташкент, 2020. - №2. - 8 часть. - С.79-85. |
| [32] | Khamdamova M. T. Аnthropometric characteristics of the physical status of women in the first and second period of middle age // A new day in medicine. Tashkent, 2020. - № 1 (29). - C.98-100. |
| [33] | Khamdamova M.T. Age-related and individual variability of the shape and size of the uterus according to morphological and ultrasound studies // News of dermatovenereology and reproductive health. - Tashkent, 2020. - No. 1-2 (88-80). - P.49-52. |
| [34] | Khamdamova M. T. Аnthropometric characteristics of the physical status of women in the first and second period of middle age // Тиббиётда янги кун. Ташкeнт, 2020. - № 1 (29). - C.98-100. |
| [35] | Khamdamova M.T. Age-related and individual variability of the shape and size of the uterus according to morphological and ultrasound studies // News of dermatovenereology and reproductive health. - Tashkent, 2020. - No. 1-2 (88-80). - P.49-52. |
| [36] | Khamdamova M.T. Ultrasound features of three-dimensional echography in assessing the condition of the endometrium and uterine cavity in women of the first period of middle age using intrauterine contraceptives // Biology va tibbyot muammolari. - Samarkand, 2020. - No. 2 (118). - P.127-131. |
| [37] | Khamdamova M. T. Ultrasound аssessment оf changes in the endometrium of the uterus in women of the first and second period of middle age when using intrauterine and oral contraceptives // Biomedicine va amaliyot journals. – Tashkent, 2020. - No. 2. - Part 8. - С.79-85. |
| [38] | Khamdamova M.T. Features of ultrasound parameters of the uterus in women of the first and second period of middle age using injection contraceptives // Tibbiyotda yangi kun. - Tashkent, 2020. - No. 2/1 (29/1). - pp. 154-156. |
| [39] | Khamdamova M.T. Features of ultrasound images of the uterus and ovaries in women of the second period of middle age using combined oral contraceptives // Tibbiyotda yangi kun. - Tashkent, 2020. - No. 2 (30). - pp. 258-261. |
| [40] | Khamdamova M.T. Individual variability of the uterus and ovaries in women who use and do not use various types of contraceptives // Tibbiyotda yangi kun. - Tashkent, 2020. - No. 3 (31). - pp. 519-526. |
| [41] | Khamdamova M. T. Еchographic features variability in the size and shape of the uterus and ovaries in women of the second period of adulthood using various contraceptives // Asian Journal of Multidimensional Research - 2020. – N9 (5). - P.259-263. |
| [42] | Khamdamova M. T. Somatometric characteristics of women of the first and second period of adulthood using different contraceptives with different body types // The american journal of medical sciences and pharmaceutical research - 2020. – N8 (2). - P.69-76. |


 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML