-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2023; 13(12): 1870-1874
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20231312.11
Received: Nov. 14, 2023; Accepted: Nov. 29, 2023; Published: Dec. 6, 2023

The Erector Spinae Plane Blockade Efficiency as a Part of Multimodal Anesthesia During Open Kidney Surgery
P. M. Kayumova1, A. N. Musabaev1, M. B. Krasnenkova2, S. Z. Ganiev1
1Republican Specialized Scientific and Practical Medical Center of Urology, Uzbekistan
2Tashkent Medical Academy, Uzbekistan
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

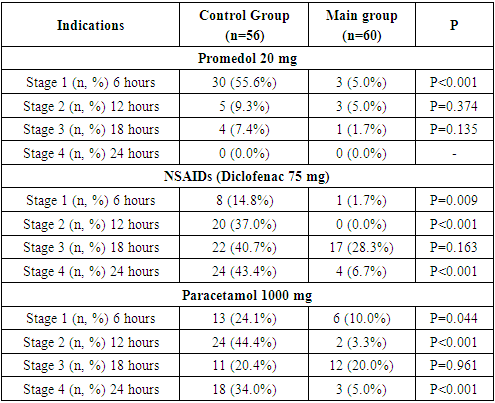
The aim of the study was to evaluate the efficiency of ESP blockade as a component of multimodal anesthesia during lumbotomy surgeries on the kidneys. Background. Currently, the ESP block is widely used both as an independent method of anesthesia and as a component of multimodal anesthesia. It creates an extensive sensor block, spreads over 5-7 segments. Material and methods. The studies were conducted on 116 patients of ASA class I – III at the age of 18-85 years (the average age was 45.35±14.97 years). All patients were performed inhalation anesthesia with Isoflurane. A nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Diclofenac 75 mg) was administered as preemptive analgesia. In the Main group (n=56), after tracheal intubation and positioning, an ESP block was performed under ultrasound control at the Th 9 level with a 0.5% solution of Bupivacaine (25 - 30 ml). In the Control group (n=65), only inhalation anesthesia was performed. A digital rating scale was used to evaluate postoperative pain, registration was carried out every 6 hours, during the day, and the consumption of opiates for postoperative anesthesia, postoperative nausea and vomiting were also assessed. Results. Patients in the ESP block group showed a low assessment of postoperative pain on the digital rating scale compared to the Control group (p<0.001). The consumption of opiates (Promedol) was also lower, especially in the first 6 hours after surgery (p<0.001). Conclusions. The results of our studies confirmed the efficiency of ESP blockade by reducing the consumption of opiates and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. The main advantage of this method is its ease of implementation and safety.
Keywords: Erector spinae plane blockade, Multimodal anesthesia, Kidney surgery
Cite this paper: P. M. Kayumova, A. N. Musabaev, M. B. Krasnenkova, S. Z. Ganiev, The Erector Spinae Plane Blockade Efficiency as a Part of Multimodal Anesthesia During Open Kidney Surgery, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 13 No. 12, 2023, pp. 1870-1874. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20231312.11.
1. Introduction
- Besides modern minimally invasive methods in urology, such as endoscopic and laparoscopic surgeries, there is still an urgent need for traditional surgical interventions performed by lumbotomic approach. A lumbotomy technique is used over the 11th or 12th rib for open surgeries on the kidney. After dissection of Gerota's fascia, the kidney and ureter are isolated.During nephrectomies, the renal pedicle is dissected from behind, followed by ligation of the renal artery and vein [1].Postoperative pain after such extensive interventions is a common problem, and its importance should not be underestimated. Despite significant progress in the pain treatment, it continues to be a problem for many patients [2].Numerous studies show that a significant number of patients after surgical procedures experience moderate or severe postoperative pain. It can significantly reduce the patient’s life quality and complicate their recovery and rehabilitation after surgery. A multimodal approach involves the use of various variants of regional blockades in a complex anesthesiological treatment - local infiltration anesthesia, peripheral blockades, central neuraxial anesthesia [3].The Erector Spinae Plane (ESP) block, which straightens the back, was first described by Forero et al in 2016. It represents a relatively new strategy for pain management in various surgical procedures, as well as for the treatment of acute and chronic pain [4]. There are many methods of treating postoperative pain during kidney surgery, in particular nephrectomy, described in literature, such as the administration of opiates or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), the use of epidural analgesia, paravertebral blockade or blockage of the quadriceps muscle [5-13]. Therefore, there is a need for further research and search for effective methods of analgesia. The aim of the study was to evaluate the efficiency of ESP blockade as a component of multimodal anesthesia during lumbotomy surgeries on the kidneys.
2. Material and Methods
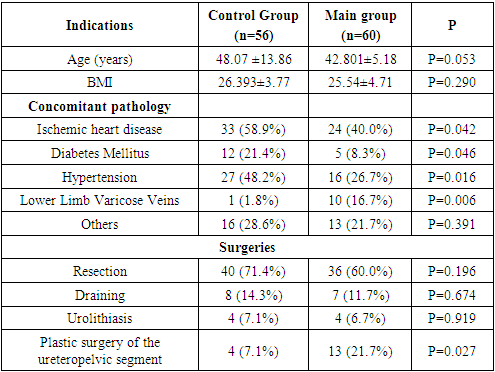
- The study design is prospective. The study was conducted at the Republican Specialized Scientific Practical Medical Center of Urology from August 2021 to September 2022 and was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Сenter (№2. 27.07.2021). The study included 116 patients operated on for urological pathology. The mean age for men was 44.87 years, for women - 45.91 years. Inclusion criteria to the study were as follows: age over 18 years; evaluation of anesthetic risk according to ASA I-III; absence of contraindications to regional anesthesia; consent of patients to anesthesia. Exclusion criteria were: age under 18 years; refusal of patients from regional anesthesia; contraindications to regional anesthesia. There were 63 (54.3%) males and 53 (45.7%) females. All patients were divided into 2 groups: main and control ones. The Control group included 56 (48.3%) patients who were performed only inhalation anesthesia. The Main group consisted of 60 (51.7%) patients who were carried out ESP block.The following surgical interventions were performed: open kidney surgery, lumbotomy access (nephrectomy, radical nephrectomy, drainage of paranephritis, opening and drainage of a kidney abscess, drainage of hematomas, heminefroureterectomy, plastic surgery of the ureteropelvic segment (UPS), opening and drainage of cysts. The main pathologies that led to the need for surgical intervention: kidney cancer, wrinkled kidney, paranephritis, urolithiasis, ureteropelvic segment stricture, kidney hematoma, kidney abscess, double kidney, festering kidney cysts. The results of quantitative indicators are presented as mean and standard deviation and/or median with interquantile rank (Table 1).
|
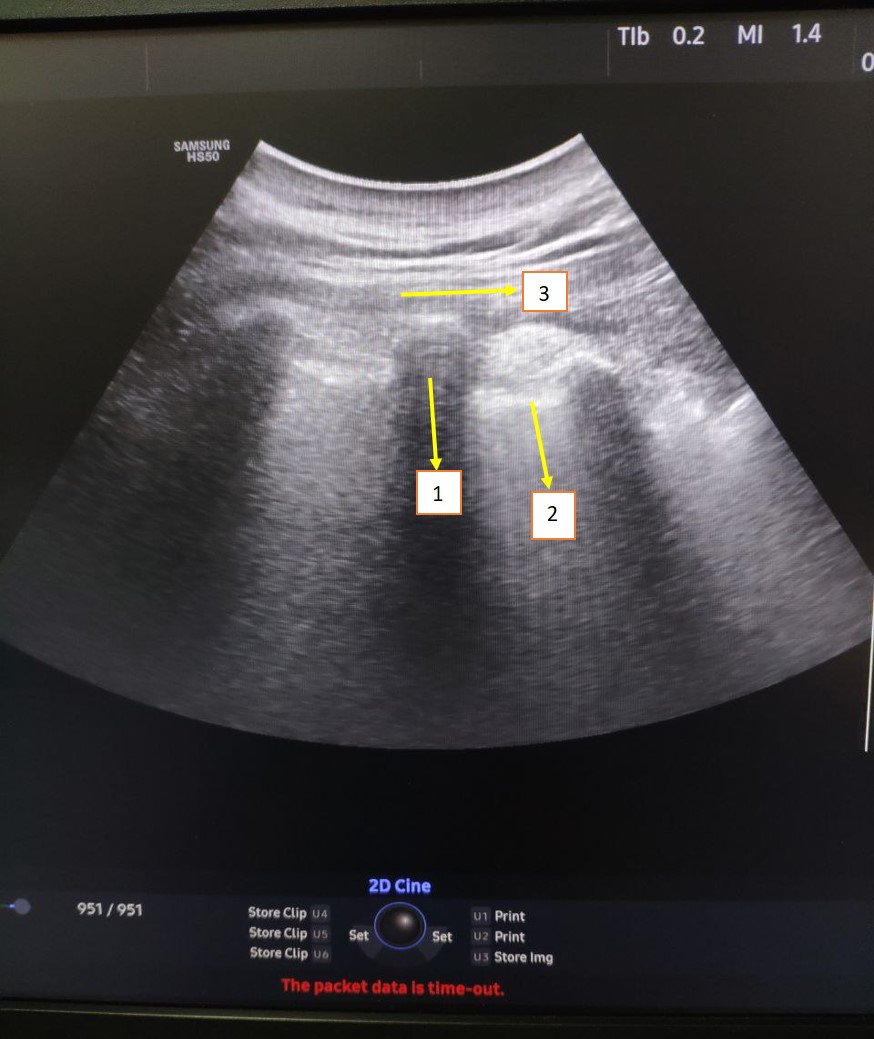 | Figure 1. Echolocation of anatomical structures during blockade of the erector spinae muscle: 1- Transverse process of Th9; 2 – Pleura; 3. Erector spinae muscle (ESP) |
3. Results
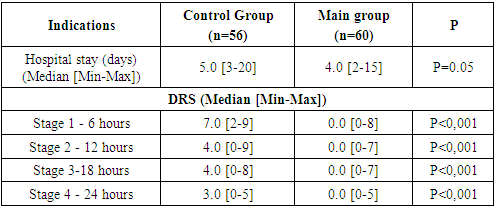
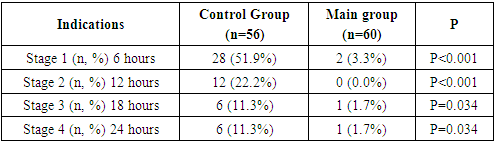
- Table 2 shows the digital rating scale (DRS) evaluation data (median pain by group, minimum and maximum at each stage of the study) at each of the 4 stages within 24 hours after surgery.
|
|
|
|
4. Discussion
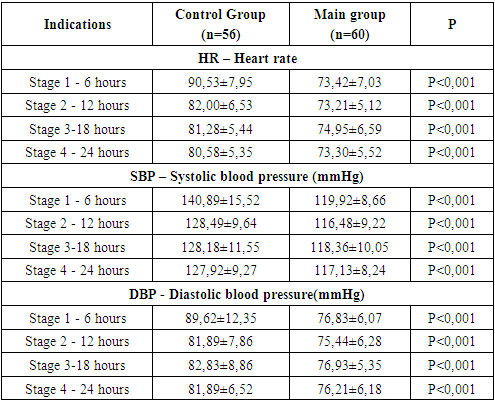
- Our study demonstrated the efficiency of ESP blockade as a means of preventing postoperative pain syndrome during open kidney surgery. It was manifested in lower DRS rates in patients who received ESP blockade, lower consumption of opiates (Promedol), as well as a decrease in the frequency of postoperative nausea and vomiting.There was a slight difference between the two groups regarding the duration of stay in the ICU and hospital after surgery up to discharge. It can be explained by differences in the volume of surgical intervention and the presence of surgical complications. Since the first publication of Forero in 2016, numerous clinical studies have confirmed the efficiency of ESP blockade in the treatment of pain syndromes and postoperative pain.In the studied literature, a limited number of publications devoted to the use of ESP block in open nephrectomies can be found. These are mainly reports on a series of cases or descriptions of individual cases. All these studies demonstrate good results in pain control in the postoperative period, reducing the need for morphine and reducing the likelihood of postoperative nausea and vomiting. Ayhan S¸ahin and Onur Baran conducted the first randomized double-blind controlled trial, in which two groups of patients were compared: one group was performed ESP blockade, and the other one received regular systemic anesthesia after nephrectomy. The results of the study showed the efficiency of ESP blockade for the postoperative pain relief in patients during the first 24 hours after surgery [14].Canturk demonstrated the efficiency of ESP blockade at the L1 level in a patient after radical nephrectomy by lumbotomy incision. Besides, the evaluation of pain intensity by DRS did not change even after repeated surgery due to bleeding in the same patient [12].Meryem Onay compared QLB 2 (quadratus lumborum) blocks with ESP blocks in lumbotomy nephrectomies. In spite of low visual analogue scale scores, there was no significant difference between groups. The same results were observed with morphine consumption. The authors conclude that both blocks can be used depending on the skills and experience of the anesthesiologist [16].The ESP block is a relatively safe method of regional anesthesia with a low risk of complications. Our study did not reveal any complications or side effects in patients. The presence of the transverse process may be an anatomical barrier to the point of injection of local anesthetic, which reduces the possibility of damage to vascular and nerve fibers.Various complications have been reported as a result of the use of ESP blockade at different levels of the spine, such as Harlequin syndrome after blockade at the thoracic Th3 level [17], priapism at the lumbar level [18], motor weakness of the lower extremities at the lower thoracic level [19]. Local anesthetic toxicity is a potentially serious complication of any regional anesthetic technique [20]. The risk of bleeding during ESP blockades is minimal. These blocks were used in patients with thrombocytopenia or bleeding disorders and in patients taking anticoagulants [21,22].There were no cases of toxicity of local anesthetics, side effects in our studies.
5. Conclusions
- The results of our study showed the efficiency of ESP blockade in the first 24 hours after open kidney surgery: a decrease in the subjective pain assessment, a decrease in the consumption of opiates and NSAIDs.The main advantage of this method is its ease of implementation and safety. When mastering the skills of ultrasound navigation, this method can become a reliable and highly effective part of multimodal anesthesia in urological patients.The authors declare no conflict of interest. This study does not include the involvement of any budgetary, grant or other funds. The article is published for the first time and is part of a scientific work.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML