-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2024; 14(1): 75-78
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20241401.17
Received: Dec. 22, 2023; Accepted: Jan. 11, 2024; Published: Jan. 12, 2024

Some Technical Aspects of Soaking Intraoperative Polyfilaments with Antibiotic Solution in Mannitol
Xasan Kurbanov1, Madamin Madazimov2
1Senior Lecturer, Department of Faculty and Hospital Surgery, Andijan State Medical Institute, Andijan, Uzbekistan
2Professor, Rector, Andijan State Medical Institute, Andijan, Uzbekistan
Correspondence to: Xasan Kurbanov, Senior Lecturer, Department of Faculty and Hospital Surgery, Andijan State Medical Institute, Andijan, Uzbekistan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

This study is based on the results of surgical treatment of 481 (100.0%) patients with various abdominal pathologies treated in the surgical department of Andijan regional multidisciplinary medical center in 2020-2023. The patients included in the study were completed by us during the primary and repeated examinations in the clinic according to the specially developed questionnaire Protocol of examination of patients after abdominal examination. Before surgical treatment, the condition of patients was assessed not only visually, but also through additional examinations. The effect of suture materials on the duration and degree of recovery of the functional state of organs and tissues after the operation was studied.
Keywords: Surgery, Abdominal, Treatment, Patient, Clinic, Tissue, Suture material
Cite this paper: Xasan Kurbanov, Madamin Madazimov, Some Technical Aspects of Soaking Intraoperative Polyfilaments with Antibiotic Solution in Mannitol, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 14 No. 1, 2024, pp. 75-78. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20241401.17.
1. Introduction
- Sex and age of patients in abdominal surgery are considered to be one of the evaluation criteria to a certain extent in eliminating pathological conditions. Physical superiority is considered a factor in the effect of suture materials on the wound and early wound healing. It should be emphasized separately that late (complicated) determination of surgical procedures causes anatomical features of injuries, tactical errors and difficulties in treatment. Improper organization of the rehabilitation period after surgical intervention or lack of dispensary control can lead to poor results.
2. Mаtеriаls аnd Mеthоds
- The following therapeutic and preventive directions used in the main group became the basis for scientific research:* in order to prevent the development of specific local complications of the treatment stage:- determination of the amount of antibiotic and mannitol solution soaking into intraoperative polyfilaments in an open method;- determination of the optimal time and exposure of immersion in polyfilament;- determination of instructions for placing non-removable subcutaneous sutures;- achieving aesthetic results by using drugs that affect the mechanism of formation of secondary hypertrophic or keloid scars by the acute dermotension method through the physiological assessment of the tissue deficit in the application of skin sutures;- to determine the distance and duration of laser light exposure to an intraoperative wound* prevention of deterioration of functional and aesthetic results in the postoperative periods.Planned surgical operations were performed in an open and closed manner, these are operations in the retroperitoneal space and pre-abdominal wall organs. Inspections are divided into two parts according to the period of execution: urgent and scheduled operations. Out of 481 (100%) examinations, 413 (85.9%) points were planned, while 68 (14.1%) patients (Pearson's χ2 test - 29.19; df=8; R=0.0012.) urgent operations done. It should be noted that the increase of the acute inflammatory process in the abdominal cavity was considered an exception criterion and an indication for urgent surgery.
3. Rеsults аnd Disсussiоn
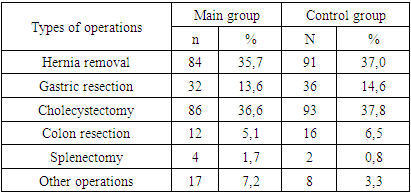
- Taking into account the implemented tactical and technical aspects, the patients were divided into two study groups: the comparison group - in 2020-2021, 246 (51.1%) patients used conventional polyfilament threads; and the main group consisted of 235 (48.9%) patients in 2022-2023, in addition to antibiotic and mannitol-soaked threads, sutures placed under the influence of laser light were used in surgical operations. These preventive measures lead to shorter rehabilitation periods, improved early and long-term results after surgery. In both groups, the use of absorbable and non-absorbable suturing materials for placing sutures on internal organs in all methods of abdominal surgery has an equal chance of comparing the results of both groups.A cross-year analysis shows that urgent surgical operations increased 1.6 times in 2023 compared to 2020. Scheduled inspections were 1.1. Pearson's χ2 test on this is -0.37; df=6; R=0.0001.Table 1 shows the distribution of patients who underwent surgical procedures according to the types of examination.
|
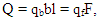 Here: special load width per qb-head m, t / (ch*m);qf-specific load 1m2 area, t/(h*m2)b-sieve width, m;l-sieve length, m;F - sieve area, m2Polished solution does not affect the properties of the thread. All experiments were carried out according to the established state standard.Mannitol is an alcohol solution of sugar that has been shown to effectively reduce swelling after injury. There is some evidence that mannitol has a function in the blood stream. Several studies have compared treatment with mannitol to "standard care." Another study compared mannitol treatment to hypertonic saline. According to sources, mannitol is an osmotic diuretic. Intensification of the reabsorption process increases the osmotic pressure in the plasma. The interstitial fluid compression property causes water to escape through renal filtration. Its widespread use in a number of medicine departments indicates that many properties of mannitol have not been studied. In particular, it is used for the preparation of the intestine in the practice of kidney transplantation, as well as in colorectal surgery. Mannitol is a very convenient drug for use, there is a 5, 10, 15, 20%, even 25% solution. Another novelty of our research is that this drug has a direct effect on the growth and development of the microflora in the intestines, and it has the ability to form correct colonies. European Union scientists have identified the effect of mucoviscidosis when applied to patients over 18 years of age. When given to babies up to 20 grams, the inside (slabitel) softened. Due to its strong cooling effect, mannitol exhibits hemostatic activity directly through soaked suture materials, besides, it has a very low hydrophobic effect and is activated at 98% humidity.The patients included in the study were subjected to general examinations before and after the operation, including expanded general blood, biochemical analyzes (determined using the biochemical analyzer "Bs-120 Chemistry Analyzer") (ALT, AST, Bilirubin, urea, creatinine, total protein) MNO, AChVT, PTI, coagulogram was performed. Intraoperative thermometry, oximetry, and x-rays were performed as directed. The above-mentioned information was recorded in the medical record, photographs were archived. However, the UTT examination occupies an important place in the examination of the organs of the abdominal cavity.Abdominal ultrasound examination is the simplest and cheapest diagnostic method, which allows to detect possible diseases and organ development abnormalities even at an early stage.Ultrasound examinationAll organs located in the abdominal cavity are assessed, including the liver, spleen, pancreas, gall bladder and urinary system. Abdominal organs are recommended for ultrasound examination in the following cases. These are:- in abdominal pain of unknown cause;- discomfort, heaviness, nausea after eating;- abdominal injuries.- regular bitter taste in the mouth;- in disorders of the intestines (constipation, diarrhea);- loss of appetite;- in the increase of gas production in the intestine;- vomiting after eating and without a previous reason;- when swelling occurs in the abdomen.Thermometry.With the help of non-contact infrared thermometers, it is possible to determine if you are standing at a distance of 10-15 cm without touching the wound. The result is a display with a storage capacity of 5-7 times. Advantages:- save in memory when measured several times at the same time;- high measurement speed;- does not require touching the wound;- it is possible to determine the temperature of the device;- ease of sterilization and availability of certification.The sensitive element of the thermometer records the temperature of the kinetic energy produced by reacting with the infrared rays coming from each object or surface. This will show it as a number on the display. We used a Sensitec NF3101 non-contact infrared thermometer in our research. The thermometer is not sterilized after use because it does not come into contact with a temperature source. For example, it is possible to apply to several organs and tissues or to several patients at the same time.Determination of transcutaneous pressureIn 73 patients at different stages of surgical procedures, 5, 10 minutes after intraoperative anastamosis, the condition of blood circulation in the wound was determined under the influence of laser light. When determined without the influence of laser light, RO2 was 86.4 mm.cm.ust, while under the influence of laser light it was 89.4 mm.cm.ust. partial oxygen pressure can be seen to rise in dynamics. It served to maximize the expansion of the micro-vessel network and create standard measurement conditions. In various pathologies, covering the mesentery with a napkin soaked in physiological solution at a temperature of 430C, and the frequency of treatment under the influence of laser light for 3 minutes led to an increase in microcirculation from 89.4 to 91.6. This results in a 93.6% increase over the first observed result. The TSM-400 device produced by the "Radiometer" company was used in this. When the obtained results are compared with each other, the average coefficient in the free state is calculated when calculating the relative value of RO2. To do this, it was measured while the patient was breathing, as well as during the transition to a stable level while breathing pure humidified oxygen through a mask. As a drawback, it should be said that the open system should be measured for at least 2 minutes. Digital graphs are displayed on the screen in tabular form. Tables can be saved, printed and transported electronically in Windows.
Here: special load width per qb-head m, t / (ch*m);qf-specific load 1m2 area, t/(h*m2)b-sieve width, m;l-sieve length, m;F - sieve area, m2Polished solution does not affect the properties of the thread. All experiments were carried out according to the established state standard.Mannitol is an alcohol solution of sugar that has been shown to effectively reduce swelling after injury. There is some evidence that mannitol has a function in the blood stream. Several studies have compared treatment with mannitol to "standard care." Another study compared mannitol treatment to hypertonic saline. According to sources, mannitol is an osmotic diuretic. Intensification of the reabsorption process increases the osmotic pressure in the plasma. The interstitial fluid compression property causes water to escape through renal filtration. Its widespread use in a number of medicine departments indicates that many properties of mannitol have not been studied. In particular, it is used for the preparation of the intestine in the practice of kidney transplantation, as well as in colorectal surgery. Mannitol is a very convenient drug for use, there is a 5, 10, 15, 20%, even 25% solution. Another novelty of our research is that this drug has a direct effect on the growth and development of the microflora in the intestines, and it has the ability to form correct colonies. European Union scientists have identified the effect of mucoviscidosis when applied to patients over 18 years of age. When given to babies up to 20 grams, the inside (slabitel) softened. Due to its strong cooling effect, mannitol exhibits hemostatic activity directly through soaked suture materials, besides, it has a very low hydrophobic effect and is activated at 98% humidity.The patients included in the study were subjected to general examinations before and after the operation, including expanded general blood, biochemical analyzes (determined using the biochemical analyzer "Bs-120 Chemistry Analyzer") (ALT, AST, Bilirubin, urea, creatinine, total protein) MNO, AChVT, PTI, coagulogram was performed. Intraoperative thermometry, oximetry, and x-rays were performed as directed. The above-mentioned information was recorded in the medical record, photographs were archived. However, the UTT examination occupies an important place in the examination of the organs of the abdominal cavity.Abdominal ultrasound examination is the simplest and cheapest diagnostic method, which allows to detect possible diseases and organ development abnormalities even at an early stage.Ultrasound examinationAll organs located in the abdominal cavity are assessed, including the liver, spleen, pancreas, gall bladder and urinary system. Abdominal organs are recommended for ultrasound examination in the following cases. These are:- in abdominal pain of unknown cause;- discomfort, heaviness, nausea after eating;- abdominal injuries.- regular bitter taste in the mouth;- in disorders of the intestines (constipation, diarrhea);- loss of appetite;- in the increase of gas production in the intestine;- vomiting after eating and without a previous reason;- when swelling occurs in the abdomen.Thermometry.With the help of non-contact infrared thermometers, it is possible to determine if you are standing at a distance of 10-15 cm without touching the wound. The result is a display with a storage capacity of 5-7 times. Advantages:- save in memory when measured several times at the same time;- high measurement speed;- does not require touching the wound;- it is possible to determine the temperature of the device;- ease of sterilization and availability of certification.The sensitive element of the thermometer records the temperature of the kinetic energy produced by reacting with the infrared rays coming from each object or surface. This will show it as a number on the display. We used a Sensitec NF3101 non-contact infrared thermometer in our research. The thermometer is not sterilized after use because it does not come into contact with a temperature source. For example, it is possible to apply to several organs and tissues or to several patients at the same time.Determination of transcutaneous pressureIn 73 patients at different stages of surgical procedures, 5, 10 minutes after intraoperative anastamosis, the condition of blood circulation in the wound was determined under the influence of laser light. When determined without the influence of laser light, RO2 was 86.4 mm.cm.ust, while under the influence of laser light it was 89.4 mm.cm.ust. partial oxygen pressure can be seen to rise in dynamics. It served to maximize the expansion of the micro-vessel network and create standard measurement conditions. In various pathologies, covering the mesentery with a napkin soaked in physiological solution at a temperature of 430C, and the frequency of treatment under the influence of laser light for 3 minutes led to an increase in microcirculation from 89.4 to 91.6. This results in a 93.6% increase over the first observed result. The TSM-400 device produced by the "Radiometer" company was used in this. When the obtained results are compared with each other, the average coefficient in the free state is calculated when calculating the relative value of RO2. To do this, it was measured while the patient was breathing, as well as during the transition to a stable level while breathing pure humidified oxygen through a mask. As a drawback, it should be said that the open system should be measured for at least 2 minutes. Digital graphs are displayed on the screen in tabular form. Tables can be saved, printed and transported electronically in Windows.4. Соnсlusiоns
- Of the 481 patients included in the study, 480 (99.8%) had early results and 472 (98.1%) had long-term results. Early and long-term outcomes included the period from the date of examination of the patients until the sutures were taken, and the factors that directly and indirectly affected the visual and local changes in the patients were compared in the main and comparative groups. Long-term outcomes were studied from 6 months to 1 year after surgery. The results were divided into good, satisfactory and unsatisfactory results based on 3 criteria. Functional and cosmetic results are evaluated as long-term results of surgical operations. In evaluating the functional and cosmetic results, we developed based on the evaluation criteria developed in our clinic. It depends on the field of examination, size, pathology topography, ogran and restoration of tissue function. It should be noted that in the event that some organ tissues were removed, the effect on the neighboring organs was evaluated as the restoration of their functional status. The effect of the threads used during the operation on the skin, subcutaneous, apaneurosis, muscles and head organs was taken into account.Conditions rated as having a good functional and cosmetic result include:- if the thread is absorbed in time;- if there is no side effect on the activity of other organs;- if a scar does not appear when palpating the wound area with the hand;- if it does not hurt, does not itch, if there is no stinging sensation;- if it does not affect the digestive tract;- if elastic;- if it is folded when it is wrinkled;- if it is flat compared to the skin level;- does not adhere to deep tissues;- if sensation is restored;- if the function is fully restored.Satisfactory functional and cosmetic results:- change in the absorption time of the yarn (fast or slow);- if there is no side effect on the activity of other organs;- if a rough scar did not appear when palpating the wound area with the hand;- if it hurts, itches, if there is a tingling sensation;- if it does not affect the digestive tract;- if it is not elastic;- if it is folded when it is wrinkled;- if it is uneven compared to the skin level;- does not adhere to deep tissues;- if sensation is restored;- if the function is partially restored.Unsatisfactory functional and cosmetic results as:- if the thread is not absorbed or ligature swish;- if it grows into other organs and tissues;- if a rough scar is clearly visible (hypertrophic or keloid scar);- it hurts, itches, stinging;- affects the digestive tract;- will not be elastic;- does not crease when wrinkle;- rises above the skin level;- adheres to deep tissues;- becomes sensitive;- the function is partially restored.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML