-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2023; 13(12): 1935-1938
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20231312.24
Received: Nov. 4, 2023; Accepted: Nov. 24, 2023; Published: Dec. 16, 2023

The Influence of Food Patients on the Quantity of Trimethylamine-N Oxide in Patients with Ischemic Heart Disease
Kholikova Dilrabo Sobirjonovna, Jo'raeva Moxigul Azimjznovna
Andijan State Medical Institute, Andijan, Uzbekistan
Correspondence to: Kholikova Dilrabo Sobirjonovna, Andijan State Medical Institute, Andijan, Uzbekistan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

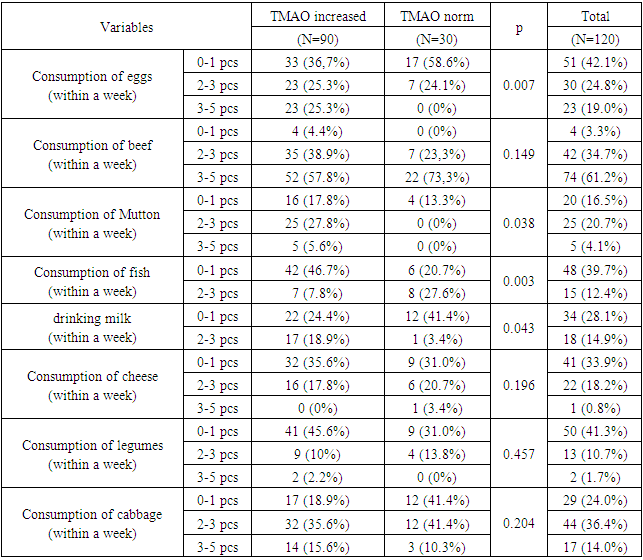
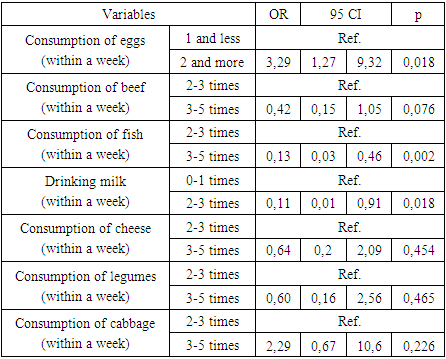
During the study, 90 patients with ischemic heart disease and 30 controls without ischemic heart disease studied the effect of diet on the amount of trimethylamine. The effect of consumption of various products (eggs, beef, lamb, dairy products, cheese) on the increase in TMAO concentration was studied and relevant results were obtained. It has been clinically proven that the probability of pathologically increased TMAO concentration in individuals who consume fish meat products 3 or more times a week is 8 times lower than in those who consume 2 or less times a week.
Keywords: Microbiota, Atherosclerosis, Ischemic heart disease, Nutrition, Choline metabolites, Trimethylamine-N-oxide TMAO
Cite this paper: Kholikova Dilrabo Sobirjonovna, Jo'raeva Moxigul Azimjznovna, The Influence of Food Patients on the Quantity of Trimethylamine-N Oxide in Patients with Ischemic Heart Disease, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 13 No. 12, 2023, pp. 1935-1938. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20231312.24.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Trimethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO), a choline metabolite, is associated with inflammation and is an active signaling metabolite in the gut microbiota leading to atherosclerotic damage and arterial thrombosis [2, p. 564–575]. When studying sterile rats, it was found that the microbiota affects the synthesis of endothelial adhesion molecules. [1, p. 691]. Red meat, egg yolks contain large amounts of L-carnitine and phosphatidylcholine. [9, p. 1585–1595; 3, p. 373–387]. This substance is converted into trimethylamine (TMA) by bacterial trimethylamine (TMA)-lyases in intestinal microbiota [1, p. 111–1; 800–804]. Such a reaction depends on the intestinal transport of choline and L-carnitine. When people eat food rich in choline, they may experience a fishy odor. Therefore, the formation of TMA depends on the dose of choline. In their research, when rats were given a low dose of choline (1.5 mmol/kg body weight), only 9 μmol of choline (6% of the dose) reached the bacteria-rich gut. In rats, 237 μmol (16% of the dose) reached the colon compared to 15 mmol choline/kg body weight. At both doses, 64–65% of administered choline was observed to be absorbed from the gut at 3 hours. [11, p. 111–1]. Therefore, TMA is converted to TMAO in the liver with the help of flavin-capturing monooxidase enzyme. [11, p. 111–1] Increased TMAO is also observed in insulin resistance, and elevated TMAO levels have been observed in diabetes. [6, p. 3699–3712]. In addition, TMAO also affects the angiotensin II signal, which has a chronic effect on hypertension [8, p. 1700–1705] and affects vascular diseases and inflammation of the vessel wall. [7, p. 964–970; 8, p. 1317–1323]. The amount of L-carnitine in plasma was determined as a predictor of cardiovascular diseases, and dietary choline and TMAO supplementation were found to cause atherosclerosis in rats [4, p. 576–585; 9, p. 1585–1595]. However, in other studies, atherosclerotic changes were not observed in rats. [5, p. d2318–2326].A separate questionnaire was distributed to all patients when we studied the level of increased TMAO in the study.Human dietary preferences have been found to be linked to gut microbes. Rational nutrition, non-drug therapy is a type of prevention of the cardiovascular system. The BJJST recommends that people eat less salt, less saturated fat and trans fat, and more fruits and vegetables.In recent years, information on TMAO as an atherogenic metabolite has increased. Reducing the potential atherogenic metabolites of foods that lead to TMAO leads to a reduction in cardiovascular risk. Intestinal microbiota is seen as a risk factor for the development of atherosclerosis and arterial thrombosis. Microbiota metabolites, trimethylamine N-oxide and short-chain fatty acids, are thought to stimulate and act as messengers of signaling mechanisms and cells of the immune system in the vascular system. In addition, microbiome-associated molecular patterns govern atherogenesis, and microbiota have been studied to induce arterial thrombosis through Toll-like receptor signaling. Increased atherogenic TMAO in patients with ischemic heart disease is associated with changes in gut microbiota and food intake.
2. Main Body
2.1. Purpose of the Study
- Studying and evaluation of the effects of products consumed by patients with ischemic heart disease on the amount of trimethylamine.
2.2. Material and Methods of Research
- The research is conducted on 90 patients with ischemic heart disease and 30 healthy control group who did not suffer from IHD and were treated in the therapeutic departments of the Andijan State Medical Institute.Short chain peptides, trimethylamine N oxide, cholesterol, low, very low and high density lipoproteins were studied in the blood of all patient.
2.3. The Results Obtained and Their Discussion
|
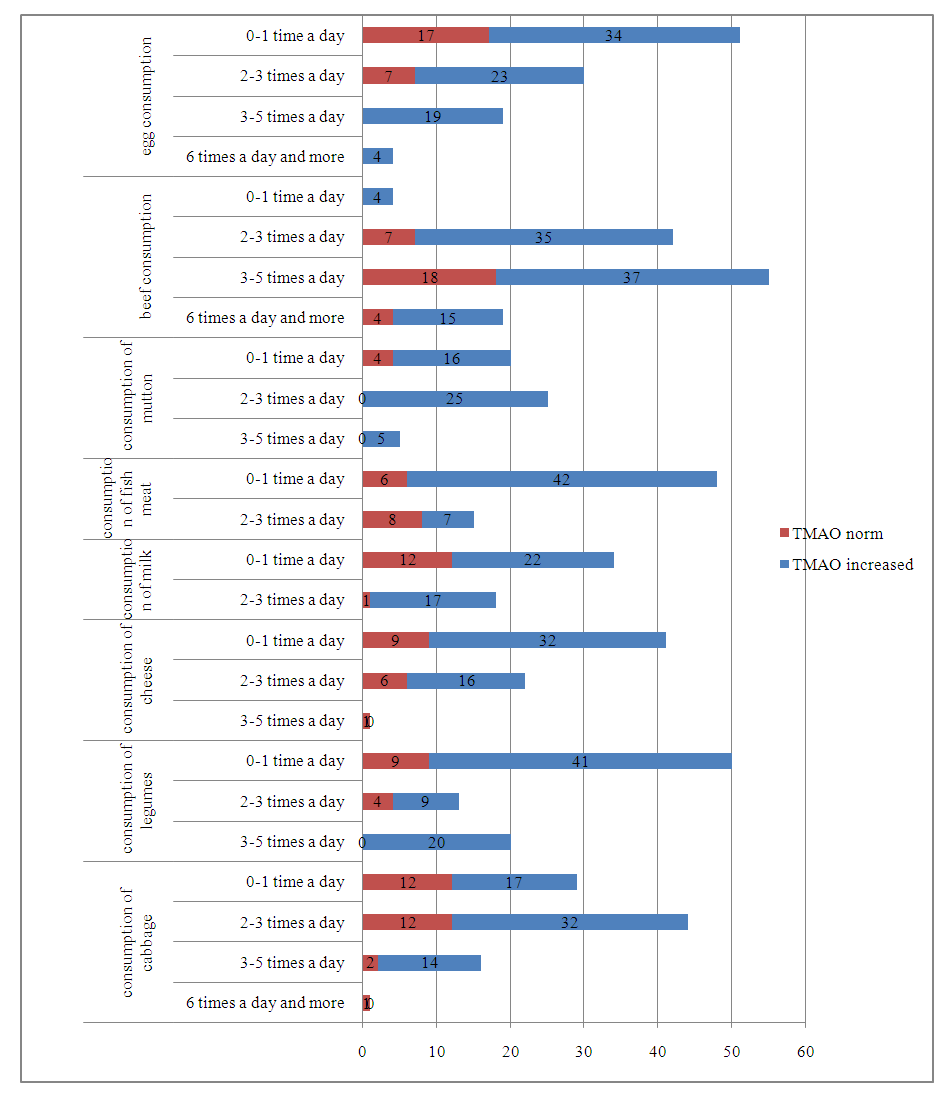 | Picture 1. Effect of consumed products on TMOA |
|
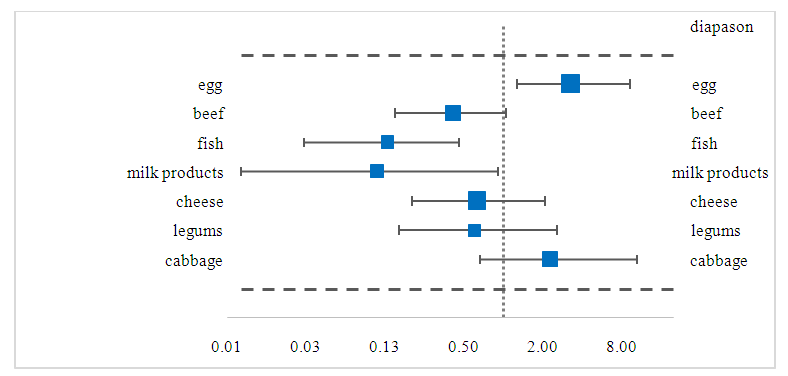 | Picture 2. Dietary reliability results |
3. Conclusions
- Compared to the control group, the consumption of products rich in phosphatidylcholine and L-carnitine in the diet of patients with IHD was 6 times greater than that of the control group: meat (r < 0.05), beef (r < 0.05), dairy products (r < 0.05), eggs 3 and higher times observed.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML