-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2024; 14(1): 139-143
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20241401.31
Received: Dec. 29, 2023; Accepted: Jan. 17, 2024; Published: Jan. 26, 2024

Tuberculous Spondylitis Clinical and Laboratory Manifestations
Babоev Abduvakhob Sakhibnazarovich, Nazirov Primkul Hujamovich
Deparment of Osteoarticular Tuberculosis of Rebuplican Specialized Scientific Practical Medical Center of Phtiziology and Pulmonology, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
Correspondence to: Babоev Abduvakhob Sakhibnazarovich, Deparment of Osteoarticular Tuberculosis of Rebuplican Specialized Scientific Practical Medical Center of Phtiziology and Pulmonology, Tashkent, Uzbekistan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Republican Specialized Scientific and Practical Medical Center of Phthisiology and Pulmonology of Republic of Uzbekistan. The age of the patients ranged from 16 to 80 years. Average age 50 years. Procalcitonin is considered as an acute-phase protein, but there is positive correlation with ESR and CRP in patients with pyogenic and tuberculous spondylitis. Procalcitonin blood level in tuberculous spondylitis patients increases, but significantly less than in patients with pyogenic spondylitis. Therefore, it can be used for the differential diagnosis of spondylitis in acute phase of inflammation.
Keywords: Tuberculous spondylitis, Pyogenic spondylitis, Laboratory tests
Cite this paper: Babоev Abduvakhob Sakhibnazarovich, Nazirov Primkul Hujamovich, Tuberculous Spondylitis Clinical and Laboratory Manifestations, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 14 No. 1, 2024, pp. 139-143. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20241401.31.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Back pain is the most common presenting symptom in spine infection patients [1], which if not timely diagnosed and treated, can lead to serious complications such as paralysis due to formation of epidural abscesses and pathologic fractures of vertebras [1,2,3].Spine infections represent a heterogeneous group of disorders that includes discitis, vertebral osteomyelitis, epidural and paravertebral abscess [4]. Spine infections is a disease caused by microorganisms that spread hematogenously and affect the vertebral body, intervertebral disc and adjacent paravertebral soft tissue [4,6].Immunosuppression due to diabetes, malignancy, corticosteroids; recent spinal surgical procedures, advanced age are risk factors for spine infection. Growing antibiotic resistant bacteria also leads to failed nonoperative treatment [4,6].Based on literature data, pyogenic spondylitis accounts for 2–7% of all cases of bone and joint infections [5,6].Tuberculosis remains a major global public health problem [3]. Tuberculosis has been recognized as the leading cause of mortality from a curable infectious disease, the majority of patients with tuberculosis live in the most populated countries of Asia [5]. Spinal tuberculosis originates from pulmonary tuberculosis and one of the most common extrapulmonary tuberculosis pathologies [1,3,4,5,6]. Tuberculous spondylitis is the most dangerous and prevalent form of skeletal tuberculosis. Tuberculous spondylitis represents 1–5% of all tuberculous infections [6].Commonly there is a prolonged period of time between onset and diagnosis of spine infection (several months), and back pain can be the only symptom while patients can remain relatively healthy until manifestation of complications [1,3,5]. Thus, early diagnosis of spine infection is difficult due to numerous similarities in the imaging and clinical manifestations between pyogenic and tuberculous spondilitis; however, different treatments are required for each disease. Therefore, the early and correct diagnosis of spondylitis is important for timely and effective intervention for reducing the occurrence of spinal deformity and dysfunction. However, there is currently a lack of adequate evidence, recommendations, and guidelines for the early diagnosis of spinal infection. Numerous investigators are identifying ways to improve the specificity and accuracy of diagnosing spondylitis according to clinical symptoms, laboratory tests and radiographic analysis [1,3,4,5,23].
2. Purpose
- The purpose of our study was evaluation of procalcitonin levels in patients with tuberculous spondylitis and pyogenic spondylitis.
3. Materials and Methods
- The study was based on the data of examination of 140 patients admitted to the Republican Specialized Scientific and Practical Medical Center of Phthisiology and Pulmonology of Republic of Uzbekistan. Study period was 2022-2023 years. Male patients was equal to 83 (59.3±4.2%) and female 57 (40.7±4.2%). The age of the patients ranged from 16 to 80 years. Average age 50 years. General condition, orthopedic and neurological status was evaluated by medical examination. Data on the main, concomitant and past diseases and injuries was collected during medical examination as well.
3.1. Laboratory Tests
- Hemoglobin, erythrocyte count, color index, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, platelet count, leukocyte formula (leukocyte count, percentage of band and segmented neutrophils, lymphocytes, eosinophils, basophils, monocytes) were tested in all patients by hematology analyzer (Mindray BC-3000 Plus, Shenzhen, China). Hemostasis status was clarified by blood hematocrit percentage, thrombotest, prothrombin index, plasma fibrinogen rate, plasma re-calcification time, percentage of blood clot retraction, fibrinogen activity in percentage according to Rutenberg technique.Procalcitonin serum levels were evaluated by Finecare™ FIA Meter Plus, Wondfo Biotech (Guangzhou, China) fluorescence immunochromatographic analysing system. Biochemical analyzes were performed on Biossays 240 Plus (Snibe Diagnostic, Shenzhen, China): Antistreptolysin O, rheumatoid factor and C-reactive protein were determined in all patients' serum. The liver function was evaluated by the level of aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT); total, free and bound bilirubin in blood. The kidney function was evaluated by the level of urea and creatinine in the blood serum. Diabetes mellitus was defined by the level of fasting and postprandial blood sugar, as well as glycated hemoglobin percentage. According to indications, serum magnesium, potassium, calcium were determined.Urine color, transparency, PH, protein content was analyzed, as well as urine sediment microscopy with the determination of the cellular composition, salts, bacteria, fungi and cylinders.
3.2. Functional Diagnosis
- Cardiac electrical activity assessed by electrocardiography on BTL-08 SD device. External respiration function diagnosed on “Valenta” (Saint Petersburg, Russia) device. Internal organs organic disorders confirmed with ultrasound technique on Siemens Acuson (Berlin, Germany) device.
3.3. Radiographic Analysis
- A radiologist's and/or a histological report, and/or a positive result of a bacteriological examination confirmed Tuberculous spondylitis diagnosis.X-ray examinations included: magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) (MRI SIGNA HD/e, 1.5 Tesla, General Electric, USA), which was performed in most patients because of its better informativeness. Computed tomography (CT) (Siemens Definition AS 64, Germany), which was performed in patients with steel implants, when MRI was not possible. Both research methods applied in differential diagnostic cases. Radiological signs of tuberculous spondylitis were one or more of the following: a focus of bone destruction with unclear edges and the presence of a bone sequester inside; presence of abscess with calcification; abscess with subperiosteal extension.
3.4. Histology
- Tissue samples collected from surgical procedures was fixed with formalin, stained with hematoxylin-eosin, and cut with a microtome, than examined under a microscope. Central necrosis, surrounded by epithelioid and Pirogov-Langhans cells confirmed tuberculous inflammation.Pathologic tissues and fluids collected from surgeries, punctures, fistulas excretions and sputum were studied bacteriologically. Molecular genetic methods were GeneXpert® MTB/Rif (Sunnyvale, California, U.S.A) and GenoType MTBDRplus (Hain Lifescience GmbH, Nehren, Germany). Cultures of mycobacteria growing studied in BACTEC MGIT 960 (Becton Dickinson India Pvt. Ltd., Gurgaon, India) and inoculation of solid Lowenstein-Jensen medium.
3.5. Statistical Analysis
- Statistical analysis of the study was carried out using modern computer systems such as IBM/PQ of the latest generation using a package of standard Excel programs.
4. Results
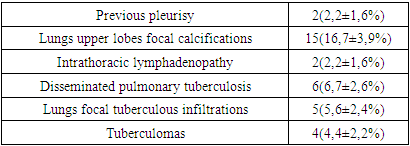
- Based on the results of the examination, 90 (100%) patients were diagnosed with tuberculous spondylitis and 50(100%) patients were diagnosed with pyogenic spondylitis.Tuberculous spondylitis in 56(62,2±5,1%) patients was presented only with spinal lesion, CT signs of previous tuberculous lesions found in 19(21,1±4,3%), intrathoracic lymphadenopathy diagnosed in 2(2,2±1,6%) patients, active pulmonary tuberculosis in 11(12,2±3,5%) patients. Diabetes mellitus had 11(12,2±3,5%) patients with tuberculous spondylitis (Table 1).
|
|
|
5. Discussion
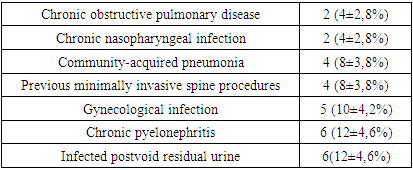
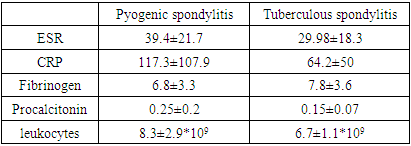
- A typical trait of chronic tuberculosis (TB) is substantial weight loss that concurs with a drop in blood hemoglobin (Hb) levels, causing anemia [7,8,9,10]. Ashenafi S et al., 2022 explored Hb levels in 345 pulmonary TB patients. Anemia was associated with a low body mass index (BMI), low mid-upper arm circumference, lower peripheral CD4 and CD8 T cells counts and IFN-γ levels, and a higher erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) [11]. In our study, we observed mild anemia in both groups of patients with tuberculous spondylitis (Hb=118±9.04 g/l, erythrocytes = 3.6±0.31*1012), and with pyogenic spondylitis (Hb=118.3±15.4 g/l, erythrocytes = 3.6±0.5*1012). Nevertheless, the stronger correlation of anemia with inflammation degree in pyogenic spondylitis patients points to superior intoxication in pyogenic inflammation.The incidence of infections in patients with diabetes mellitus is increased [12,13,14,15,16,17]. Al-Rifai RH et al., 2017 systematically reviewed the published literature to provide a summary estimate of the association between diabetes mellitus and active tuberculosis. Authors concluded that diabetes mellitus is associated with a two- to four-fold increased risk of active TB [18]. Workneh MH et al., 2017 in their systematic review revealed that there is a high burden of diabetes mellitus among TB patients at global level. The overall median global prevalence was 16%. In our study, 11(12,2±3,5%) patients with tuberculous spondylitis suffered from diabetes mellitus and 6(12±4,6%) patients with pyogenic spondylitis had diabetes mellitus as well [19]. Several case reports in current literature suggest that urinary tract infection or gynecological infection can lead to pyogenic spondylitis. Spine infection can occur through direct inoculation, local tissue invasion or most commonly via haematogeneous spread in systemic infections. Bacterial seeding is thought to occur through the valveless posterior venous plexus and Baston’s vein [20,21].Five (10±4,2%) female patients had gynecological infection and gynecological surgical procedures before the admission to our hospital. Twenty eight (56±7,01%) patients presented with urinary tract infections with hyperproteinuria, leukocyturia and erythrocyturia. Six (12±4,6%) of the patients with urinary tract infection, had chronic pyelonephritis with inflammation of the renal parenchyma on ultrasound and early chronic renal failure. Another 6(12±4,6%) male patients with urinary tract infection had postvoid residual urine due to benign prostatic hyperplasia. Leboueny M. et al., 2023, studied CRP and procalcitonin levels in HIV-negative pulmonary TB patients. The mean concentration of CRP in TB patients was 114.7 mg/L at diagnosis. The average concentration of PCT at the time of diagnosis was 0.3 ng/mL [22]. In our study, tuberculous spondylitis patients presented with high CRP 65.3±50.7 mg/ml, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) 30.5±18.4 mm/h, procalcitonin 0.16±0.07 ng/ml and fibrinogen 7.75±3.8 g/l levels. Pyogenic spondylitis patients had much higher CRP (117.3±107.9 mg/ml), ESR (39.4±21.7 mm/h) and procalcitonin (0.3±0.2 ng/ml) levels, but lower fibrinogen (6.8±3.3 g/l) levels.
6. Conclusions
- Thus, chronic intoxication in tuberculous infection leads to loss of appetite and mild anemia. The stronger relationship between a decrease in hemoglobin and an increase in ESR in pyogenic spondylitis appears to be associated with greater intoxication in nonspecific lesions, which leads to greater anorexia, which is the most obvious cause of a decrease in hemoglobin.Procalcitonin blood level in tuberculous spondylitis patients increases, but significantly less than in patients with pyogenic spondylitis. Therefore, it can be used for the differential diagnosis of spondylitis in acute phase of inflammation.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML